
In 1906 a newspaper contributor calling himself ‘The Rover’ wrote an account of four months’ hunting in a mountain valley near Lake St Clair. The party of four was from Queenstown. They started for the lake through heavy rain in April, each member bearing a pack weighing 23 kg up the Linda Track, precursor of the Lyell Highway—while a mule carried the rest, a mere 141 kg! First stop was the ‘cockatoo hut’, which at the time was a well-known shelter at the Franklin River.[1] Next day, high on Mount Arrowsmith, the grave of John Largan, who had frozen to death there in 1900, served to warn them of the dangers of the highlands.[2] Arriving at Lake St Clair on the second evening after their long tramp, they spent two days exploring the surrounds before settling on a ‘beautiful valley’ 11 km from the lake. Over four days the party built a log hut with a bark roof as their base.
Then, instead of laying down their snare lines, they ‘waited with feverish impatience for the first fall of snow’. Unleash the hounds! ‘The Rover’ knew what many hunters knew: that in heavy snow wallabies were easy prey for dogs:
‘As we had been at the business before, no time was lost in getting to work, two of us going out and two remaining in camp every alternate day … The same remark applies to the dogs, for they soon knock up if the work is not divided between them. The best plan is to take four dogs at a time, for if the kangaroos [Bennett’s wallabies] are plentiful the dogs will kill faster than a man can skin them, it being a common occurrence to have four or five killed within as many minutes. The fastest kangaroo falls a victim to the slowest dog when pursued through three feet of snow’.
The two men back at camp were kept busy pegging out skins, fetching wood for the fire and cooking supper. No mention was made of a skin shed—but the existence of one is implied by the volume of skins obtained and the duration of the expedition. Mouldy or frozen skins were worthless. They needed to be cleaned and kept dry. The skin shed, a unique Tasmanian invention, was developed at about the beginning of the twentieth century. Its inception was one of the reasons for an escalation in the Tasmanian fur industry, enabling longer stints and greater, more valuable hauls in the highlands where possum furs in particular grew thicker.
After one month the mule was revisited at the Clarence River, and divested of its load—which presumably it had not borne in the interim. The snow was then two feet deep, and in June it got deeper, with metre-long icicles draping the eaves of the hut. Now the ‘rough-coated mongrel’ dog showed his superiority to the purebred, with wallabies being slaughtered in all directions.
One day the hunters found the tracks of a ‘hyena, or Tasmanian tiger’. The dogs took up the scent
‘and in a few minutes discovered the enemy. Their angry growls brought us on the scene, when it was plainly to be seen that the tiger intended to fight to the bitter end. With a cry of encouragement to the dogs we urged them on, and immediately they were engaged in mortal combat with their fierce opponent. The struggle was a long one, but at last the combined strength of the four dogs began to tell, and the battle was over. We found on examination that the tiger was one of the largest of its class, measuring 5 ft 6 in [1.69 m] from the end of his nose to the tip of his tail’.
‘The Rover’ claimed a haul of 91 dozen (1092) wallaby skins—and a weight loss of from 15 to 22 kg per man.[3] The mule, not the men, would have borne the skins back to Queenstown. Providing they were in good condition, they would have fetched something in the region of £80–£140 on the fur market, or an average of about £20–£35 per man.[4] While this would have been a very useful income supplement, better money was to be had in an open season on brush possum.
How credible is this anonymous tale? Let’s start with the hunting season. No year is given, but the events described, if they are real, must have taken place in the period 1901–05. Which season is it likely to be? Throughout the period 1901–05 the season for wallaby was four months, 1 April to 31 July, with closed season for possums in 1903 and 1904 and a one-month season (July) in 1901, 1902 and 1905.[5] So wallabies would have been the focus for many hunters during these seasons, and almost without exception in 1903 and 1904. As for the very heavy snow falls, there was plenty of snow at Cradle Mountain in July 1905 when hunter Bert Hanson disappeared in a blizzard. Hanson and his mate Tom Jones were also using dogs to hunt down wallabies.[6]
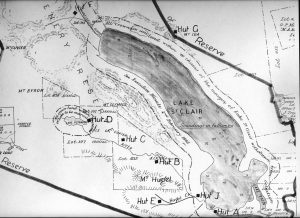
What was the ‘beautiful valley about 10 miles long by two in width, and bounded on each side by high ranges extending as far as the eye could reach, rising almost perpendicularly from the valley below’? Allowing for a little poetic licence, it could be the Cuvier Valley west of Mount Olympus, where hunters like Bert and Dick Nichols operated two decades later.[7]
What about the thylacine: was the carcass submitted for a government thylacine bounty? Plenty of applications were made for the bounty in the spring of the years 1901–05, but without knowing the origin of each application it is very difficult to track down ‘The Rover’ or his mates from Queenstown.[8] Given the value of the wallaby skins they obtained, carting a single thylacine carcass back to Queenstown in order to submit it for a £1 bounty may not have been a priority for them anyway.
In short, the story is plausible. I hope there are further missives from ‘The Rover’, giving more insight into the task of feeding the world’s craving for furs.
[1] See, for example, JW Beattie, ‘Out west with salmon fry’, Mercury, 18 February 1903, p.6; ‘Alluvial gold’, Mercury, 25 August 1935, p.8.
[2] See ‘Mount Arrowsmith tragedy’, Mount Lyell Standard and Strahan Gazette, 3 September 1900, p.2.
[3] ‘The Rover’, ‘A Tasmanian winter camp’, Weekly Courier, 26 May 1906, p.37.
[4] In August 1901 ‘kangaroo’ skins free from shot were fetching £0-1-6 to £0-1-8 each (‘Commercial’, Mercury, 17 August 1901, p.2); in August 1905 ‘kangaroo’ fetched from £0-1-11 to £0-2-6 (‘Commercial’, Examiner, 12 August 1905, p.4). My calculations assume that all the skins obtained were Bennett’s wallabies, when it is likely that some were pademelons. ‘The Rover’ does not specify.
[5] Editorial, Daily Telegraph, 30 July 1901, p.2; ‘To correspondents’, Zeehan and Dundas Herald, 31 July 1902, p.2; ‘Current topics’, Examiner, 31 March 1903, p.4; ‘Warning to possum poachers’, Examiner, 19 June 1903, p.6; ‘To correspondents’, Examiner, 13 April 1904, p.4; ‘Kangaroos and opossums’, Daily Telegraph, 3 May 1905, p.2.
[6] ‘The Tramp’ (Dan Griffin), ‘The mountain mystery’, Daily Telegraph, 5 August 1905, p.6.
[7] See Gerald Propsting to the Secretary for Public Works, 4 August 1927, file AA580/1/1(Tasmanian Archive and Heritage Office [afterwards TAHO]); ‘Lake St Clair Reserve: allegations of poaching’, Mercury, 26 May 1927, p.10.
[8] Government thylacine bounty payments in the years 1888—1909 are recorded in LSD247/1/2 and LSD247/1/3 (TAHO).