by Nic Haygarth | 21/07/19 | Tasmanian high country history, Tasmanian landscape photography
Hikers love drama. Launceston photographer Steve Spurling (Stephen Spurling III, 1876‒1962) manufactured some in 1908 when he set out on a hike with his mates Knyvet Roberts (1872‒1959) and John Burns (Jack) Scott (1873‒1915). Their journey to Lake St Clair was ‘a terror incognito!’, since they could get ‘no reliable information as to what lay before us, and were not encouraged by rumours of precipitous valleys and impassable bogs …’[1]
In other words, Spurling didn’t know who to ask for information on his proposed route. In 1908 there were no walking clubs which later acted as a repository of local hiking knowledge. Spurling had few useful maps and no access to the shepherds and hunters who had been working the lake country for decades. Had he only known, in five minutes he could have hotfooted it from his office at Spurling Studios down to the legal firm of Law & Weston & Archer, two of the principals of which had, as schoolboys, crossed the lake country to Lake St Clair 22 years earlier.[2] Or called on Delorainite Dan Griffin, the temperamental highland journalist who had scouted the Lake Ina area for a west coast stock route, finding only a thylacine in the business of taking a leg of mutton home to her family.[3] These men could have told him where to go and what to expect.

Clean-shaven and steely-eyed, Jack Scott, Knyvet Roberts and Stephen Spurling III ready themselves for their two-week hike, 1908. Stephen Spurling III photo courtesy of the late Barney Roberts.
Spurling was then at the height of his physical powers, being instructor to the Union Jack Gymnasium Club.[4] Knyvet Roberts, a fellow traveller on Spurling’s 1905 Cradle Mountain climb, and Jack Scott, with whom Spurling had sporting connections (Union Jack Gymnasium Club, lacrosse and rifle shooting), are also likely to have been in fine fettle. They sure looked that way when Spurling photographed them gazing steely-eyed across a paddock somewhere between Deloraine and Western Creek. While his mates toted simple haversacks, Spurling, in addition to his swag and photographic case, slung a bag around his neck. How did his glass plates ever survive long enough to be processed, let alone exposed? More importantly, when did the cravat cease to be a bushwalking accessory and are we the poorer for it?

‘A pine belt, Western Highlands’, 1908, Roberts and Scott approaching a pencil pine grove on a highland lake. Stephen Spurling III photo courtesy of Stephen Hiller.

‘On the Pine River Divide, Central Plateau’, 1908, Roberts and Scott take a breather on the Great Pine Tier at one of the many tarns encountered. Brooding skies are a feature of this excursion record. Stephen Spurling III photo courtesy of Stephen Hiller.
Spurling’s purpose was to supplement the landscape catalogue of Spurling Studios. The Daily Telegraph’s Deloraine correspondent must have been suffering his own ‘terror incognito’, judging by his description of the party’s plans to cross ‘via Mount Ironstone and Lake St Clair for Cradle Mountain’.[5] The trek started inauspiciously. Alighting from the Higgs Track into a Lake Balmoral blizzard, the men set the compass for Mount Olympus, about 50 kilometres away as the crow flew. Twenty-seven-kilo packs barely provisioned them for the five days of tramping ahead, with innumerable detours around tarns, battles with bauera and dense Richea scoparia (‘gas bush’), and even a near thing with quicksand. At nightfall on Day Two they camped near ‘the lakes of the Hay Moon Marshes’ (presumably Chummy Lake and Lake Denton, near Halfmoon Marsh, Pine River) on the Great Pine Tier.

‘The Courier Lake, Western Highlands’, 1908. Stephen Spurling III photo courtesy of Stephen Hiller.

Lake Spurling (now Lake Riengeena), 1908, Stephen Spurling III photo from the Tasmanian Mail, 12 September 1912, p.24.

‘Lake Laura, Western Highlands’, 1908. In 1896 Beattie had taken the Sublime approach to Mount Ida’s towering form above this lake. Spurling’s elegantly framed photo instead captured the mountain reflections, belying the difficulty of access to the site. Stephen Spurling III photo courtesy of Stephen Hiller.
From here the trio must have swung around to the west. On Day Four they approached a large, uncharted, unnamed lake ‘almost due south of Rugged Mt [a named then used to describe the group of peaks from the Walls to Mount Rogoona and those overlooking Lees Paddocks], ’ measuring about three miles long and three-quarters of a mile wide—possibly Lake Norman or Lake Payanna in the Mountains of Jupiter. This was probably the feature Spurling dubbed the Courier Lake. Was he buttering up the Weekly Courier newspaper that bought so many of his photos? Spurling’s companions also named another lake (now Lake Riengeena) after him at the time. The serrated head of the Acropolis now loomed high in the summer haze far across the Narcissus Valley. Rounding the shoulder of ‘an unnamed mountain’ (now Mount Spurling), they scrambled down the Traveller Range to camp at Lake Laura, just to the north-east of Lake St Clair.

‘From Mount Olympus, Lake St Clair’, 1908, a misty lake shot from the rock scree high on the mountain. Stephen Spurling III photo courtesy of Stephen Hiller.

‘Drifting mists, Mount Olympus’, 1908, showing the party’s campsite at Narcissus River. Stephen Spurling III photo courtesy of Libraries Tasmania.
On Day Seven Spurling’s party resettled at the mouth of the Narcissus River, a site which would find favour with future Lake St Clair campers. After a week’s exertion, the photographer was too knackered to attend the usual dawn service of his profession. He had not stirred from his bed next morning when one of his mates roused him, ‘Steve, get up, there’s a cloud over Mount Olympus!’ By the time the lens was brought to bear, the rising mist cloaked only the mountain’s lower baffles, resulting in one of Spurling’s most striking compositions.

‘The Du Cane Range [the Guardians] from Lake Marion’, 1908. Stephen Spurling III photo courtesy of Stephen Hiller.

Spurling’s ‘Mount Gould, Lake Marion’, 1908, seems rather tame compared to Beattie’s Sublime version shot twelve years earlier. Was the pandanus planted? Stephen Spurling III photo courtesy of Stephen Hiller.

‘Cuvier Valley and Mount Olympus’, 1908. The party pauses for the photographer on its half-starved rush to Cynthia Bay. Stephen Spurling III photo courtesy of the late Barney Roberts.
Food supplies were now desperately low. After conquering Mount Olympus, base camp was moved to the Byron Gap in hope of landing some game. ‘Hedgehog’ (echidna) stew had fed the party for a while, but their snares continued to draw a blank. Lake Marion, Mount Gould and the Cuvier Valley completed the sightseeing, before the visitors made a dash for the accommodation house at the southern end of the lake, hoping to beg provisions from other tourists. The place was empty—but for a small packet of flour. Spurling, Scott and Roberts quickly turned this into a barely edible rock-hard damper. Appetites whetted, they determined to partake of the superior cuisine available at the Pearce residence, 20 kilometres away. There the ‘three wild eyed haggard bearded sun-downers’ must have presented quite a sight hoeing into their ‘Lord Mayors Banquet’.
Homeward bound, they took the stock track from Bronte to Great Lake, reaching the shepherd’s hut at the Skittleball Plains near Great Lake on the twelfth night of their journey. The 4139-acre sheep run between the Ouse and Little Pine Rivers was stocked by Edmund Johnson of Lonsdale, near Kempton. The identity of his shepherd is unknown, but he kindly offered the party his floor. Revived by their hearth-side sleep, Spurling, Scott and Roberts pulled out all stops for the final dash along the lake and down Warners Track, taking their tally for the last three days of the tramp to 130 kilometres. The reason for their haste was that at the Pearce homestead arrangements had been made to have a driver await the party with a dray at Jackeys Marsh. ‘The luxury of driving was unspeakable’, Spurling wrote in an excursion diary which, like the 1840s survey maps that might have aided him, was never published.
Spurling’s photos from the trip featured in the Weekly Courier newspaper over many months.[6] They also appeared as postcards (they are collectables today) and in ‘bioscope’ lantern slide performances which Spurling conducted in Launceston, that is, as slides incorporated into a moving picture show.[7] In 1913 he would return to Lake St Clair with a movie camera, as Simon Cubit and I detailed in Historic Tasmanian mountain huts.[8]
Major Jack Scott was killed in action at Gallipoli on 8 October 1915, having joined up in Western Australia alongside his brother Joe Scott—who likewise lost his life during the Dardanelles Campaign.[9] Knyvet Roberts, after whom Knyvet Falls, Pencil Pine Creek, are named, became a Flowerdale farmer. His son, the writer Bernard (Barney) Roberts, treasured an album of 30 photos which Spurling had given his father after the 1908 Lake St Clair trip. Barney used these photos to introduce me to the photography of Steve Spurling, for which, 30 years later, I am extremely grateful.
[1] Spurling’s unpublished account of the trip, ‘Across the Plateau’, is held by the Spurling family in Devonport. It appears to be a typed version of hand-written Spurling notes and is wrongly dated February 1913, giving the impression that the author and the typist were not one and the same.
[2] For the accounts of this trip see ‘The Tramp’ (William Dubrelle Weston), ‘About Lake St Clair’, The Paidophone, (Launceston Church of England Grammar School magazine), vol.II, no.7, September 1887, pp.7‒8; and ‘Shanks’s Ponies’ (William Dubrelle Weston), ‘A trip to Lake St Clair’, Examiner, 22 December 1888, p.2 and 29 December 1888, p.13. For Weston and Law’s hiking careers, see Nic Haygarth, ‘”The summit of our ambition”: Cradle Mountain and the highland bushwalks of William Dubrelle Weston’, Papers and Proceedings of the Tasmanian Historical Research Association, vol.56, no.3, December 2009, pp.207‒24.
[3] ‘Lake Ina’, Daily Telegraph, 24 May 1907, p.4.
[4] ‘Union Jack Gymnasium Club Annual Meeting’, Daily Telegraph, 17 March 1908, p.8.
[5] ‘Deloraine’. Daily Telegraph, 18 February 1908, p.7.
[6] Photos from the 1908 trip appeared in the Weekly Courier on 16 April 1908, p.27; 23 April 1908, p.19; 30 April 1908, p.17; 7 May 1908, p.17; 14 May 1908, p.17; 21 May 1908, pp.21 and 22; 28 May 1908, p.17; 11 June 1908, p.24; 2 July 1908, p.17; 9 July 1908, pp.17 and 23; 16 July 1908, p.22; 23 July 1908, p.23; 6 August 1908, pp.20 and 24; 31 December 1908, pp.21 and 24.
[7] See, for example, ‘Bioscope entertainment’, Daily Telegraph, 29 September 1908, p.3.
[8] ‘Hartnett’s huts’, in Simon Cubit and Nic Haygarth, Historic Tasmanian mountain huts: through the photographer’s lens, Forty South Publishing, Hobart, 2014, pp.76‒83.
[9] ‘Major JB Scott killed: brothers make the supreme sacrifice’, Examiner, 16 October 1915, p.6.
by Nic Haygarth | 12/03/19 | Tasmanian high country history, Tasmanian landscape photography
It would be easy to dismiss hiking trips as frivolous. Urban people taking the airs. Weekenders marvelling at ‘new’ landscapes others work in all week. Spiritual awakenings in firestick farmlands. Bushwalkers are rarely explorers even in the European sense of discovering a place known to the Aborigines for 60,000 years. Generally they tread a well-trodden path.
But I do get interested when bushwalking accounts give us historical insights. They can tell us when something happened, when a structure was built or destroyed or a track cut. They can help trace the development of technology. Take, for example, the story of photographer Stephen Spurling III (1876–1962) lugging 12 x 10-inch glass plates up Stacks Bluff through snow drifts on home-made snow-shoes to take the first Tasmanian highland snow scenes.[1]
There is a charming naivety about all Spurling’s accounts of hiking the northern ranges in the years 1895–1913. These were young men plunging agreeably into what was to them the unknown. In his report of a 1908 trip from Ironstone Mountain to Lake St Clair Spurling described the Central Plateau as ‘A Terror Incognito’, his party being unable to score reliable information as to what lay ahead of them, just ‘rumours of precipitous valleys and impassable bogs dense belts of scrub and other obstacles to progress …’[2] Highland stockmen and hunters, or experienced Launceston hikers such as William Dubrelle (WD) Weston and Richard Ernest ‘Crate’ Smith could have advised him, had he known to ask them. There were no walking clubs then to act as a repository of hiking knowledge. There was no digital newspaper index to search. This was a world not over-stimulated by visual images. No internet, no TV, no neon billboards. You could buy albums of Tasmanian views from photographers like John Watt (JW) Beattie, but the era of press photography was just dawning.
Spurling could see a market for Tasmanian scenery in both albums and illustrated weekend newspapers. He loved the Central Plateau. In 1899 he and a group of friends climbed the Great Western Tiers at Caveside and crossed the Plateau to see Devils Gullet.[3] In early 1901 he was part of a group that ascended the Tiers above Meander and worked its way west past Lake Mackenzie, once again to Devils Gullet.[4] Spurling scenes of the Tasmanian highlands were a striking feature of the Weekly Courier from its inception in July 1901.
Devils Gullet was then known as ‘The Gulf’. However, Spurling had heard of a ‘magnificent’ ‘Second Gulf’ ten miles (sixteen kilometres) back from the escarpment where the Fish River—actually the Little Fisher River—made its escape to the Mersey. Spurling’s map placed this gulf, quite correctly, in the vicinity of the Walls of Jerusalem—something of a mythic land for bushwalkers well into the twentieth century. Although surveyor James Scott had charted the Walls of Jerusalem as early as 1849, and the mountain complex was well known to highland graziers and hunters, hikers were in the dark about it. Scott’s map was not in circulation, nor were the earlier exploratory accounts of John Beamont and Jorgen Jorgensen.[5] Launceston walkers WD Weston and probably Ernest Law had visited the Walls of Jerusalem and the so-called Rugged Mountains after Christmas in 1888, but the only copy of their account of the expedition disappeared in the Daily Telegraph newspaper office and was never published.[6]
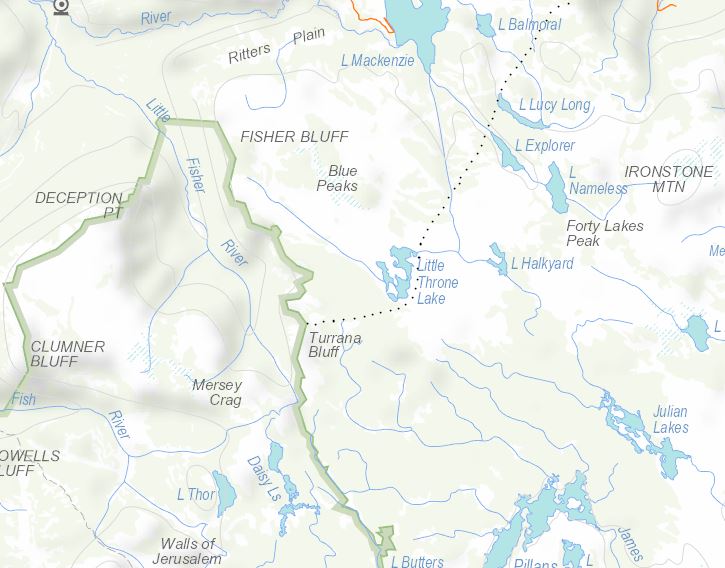
Approximate route of Spurling party to Little Fisher Gulf 1903, map courtesy of DPIPWE.
Blissful in their ignorance, Spurling and his three mates set out for the Second Gulf one autumn weekend in 1903. This time they chose the Higgs Track up the Great Western Tiers near Western Creek. Although Spurling’s report of the trip was not his most entertaining, he observed familiar picaresque conventions of the time. A ‘Jehu’ (biblical chariot driver) delivered the party from Deloraine Railway Station to Dale Brook and back. Only one of the party, the ‘Infant’, received a nickname, that being punishment for describing photography as ‘funny business’.

Campsite on the Higgs Track below the lip of the plateau. Stephen Spurling III photo from the Weekly Courier, 4 April 1903, pp.20-21.
Moist westerly winds impeded their progress up the valley of Dale Brook. The four made base camp in a canvas-roofed shelter just below the lip of the plateau, and spent the rest of the day battling the wind as they reconnoitred around Lake Balmoral. From a hill they sized up the ‘unknown’ country to the south-west that they hoped to penetrate.

One of the Blue Peaks and its accompanying lake, Stephen Spurling III photo, from the Weekly Courier, 4 April 1903, p.21.
Next day they made their push for the Second Gulf. Leaving Lake Balmoral to their right, they reached lake Lucy Long, forded Explorer Creek and the Fisher River, and by 9 am had attained the summit of one of the Blue Peaks. A tongue of land separating Little Throne Lake from its northern neighbour provided a bridge, and by 11.30 am, after six hours’ hard walking, the party stood near Turrana Bluff on the brink of ‘a tremendous gorge, known to a few hunters and shepherds as the Second Gulf, and which corresponds on the map with the Walls of Jerusalem’.
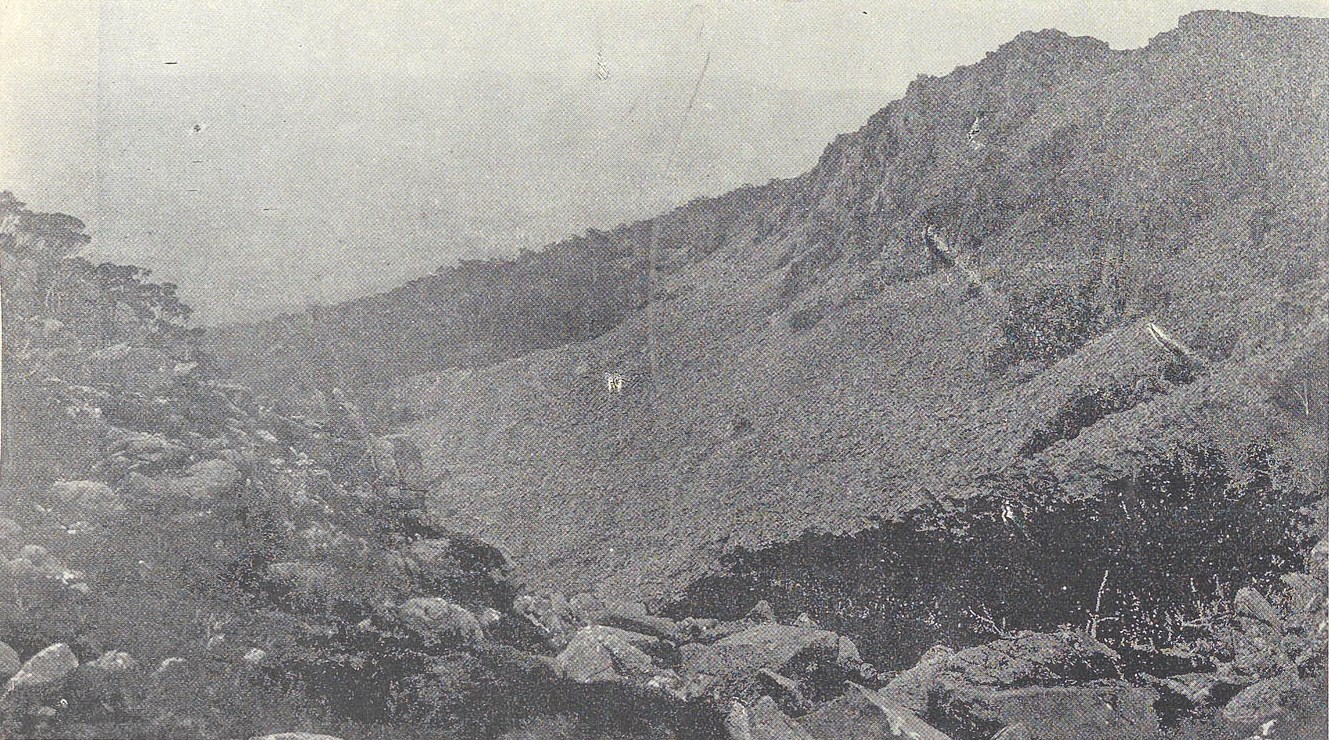

View of the ‘Second Gulf’ (Little Fisher River ‘Gulf’), Stephen Spurling III photo from the Weekly Courier, 4 April 1903, p.20.
Dazzled, perhaps, by his view of the Walls, Spurling described only the ‘wild, serrated form’ of the ‘Rugged Mount’, which made ‘a most impressive background’. Four long silvery streaks of waterfalls dropped over the chasm in the distance. Despite tramping from Ironstone Mountain to Lake St Clair in 1908, this is as close as he would ever get to the Walls of Jerusalem.
Mist cut short the day’s exploration. Yet, with practical ingenuity typical of the time, Spurling’s party cornered and killed a wallaby, part of which they roasted for their evening meal back at base camp. Their final day was spent revisiting Devils Gullet and exploring the course of the Fisher River above it without, apparently, finding the Parsons Hut which Spurling would photograph on his next expedition to these parts—the winter 1904 snow-shoe extravaganza.[7]
[1] Stephen Spurling, ‘Ben Lomond in winter’, Weekly Courier, 19 September 1903, pp.25–26; 26 September 1903, p.26; 3 October 1903, pp.25–26; 10 October 1903, p.35.
[2] S Spurling Junior (Stephen Spurling III), ‘Across the plateau’, unpublished account held by the Spurling family, Devonport. The account is dated February 1913, but the numbering of Spurling’s photos from this trip suggests 1908. The many typographical errors in the paper suggest that someone else transcribed it from Spurling’s handwritten original. The date may be another transcription error.
[3] ‘Union Jack’ (Stephen Spurling III), ‘A trip to the Gulf and Westmoreland [sic] Falls’, Examiner, 20 January 1900, p.7.
[4] ‘The Hermit’ (Stephen Spurling III), ‘In the highlands of Tasmania’, Weekly Courier, 20 July 1901, pp.123–24.
[5] For Beamont: ‘Copy of Mr Beamont’s journal taken on his tour to the Western Mountains, Van Diemen’s Land, Monday, 1st Decr, 1817’, Historical Records of Australia, series III, vol.III, Library Committee of the Commonwealth Parliament, Canberra, 1921, pp.586–90. For Jorgensen: His travels were deciphered by Arch Meston and CJ Binks, see Binks, Explorers of western Tasmania, Mary Fisher Bookshop, Launceston, 1980, pp.48–57.
[6] Weston alludes to the Walls of Jerusalem trip twice in an account of a Cradle Mountain trip in 1890–91. See ‘Peregrinator’ (WD Weston), ‘Up the Cradle Mountain’, Examiner, 4 March 1891, supplement, p.2 and 11 March 1891, supplement, p.1. Weston also appears to allude to this trip in a letter to AV Smith (2 May 1889, CHS47 2/56, QVMAG) and comments on its disappearance in a letter to RE ‘Crate’ Smith (24 September 1889, CHS47 2/55, QVMAG). For
[7] S Spurling jun, ‘On the Western Tiers: trip to the Fish River Gulf’, Tasmanian Mail, 4 April 1903, p.4. For the winter 1904 snow-shoe extravaganza, see Simon Cubit and Nic Haygarth, ‘Sandy Beach Lake Hut’, in Historic Tasmanian mountain huts: through the photographer’s lens, Forty South Publishing, Hobart, 2014, pp.84–91.
by Nic Haygarth | 22/01/17 | Tasmanian high country history, Tasmanian landscape photography

Up one side … a Citröen-Kegresse on the Kensington Sandhills near Sydney. From the Weekly Courier, 27 September 1923, p.23.

Down the other …. the Citröen-Kegresse prototype on its way to Waldheim, 1924. Stephen Spurling III photo courtesy of Anton Lade.
They don’t make Citröens like that anymore. Gustav Weindorfer of Waldheim Chalet, the highland resort at Cradle Valley, beat the snow by shooting for meat on skis when he began living there in isolation in 1912.[1] At around the same time, Tsar Nicholas II of Russia understandably ordered a grander hunting vehicle for snow conditions—with caterpillar tracks for back wheels. Hannibal’s elephantine passage through the Alps to surprise the Romans had nothing on the Citröen-Kegresse, the assault vehicle which resulted from the meeting of French car manufacturer André Citröen and the Tsar’s resourceful mechanic, Adolph Kegresse, after the Russian Revolution.[2]
The Tsar’s caterpillar-tracked hunting technology now drove a prototype that breached the Himalayas en route to China and crossed the Sahara to Timbuktu. It also took a crack at Cradle. In 1924 Latrobe garage owner William Lade publicised his acquisition of a Citröen-Kegresse in Wynyard, Penguin, Latrobe and Devonport, being fined in the last town for demonstrating its ability to climb the steps of the Seaview Hotel.[3] There were fewer rules and few police in the highlands. Rearing over hills and plummeting down the other side, Lade’s vehicle roared up to Waldhiem with ten people aboard close to midnight on 12 April 1924.[4] Launceston’s Daily Telegraph newspaper had high expectations of the Citröen-Kegresse trip:
‘It had been expected that the machine would attempt the last 1½ miles [from Waldheim] to the [Cradle Mountain] summit, but as the rain continued to fall throughout the whole of Sunday the attempt had to be abandoned’.[5]

‘An obstacle surmounter on its hind legs’. The prototype on the inaugural Cradle trip. Don’t forget to pack a newspaper. Stephen Spurling III photo courtesy of the St Helens History Room.
The effect of this visitor on Weindorfer, who may have imagined himself awakened from years of isolation from tourists and supplies, can also be imagined. In preparation for the following summer’s business, Lade then built a shed to house the Kegresse at Moina, about three-quarters of the way to Cradle Valley, the idea being to use conventional transport to bring passengers from the coast that far, swapping to the Kegresse only for the challenging final section. The prospects for tourism seemed rosy. At the time, Weindorfer’s friend Ronald Smith was building a family shack on his own land at the edge of Cradle Valley. ‘Have you finished your place?’, Weindorfer, who called the Kegresse the ‘platypus motor’, asked Smith in October 1924. ‘There might be some business for you’.[6]

Gustav Weindorfer. Photo by Ron Smith courtesy of Charles Smith.

Waldheim Chalet in the snow during the Weindorfer era. CF Monds photo courtesy of DPIPWE.
The ‘platypus motor’ made four further trips to Cradle in the period January–March 1925. However, tank technology did not take root on the slopes of Cradle Valley or on the road to Cradle. Snowfalls were too inconsistent to attract skiers, and the Citröen-Kegresse disappeared from service after only one further trip, in December 1927.[7] Weindorfer stuck to his skis and joined the Indian corps instead. In 1931 he acquired an Indian Scout motorcycle, meaning that, for the first time, he could motor to and from Cradle Valley at will.
At least, that was the theory. Weindorfer was found dead next to his Indian half a kilometre from Waldheim in May 1932. It appeared that he had suffered a heart attack while trying to kick start the machine.[8] Cradle’s isolation had finally silenced him.
[1] Gustav Weindorfer diary, 17 July 1914, NS234/27/1/4 (Tasmanian Archive and Heritage Office [hereafter TAHO]).
[2] See, for example, John Reynolds, André Citröen: the man and the motor cars, Alan Sutton, 1996.
[3] ‘Motor demonstrations’, Advocate, 9 April 1924, p.2.
[4] Gustav Weindorfer diary, 12 April 1924 (Queen Victoria Museum and Art Gallery [hereafter QVMAG]).
[5] ‘To Cradle Mountain by tractor’, Daily Telegraph, 19 April 1924, p.16.
[6] Gustav Weindorfer to Ronald Smith, 2 October 1924, p.141, LMSS150/1/1 (LINC Tasmania, Launceston).
[7] Gustav Weindorfer diary, 13 December 1927 (QVMAG).
[8] See Esrom Connell to Percy Mulligan, 20 September 1963, NS234/19/1/22; and the coronial enquiry into Weindorfer’s death, AE313/1/1 (TAHO).
by Nic Haygarth | 21/01/17 | Tasmanian high country history, Tasmanian landscape photography, Tasmanian nature tourism history

Starting out from the Ouse River in the Hupmobile, 1914-15 trip. Ray McClinton photo from the Weekly Courier, 28 January 1915, p.18.
It was the first motor trip to Lake St Clair. In 1915 pioneering motor tourers Ray and Edith McClinton mounted a two-week expedition from Launceston to the highland lake, with ‘Nina’, social pages and women’s editor of the Weekly Courier newspaper, as their guest. The Hupmobile party, towing an additional 120 kg of motor boat engine and luggage, battled rocks, ruts, rain and button grass up the Derwent Valley, breaking their trip at Ouse, the Ellises’ house near the Dee River, Weeding’s at Marlborough and Pearce’s at the Clarence River.[1]
McClinton, a San Francisco dentist who with his wife lived in Launceston 1904–28, would soon become one of Tasmania’s great tourism ‘boosters’.[2] Like fellow Launceston rev-heads Stephen Spurling III, Fred Smithies and HJ King, McClinton worshipped both nature and technology. He wanted to crash deep into the highlands, breaking down the physical and virtual isolation with carburettors and cameras. He was also imbued with fervour for worthy objects and the nineteenth-century tradition of public education that made him a consummate lantern slide lecturer on anything from x-raying teeth to colour photography.[3] Soon he would turn those skills to promoting Tasmania’s scenic wonders. Visiting Lake St Clair was one of the foundation stones of his eventual campaign in support of plans for a Cradle Mountain-Lake St Clair national park.[4]

The Hup party at the government log cabin, Cynthia Bay, Lake St Clair, 1914-15 trip, with the unmistakable figure of Paddy Hartnett closest to the camera. Ray McClinton photo from the Weekly Courier, 28 January 1915, p.18.

The motorboat and Paddy Hartnett in the lake, 1914-15 trip. Ray McClinton photo from the Weekly Courier, 28 January 1915, p.18.
Already there was rudimentary infrastructure at the lake. The Hup party took advantage of the government-built three-room log cabin at Cynthia Bay. On foot at last they crossed the Cuvier River on a rustic bridge. McClinton attached his engine to the boat at the lake, enabling communication with the Perrin party —a pedestrian party—camped near the Narcissus at the northern end of the lake. Highland guide Paddy Hartnett had led them to Lake St Clair via the Mersey River.[5] ‘Nina’ marvelled at the reflections in the Narcissus River and the gambolling of a platypus. She made even the ‘perfume of petrol’ mingle poetically with the ‘sweet scent of the woods’, as the first propeller churned the waters of Lake St Clair. A storm disrupted the return journey down the lake but, with the aid of axe, saw, lamp and candles, McClinton soon fashioned ‘Nina’ a comfortable bower in the forest:
‘Imagine myrtle trees towering over a hundred feet high, and their branches interlaced, so that only patches of sky could be seen above, and only glimpses of the lake between. Then picture tree-ferns all around, and green moss for a carpet. Add to his a vision of remnants of fallen trees of age untold, coated with moss inches thick, like green plush. The imagine crystal streams trickling down the mountain side … The whole scene was fairyland …’[6]
But who was ‘Nina’? She was an outstanding journalist called Kate Farrell, better known by her pseudonyms ‘Nina’ and ‘Sylvia’. Her literary career spanned 33 years and included both Launceston dailies, the Daily Telegraph and the Examiner, plus their respective weekend newspapers, the Colonist and the Weekly Courier.[7] The scale of her anonymity can be tested quite easily by searching the Trove digital database: during her literary career c1894–1927 the name Kate Farrell has only 7 hits, while ‘Woman’s World’ by ‘Sylvia’ occurs 1933 times.[8] ‘Woman’s World’ was generally frocks, recipes and home hints. In 1914 Farrell published her 96-page Sylvia’s cookery book.[9] During World War One she turned her attention to bringing comfort to those at the front, and she was also a ‘booster’, penning tourist guide The charm of the north in 1922.[10] Farrell had been motor touring with the McClintons for years, having accompanied them to Lake Sorell in their Winton Four and on Edith McClinton’s one-woman non-stop run from Launceston to Richmond in the Hupmobile. [11] Farrell preceded Ray McClinton as a tourism ‘booster’, and at Lake St Clair she quickly got into her stride:
‘The beauty of the scene is inexpressible. One can imagine the crowds of tourists who would visit Lake St Clair if the road were made. A number of small chalets built, with a caretaker in charge, and a motor boat available for the use of visitors, would help matters along considerably. I hope it will not be long before such dreams come true’.[12]

Stuck in a wash-out near Ellendale, 1916-17 trip, King and McClinton in action. HJ King photo courtesy of Daisy Glennie.

The Hupmobile, containing the two ladies, and McClinton in the ‘Baby Grand’ Chevrolet, posed as if tackling the corded track, 1916-17 trip. HJ King photo courtesy of Maggie Humphrey.

‘The darkroom at Lake St Clair’, HJ King despairs over the photographic facilities, 1916-17 trip. HJ King photo courtesy of Maggie Humphrey.

The 1916-17 party at Bushy Park, Sir Philip Fysh with the white beard, the McClintons at centre, with Kate Farrell fourth from left. Bushwalker and park administrator WJ Savigny is second from left. HJ King photo courtesy of Maggie Humphrey.
The McClintons and Farrell repeated their Lake St Clair excursion two years later, this time with the established amateur photographer HJ King. While King drove McClinton’s faithful old Hupmobile (registration number 586), the dentist was at the helm of his new ‘Baby Grand’ Chevrolet (number 4465). Both vehicles survived—but, in the true tradition of motor touring, it was a near thing for much of the way. The government accommodation house had been destroyed by fire in the intervening two years. However, rather than repeat herself, Farrell minimised her tourism boosting and concentrated on describing the route taken and the social pleasantries of a visit to former premier Sir Philip Fysh’s Bushy Park estate.[13] The real reporter was King. McClinton deferred to the superior shutterbug, allowing him to be the official tour photographer, and many King photos from this trip appeared in the Weekly Courier during 1917, including his light-hearted ‘Lake St Clair Darkroom’.[14] King’s keen eye captured the logistical difficulties of the corrugated track, with block and tackle deployed near Ellendale, some pick and shovel work on the Sandhill at Lawrenny and rescue by a bullock team near Derwent Bridge. McClinton also appears to have had a long stint with a hand saw clearing a fallen tree. One of the most interesting images from the trip was McClinton, the ex-patriate American, recalling his military training by posing with a gun upon his shoulder, as if guarding the beauty of Lake St Clair.[15] How far they were from the European War (King was a conscientious objector, McClinton effectively neutral), yet the connection remained even here.[16]

Ray McClinton posed militarily in front of Mount Ida, 1916-17. HJ King photo courtesy of Maggie Humphrey.
‘To Lake St Clair with car and camera’ became one of first outings of the McClinton–King lantern lecturing team.[17] Later, with Fred Smithies, they would add Cradle Mountain and the Pelion region to their lecturing repertoire. At her retirement in 1927 Kate Farrell was ‘Launceston’s senior press woman’ and the last of the Weekly Courier’s original staff. [18] The McClintons were there to farewell her, just ahead of their departure from Tasmania.[19] Farrell died in 1933, after a long battle with illness, leaving only King to enjoy the road they had craved, the ‘missing link’—forerunner of the Lyell Highway—between Marlborough and Queenstown.[20] By then Lake St Clair was well on its way to becoming a tourism hub.
[1] See ‘Nina’ (Kate Farrell), ‘A trip to Lake St Clair’, Weekly Courier, 21 January 1915, p.29; 28 January 1915, pp.27–28; 4 February 1915, pp.28 and 29; and 11 February 1915, p.28.
[2] Edith McClinton actually left Tasmania for Honolulu in June 1927 (‘Social notes’, Daily Telegraph, 22 June 1927, p.2), Ray MClinton joining her there in November 1928 (‘Dr Ray McClinton’, Mercury, 8 November 1928, p.11).
[3] See, for example, ‘X-rays and the teeth’, Examiner, 18 June 1925, p.5.; and ‘Local and general’, Daily Telegraph, 5 July 1923, p.4. For Launceston rev-head photographers generally, see Nic Haygarth, The wild ride: revolutions that shaped Tasmanian black and white wilderness photography, National Trust of Australia (Tasmania), Launceston, 2008.
[4] McClinton and Smithies had visited the Du Can Range area in 1913, and may have visited Lake St Clair at that time, but that was a pedestrian trip.
[5] See ‘The adventures of Paddy’s Gang: an account of a Perrin family trip to Lake St Clair guided by Hartnett over the Christmas–New Year period in 1914–1915’, diary in possession of Bessie Flood.
[6] ‘Nina’ (Kate Farrell), ‘A trip to Lake St Clair’, Weekly Courier, 28 January 1915, p.28.
[7] ‘Miss K Farrell’s death’, Examiner, 4 July 1933, p.9. Thanks to Ross Smith for identifying ‘Nina’.
[8] The Weekly Courier is not yet indexed on Trove, making it impossible to search on ‘Social notes’ by ‘Nina’. Propriety of the time contributed to this disparity, insisting that she be referred to simply as ‘Miss Farrell’ throughout her life.
[9] ‘Social notes’, Daily Telegraph, 25 May 1927, p.2. The full details are K Farrell, Sylvia’s cookery book: tested recipes and items of interest, Launceston, 1914.
[10] K Farrell, The charm of the north, Launceston City Council, Launceston, 1922.
[11] ‘Nina’ (Kate Farrell), ‘Camping at Interlaken’, Weekly Courier, 21 January 1909, p.29; ‘Exhaust’, ‘Motor notes’, Daily Telegraph, 9 November 1911, p.11.
[12] ‘Nina’ (Kate Farrell), ‘A trip to Lake St Clair’, Weekly Courier, 11 February 1915, p.28.
[13] ‘Nina’ (Kate Farrell), ‘A trip to Lake St Clair’, Weekly Courier, 11 January 1917, p.27. The trip was also written up by ‘Spark’ (Charles George Saul), ‘Motoring’, Examiner, 13 January 1917, p.4. Thanks to Ken Young for identifying ‘Spark’.
[14] See Weekly Courier, 11 January 1917, p.17; 18 January 1917, p.18; 25 January 1917, p.17; 1 February 1917, p.17; 15 February 1917, p.17; 22 March 1917, p.20; 5 April, pp.17, 20 and 21; 31 May, p.21; 13 September, p.17; 18 October 1917, p.17; and 1 November 1917 (Christmas issue), p.22.
[15] Ray McClinton performed military training 1900–02 in California, film no.981549, MF4:2, National Guard Registers v.61, 1st Infantry, 2nd Brigade, Enlisted Men, 1883–1902, California, Military Registers, 1858–1923.
[16] McClinton supported the Allied war effort, but America did not enter World War One until April 1917.
[17] See ‘Spark’ (Charles George Saul), ‘Motoring’, Examiner, 3 February 1917, p.4; ‘Plug’, ‘Motor notes’, Daily Telegraph, 13 February 1917, p.6.
[18] ‘Journalist honoured’, Examiner, 24 May 1927, p.7, ‘Social notes’, Daily Telegraph, 25 May 1927, p.2.
[19] The McClintons’ names were accidentally omitted from the Examiner’s story of this event. See the correction, Examiner, 25 May 1927, p.7.
[20] ‘Miss K Farrell’s death’, Examiner, 4 July 1933, p.9.
by Nic Haygarth | 14/01/17 | Tasmanian high country history, Tasmanian landscape photography, Tasmanian nature tourism history

‘The darkroom at Lake St Clair’, HJ King despairs over the photography facilities, 1917. HJ King photo, courtesy of Maggie Humphrey.
The young Herb (HJ) King was a rev-head with an artist’s eye, a man beguiled by cameras and carburettors. The frontage of his father’s motorcycle shop, John King and Sons, which he eventually took over, remains a landmark of the Kingsway, off Brisbane Street, Launceston, long after it closed. In 1921 the rival Sim King’s motorbike shop at the other end of Brisbane Street ran an advert for machines with ‘double-seated’ sidecars: ‘Take her with you!’[1] That is exactly what Herb King was already doing, the sight of his wife Lucy in the sidecar of his Indian motorbike becoming a signature of his photography in the period 1919–25.
It was perhaps King’s conservative Christadelphian faith that determined that he marry young, have children and place the role of family man before all else. He married Lucy Minna Large in Hobart in December 1918. Lucy recalled that King drove her father from Hobart to Launceston. Alighting from the car, Charles Large said ‘Oh, my boy, it’s a long way’, to which King replied, ‘Yes, Charles, what about letting Lucy and I get married at Christmas, instead of waiting?’ She was eighteen years old. He was 26.[2]

Lucy in the sidecar at Moina, just off the Cradle Mountain Road, 1919. HJ King photo courtesy of Maggie Humphrey.
After this, before their first child was born, Lucy was a feature of King’s photography, accompanying him on most of his photographic trips. King got to Cradle Mountain slightly ahead of his nature-loving friends Fred Smithies and Ray McClinton. In December 1919 Herb, Lucy, her sister and a friend started for Cradle on motorbike and sidecar. After staying a night at Wilmot, they had Christmas dinner at Daisy Dell, Bob Quaile’s half-way house, with Lucy making a success of her first Christmas pudding. The track from Daisy Dell across the Middlesex Plains to Cradle Valley was so rough that Quaile bore most visitors along it on various horse-drawn wagonettes. Lucy recalled that on this occasion he was equipped with a two-seater:
‘He could only take one passenger and himself, and he had a horse for other people to ride. I had grown up on a farm and I was happy to ride, but my sister wouldn’t get on, and my husband got on one side and got off the other, and said ‘That’s all I’m having’. We arrived at Cradle Mountain with pounds of sausages around someone’s neck because it had rained and washed the paper off … ‘[3]
This was King’s first meeting with Gustav Weindorfer, the proprietor of Waldheim Chalet at Cradle Valley, who was then campaigning to establish a national park at Cradle Mountain. Weindorfer guided the Kings to the summit of Cradle, and it was there, with numerous peaks and Bass Strait spread out before him, that King’s plan to map the country by aerial photography was developed. ‘It was a glorious day’, King recalled, but the ‘progressive’ man of machines was impatient with foot transport:
‘ … as the afternoon was now getting on, we made a laborious descent over the great boulders and across the plateau to Waldheim. How slow the travelling was!—nearly three hours to cover a short three miles—but amidst such scenery we made light of it. We said to ‘Dorfer’ (as he afterwards became known to his friends): ‘Just fancy; if we had a ‘plane we could do the distance in under three minutes …’ Afterwards we talked as we sat inside the great fireplace of the possibilities of preparing an aerodrome in Cradle Valley, and of landing in Lake Dove with a seaplane’.[4]

Car trouble for McClinton on the road to the Wolfram mine, Easter 1920, with (left to right) Paddy Hartnett and Fred Smithies helping out; Lucy King ensconced in the Indian sidecar; and either Ida Smithies or Edith McClinton blurred in motion in the foreground. HJ King photo courtesy of Maggie Humphrey.

Lucy looking distinctly unimpressed on the road to Pelion at Easter 1920: was it the rough ride or the close attention that dismayed her? HJ King photo courtesy of Maggie Humphrey.
Lucy’s passive role in King’s photos belies that she could not only ride a horse, but was the first Hobart woman to own a motorcycle driver’s licence. She proved her mettle as a walker, too, when at Easter 1920 the Kings visited Pelion Plain and the upper Mersey River, with Fred and Ida Smithies, Ray and Edith McClinton, and Paddy Hartnett as a guide. This was the first time motor vehicles—that is, McClinton’s Chevrolet and King’s Indian—had entered the valley of the upper Forth River. The steep, rutted climb out of Lemonthyme Creek defeated the car until Hartnett cut wooden blocks to support the wheels. The guide also cleared a large tree off the track next day, after the party had spent a night at ‘the Farm’, that is, Mount Pelion Mines’ hut and stables near Gisborne’s Farm. The ‘Bark hut’, 3 km north of the Lone Pine wolfram mine (aka the Wolfram mine), was the terminus for the vehicles. Only Hartnett’s ingenuity and McClinton’s kit bag of cross-cut saw, axe and shovel got them that far. Now they started on foot for the mine and beyond that the Zigzag Track to the copper mine huts at Pelion Plain, a pack horse carrying much of their gear.[5] Lucy recalled walking
‘eight miles in the pouring rain and when he reached the hut at the top nobody had a dry stitch. Fortunately for the ladies there were two trappers there, and they obligingly said, ‘You come into the hut where this fire is, and get yourselves dried out, and the men will go to the other hut and make a fire for the same purpose’. The next morning when we woke up it was one of the most beautiful sights that was possible. There wasn’t a blade of grass that wasn’t covered in snow’.[6]

Mount Oakleigh and Old Pelion Hut, still with their dusting of snow, Easter 1920. HJ King photo courtesy of Maggie Humphrey.
That view included Mount Oakleigh, which Herb King photographed. Members of the party visited Lake Ayr and the head of the Forth River Gorge before starting on the return journey.[7]

‘The huntsman’s story’, taken in the mine workers’ hut at Pelion Plain, with (left to right) Ray McClinton, Paddy Hartnett, Lucy King, HJ King, Ida Smithies and Fred Smithies. HJ King photo courtesy of Maggie Humphrey.
Although Paddy Hartnett never used the media, he was equally significant as Weindorfer in the development of a Cradle Mountain‒Lake St Clair National Park. Hartnett’s Du Cane Hut, also known as Cathedral Farm and Windsor Castle, was effectively his Waldheim, a tourist chalet among the mountains. King’s treks to Cradle Mountain and Pelion with their respective guides were transformational in the sense that, although he never became a hardened bushwalker like his fellow photographers Spurling, Smithies and McClinton, he did become a promoter of the Cradle Mountain-Lake St Clair National Park proposal. McClinton photos from this trip appeared in the Weekly Courier, and he, Smithies and King lantern lectured about the proposal.[8]
A slide survives of King promoting himself as a nature photographer, suggesting that he toyed with the idea of turning professional. Presumably, he decided it would not pay. The Kings were a very conservative family. His grandmother, said to be the first Christadelphian in Tasmania, was reputedly disgusted by King’s spending on photographic materials. Perhaps family influenced his choice of career. It is possible that the family motorcycle business seemed a safer bet, or that he felt obliged to follow in his father’s footsteps. Ultimately, people, family and faith meant more to King than any machine or any gadget. It was probably not just for artistic purposes—the compositional need for a foreground—that he placed Lucy in so many of his images. It signalled that she was foremost in his thinking.
[1] See, for example, Sim King advert, Examiner, 2 July 1921, p.14.
[2] Lucy King, transcript of an interview by Ross Case, 18 March 1993, OH18 (Queen Victoria Museum and Art Gallery [hereafter QVMAG]).
[3] Lucy King, transcript of an interview by Ross Case, 18 March 1993, OH18 (QVMAG).
[4] HJ King, ‘A flight to the Cradle Mountain’, Weekly Courier Christmas Annual, 3 November 1932, p.12.
[5] ‘Motors, cycles and push bikes’, Daily Telegraph, 17 April 1920, p.5.
[6] Lucy King, transcript of an interview by Ross Case, 18 March 1993, OH18 (QVMAG).
[7] ‘Motors, cycles and push bikes’, Daily Telegraph, 17 April 1920, p.5.
[8] See Weekly Courier, 15 July 1920, p.24. McClinton’s photos of the Easter 1920 trip with the Kings, Smithies and Hartnett was used here to illustrate part one of George Perrin’s account of a January 1920 trip into the same country with his wife, Florence Perrin, their friend Charlie MacFarlane and Hartnett (‘Trip to Tasmania’s highest tableland’, Weekly Courier, 8 July 1920, p.37).
by Nic Haygarth | 16/12/16 | Tasmanian landscape photography, Tasmanian nature tourism history

Joshua Anson’s 1877 and 1896 mug shots, from GD128-1-2, Tasmanian Archive and Heritage Office (TAHO).
Reinvention is part of the Australian convict story. Many convicts transported to the antipodes reinvented themselves as respectable society figures after serving their sentences. Joshua Anson’s surname was a byword for convictism, Anson being the name of a convict hulk which for years was stationed in the River Derwent, Tasmania. Born in Hobart with a hint of the stigma of convictism already attached to him on 29 October 1854, he would not only serve time and reinvent himself twice but he would pioneer convict tourism, making him almost a post-Modernist of the post-transportation era.
The second of three brothers born to Joshua Anson senior and Eliza Anson née Smith, Joshua Anson grew up to be a physically small man with large ambitions.[1] Unfortunately, his ambition as a landscape photographer shamed him before it famed him. In 1875, at the end of a three-year apprenticeship, 20-year-old Anson was placed in charge of his employer Henry Hall Baily’s Liverpool Street, Hobart shop, and offered an interest in the business. Anson was already a keen photographer, habitually rising at 5AM in order to utilise the morning light, and processing his own prints in his spare time in his home workshop.
About eighteen months after graduation as a ‘photographic artist’, however, Anson came under Baily’s suspicion. Four of the latter’s missing Souvenirs of Tasmania view albums were eventually found in Anson’s workshop. Further police searching revealed landscape and portrait prints, mounts and negatives stolen from Baily. Testimonials to Anson’s good character, including one from the photographer Samuel Clifford, failed to save him from a two-year gaol term for ‘larceny as a servant’.[2]

A shot of Port Arthur rebranded by JW Beattie. Joshua Anson was marketing the old penal settlement before Beattie began work as a professional photographer. Courtesy of TAHO.
He served eighteen months—not at Gothic Port Arthur, but at the Hobart Gaol in Campbell Street. In July 1879, after his release, Joshua and his brothers Henry (1853–90) and William (1857–81) Anson established a photographic studio at 132 Liverpool Street, Hobart.[3] This had been Clifford’s address until 1878, and the Anson brothers seem to have acquired the Clifford photo stock. Joshua’s experience with Baily and his own previous photographic efforts presumably gave the brothers a head start in this new enterprise. He set to work with a series of 26 10-inch by 8-inch views of the Hobart and Launceston regions, including Silver Falls, Mount Wellington, Hobart and Launceston Main Line Railway Stations, Launceston’s Princes Square, People’s (City) Park, St Joseph’s Church and School (in Margaret Street, Launceston), Corra Linn and Cataract Gorge.[4] The immediate purpose of this exercise was probably submission of a dozen scenic prints to the Sydney Exhibition during August 1879.[5] The ultimate purpose would have been to establish a souvenir trade in Tasmanian scenic views. The Tasmanian newspaper reported that Anson would supply his new images to the public at a moderate price, and suggested that ‘if he would mount them in convenient portfolios, they would become popular with strangers, as souvenirs of their visit to Tasmania’.[6]

Beattie comes aboard … and so does the Mount Bischoff tin mine, in Just the Thing III, the Anson Studio advertising album from 1884. Edward Ash was a Hobart chemist and amateur photographer who not only set up a Waratah branch but started a newspaper in Waratah. This photo could have been taken by Ash or by Beattie. Courtesy of TAHO.
This is exactly what the Anson Brothers did. However, their biggest coup was recruiting Scottish immigrant John Watt (JW) Beattie, who became not only the shop manager but the firm’s leading landscape and portrait photographer. The Ansons needed help. All three were epileptics. Twenty-three-year-old William Anson died as the result of a swimming pool accident in 1881; Henry Anson, a married father, would eventually leave the firm but rely on Joshua’s financial help up until his death in 1890, aged only 36.[7]
Beattie has been credited with pioneering convict tourism in Tasmania, but the Port Arthur penal establishment was a subject of Anson photography from 1880, when it appeared in the firm’s Just the Thing photo album. The assumption that Beattie, who joined the Anson Studio two years later in 1882, infused it with his appreciation of history ignores the historical impulse that already existed among Hobart’s professional portraitists. It was almost obligatory in the 1860s and 1870s to photograph or paint the ‘Last of the Aborigines’. In 1880 Ansons photographed a 60-year-old pencil sketch of Hobart Town, featuring Aborigines, and both their ‘Photographs of Hobart and Surroundings, Huon Valley’ (1880?) and Tasmanian Views (1883) albums opened with a photo of the recently deceased Truganini, the former album giving her King Billy (William Lanne) as a consort.[8] . In 1884 ‘Mr Anson the photographer’ stepped off the fishing smack Surprise at Carnarvon, the sanitised name for Port Arthur, where he was reported to have shot several more Port Arthur images.[9]

Browning Falls (Russell Falls) on the Russell River, probably shot for Anson Studio by JW Beattie and later re-branded as his. From Anson Studio’s Picturesque and Interesting Tasmania album (1890), courtesy of TAHO.

Anson Studio advert from Picturesque and Interesting Tasmania (1890), courtesy of TAHO.
Joshua Anson’s offer of partnership to his shop manager JW Beattie in 1890 not only demonstrates the high regard in which the latter’s services were held, but also Anson’s financial problems. Like many a businessman, he became bankrupt during the economic depression of the early 1890s. Court proceedings in April 1892 revealed that Anson had been in serious financial trouble for at least five months, struggling even to pay rent at his lodgings. [10] Part of his downfall was his speculation in shares in the Zeehan–Dundas mining field which had collapsed with the closure of the Bank of Van Diemen’s Land. He claimed to have little idea of the true state of the books until advised by an accountant, although this could have been a ploy to try to avoid culpability for his debts.[11] It was at this point that Beattie bought the Anson Studio, and with it the rights to all the Anson brothers photos taken not only by himself and Joshua Anson but the stock secured from Samuel Clifford. Many Anson Studio photos were re-branded ‘JW Beattie’.
Having lost his studio and his back catalogue, and still being subject to bankruptcy proceedings, Anson tried to re-establish himself as a photographer. Perhaps the strain showed when in March 1893 he was hospitalised with a head injury after collapsing during an epileptic episode in Collins Street.[12] He offered unsuccessfully to photograph lighthouses for the Marine Board of Hobart in July 1893.[13] He was finally discharged from bankruptcy in September 1893.[14]
How did Anson make a living? It is possible he worked for Beattie in his old studio, their positions reversed. In October 1895 he failed in an application to recoup £25 from the government for some Tasmanian tourism photos which had been displayed in the Agent-General’s Office in London years before.[15] With that effort to start afresh defeated, Anson made no further public appearances until May 1896 when he returned to the dock after nineteen years on a charge of robbery from the person. He was alleged to have stolen almost £33 from Strahan storekeeper Charles Perkins at the bar of the Royal Hotel. Anson, who was arrested at Mrs Hanson’s boarding house in Collins Street, appeared in court with bruises on his face resulting from two epileptic fits suffered while in custody.[16] Two months later he was found guilty of receiving and sentenced to twelve months’ gaol.[17]
Anson’s rap sheet records the legacy of epilepsy, noting scars on both side of his forehead. He also had a disfigured left thumb and was missing a second toe from some mishap.[18] When it seemed things could get no worse for Anson, while he was in gaol a newspaper advertisement was run threatening to sell his uncollected clothes.[19] He was released on 26 July 1897: ‘freedom’ was the single word recorded on his rap sheet.[20] Whereupon he disappeared. There is no record of Anson living or dying in Tasmania after that date, although of course he could have changed his name. Forty-two years old, he had plenty of time to start a new career if bankruptcy and two prosecutions for dishonesty could not be held against him.
It is possible that he re-established himself in Western Australia. In November 1897 a John Anson proceeded against a photographer named Flegeltaub for wages due in the Police Court in Perth, Western Australia.[21] In July 1898 a ‘Mr Anson, a photographer engaged by the government to procure photographs of the district for railway carriages etc’, visited Bridgetown in southern Western Australia.[22] Two months later he was on a similar mission at Albany, procuring photos of the harbour, King Georges Sound, the Denmark forests, and in the York area. His employer was named as the Under Secretary of Railways.[23] Taking scenic tourism photos for the government would have been a familiar task for Joshua Anson, and mimicked Beattie’s on-going role as photographer to the Tasmanian government. In October 1904 a John Anson was initially named as one of seven people who went missing when a yacht called the Thelma disappeared in a squall off Fremantle. The men had set out with the intention of visiting Garden Island.[24] However, later reports of the same incident omitted Anson and put the toll at only six people. Joshua Anson may well have become Joshua Anon, reinvented itinerant landscape photographer, posthumous portraitist, a man without a past in a post-convict world.
[1] Birth registration no.1476/1854.
[2] ‘Supreme Court: Second Court’, Mercury, 11 July 1877, p.2; ‘Supreme Court: sentencing’, Mercury, 12 July 1877, p.3.
[3] The Hobart Assessment Roll, Hobart Town Gazette, 1 January 1878, p.36 places Clifford at 132 Liverpool St; whereas Charles Hartam is both owner and occupier of that property at 1 January 1879, p.35. Anson Brothers first advertised their 132 Liverpool St ‘(LATE “CLIFFORD’S”)’ studio in the Mercury on 30 July 1879.
[4] ‘Photographic views’, Tasmanian, 19 July 1879, p.11.
[5] ‘For the Sydney Exhibition’, Mercury, 22 August 1879, p.2.
[6] ‘Photographic Views’, Tasmanian, 19 July 1879, p.11.
[7] ‘Fatal accident at the Domain Baths’, Mercury, 16 February 1881, p.2; ‘The accident in the Domain Baths’, Mercury, 24 February 1881, p.3; ‘Sudden death’, Mercury, 26 March 1890, p.2.
[8] Charles Woolley, for example, submitted portraits of Tasmanian Aborigines to the 1866 Intercolonial Exhibition (Mercury, 25 September 1866, p.3), while HH Baily painted Truganini, the so-called ‘last queen’ of the Aborigines (‘Pictures for the Sydney Exhibition’, Mercury, 5 August 1879, p.2). For the pencil sketch, see ‘An interesting relic’, Mercury, 2 April 1880, p.2.
[9] ‘Carnarvon’, Tasmanian Mail, 19 April 1884, p.20.
[10] ‘Bankruptcy Court’, Launceston Examiner, 14 April 1892, p.3.
[11] ‘Supreme Court’, Mercury, 24 May 1892, p.4.
[12] ‘Hospital cases’, Mercury, 17 March 1893, p.2.
[13] ‘Marine Board of Hobart’, Mercury, 29 July 1893, p.1.
[14] ‘Application in bankruptcy’, Mercury, 2 September 1893, p.3.
[15] ‘House of Assembly’, Mercury, 12 October 1895, p.1.
[16] ‘Alleged robbery’, Tasmanian News, 29 May 1896, p.2.
[17] ‘Second court’, Mercury, 29 July 1896, p.4.
[18] GD128/1/2, p.257 (TAHO).
[19] ‘Late advertisements’, Tasmanian News, 4 August 1896, p.4.
[20] GD128/1/2, p.257 (TAHO).
[21] ‘City Police Court’, West Australian, 9 November 1897, p.7.
[22] ‘Bridgetown’, Bunbury Herald, 2 July 1898, p.3.
[23] ‘England’s fleet’, Albany Advertiser, 13 September 1898, p.3; ‘York Municipal Council’, Eastern Districts Chronicle, 10 September 1898, p.3.
[24] ‘Disappeared in a squall: seven men missing’, Evening News (Sydney), 26 October 1904, p.4.