by Nic Haygarth | 23/05/25 | Story of the thylacine

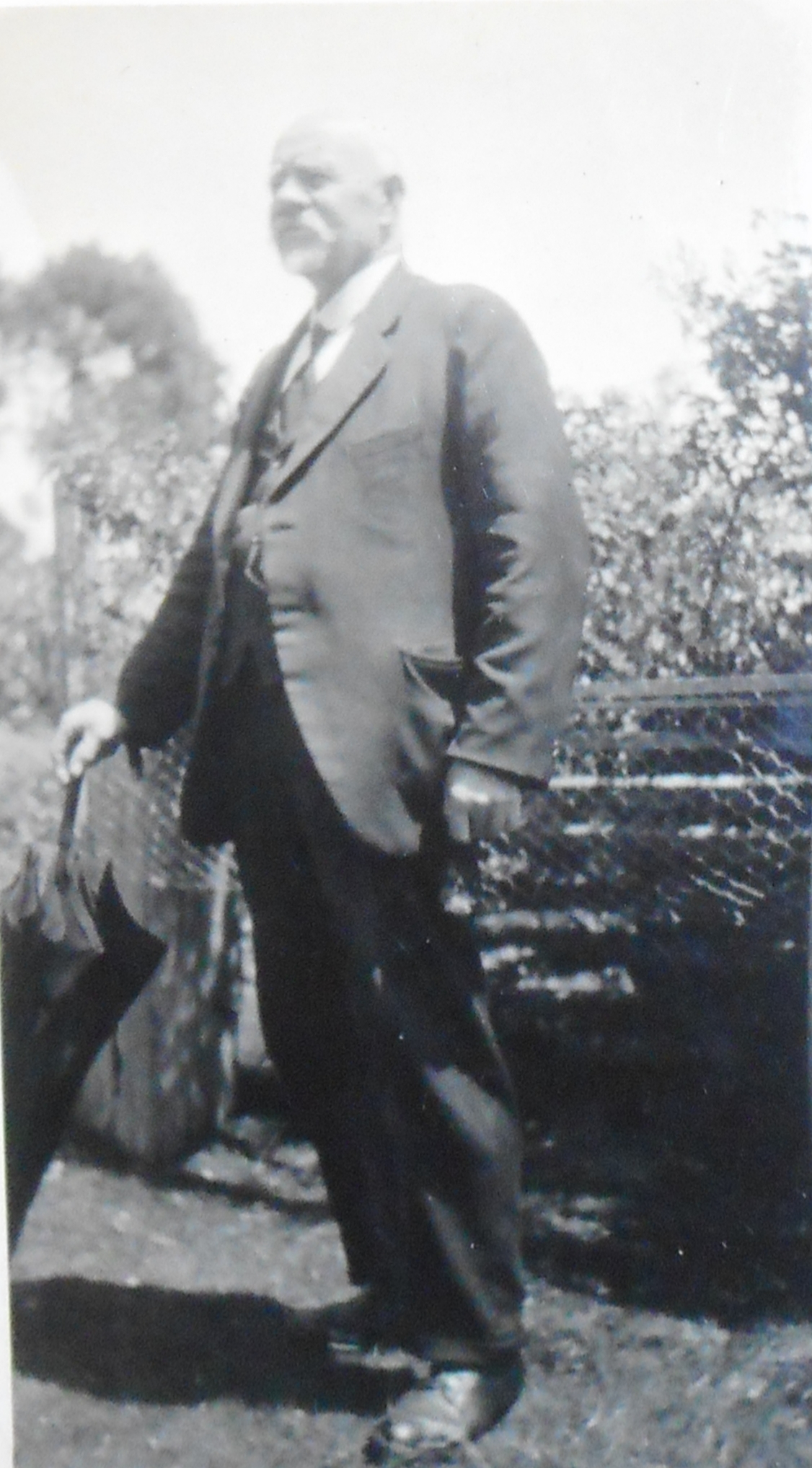
James ‘Tiger’ Harrison, Wynyard native animals dealer, snarer, prospector, track cutter, estate agent, shipping agent, Christian Brethren registrar, tourist chauffeur, human ‘cork’ and Crown bailiff of fossils. Photo from the Norman Larid files, NS1143, Tasmanian Archives (TA).
In the mid-1920s thylacines were still reported by bushmen in remote parts of the north-west. Luke Etchell claimed there was a time when he caught six or seven ‘native tigers’ per season at the Surrey Hills.[1] Like Brown brothers at Guildford, Van Diemen’s Land Company (VDL Co) hands at Woolnorth were still doing a trade in live native animals—although the latter property was out of tigers. On 7 July 1925 Hobart City Council paid the VDL Co £60 10 shillings for what can only be described as two loads of ‘animals’—presumably Tasmanian devils and quolls—recorded as being carted out to the nearest post office at Montagu during the previous month.[2] A further transaction of £30 was recorded in October 1925, when it is possible Woolnorth manager George Wainwright junior hand delivered a crate of live native animals to Hobart’s Beaumaris Zoo.[3]
James ‘Tiger’ Harrison (1860–1943) of Wynyard took his animals dead or alive. He bought and sold living Tasmanian birds and marsupials, including tigers, but also hunted for furs in winter. In July 1926 Harrison and his Wynyard friend George Easton (1864–1951) secured government funding of £2 per week each to prospect south of the Arthur River for eight weeks.[4] However, their main game was hunting: the two-month season opened on 1 July 1926.

James Harrison’s collaborators George Easton and George Smith with a bark boat used to rescue Easton at the Arthur River in 1929. Photo courtesy of Libby Mercer.
TOPOGRAPHIC BASEMAP FROM THELIST©STATE OF TASMANIA
Easton, an experienced bushman in his own right, made snares most evenings until the pair departed Wynyard on 14 July.[5] At Trowutta Station they boarded the horse-drawn, wooden-railed tram to the Arthur River that jointly served Lee’s and McKay’s Sawmills.[6] Next day, Arthur Armstrong from Trowutta arrived with a pack-horse bearing their stores, and the pair set out along the northern bank of the Arthur towards the old government-built hut on Aylett’s track.[7] However, on a walk to the Dempster Plains to shoot some wallaby to feed their dogs, Harrison injured his knee so badly that he couldn’t carry a pack. So before they had even set some snares the pair was forced to return home.[8] On their slow, rain-soaked journey they sold their stores to the Arthur River Sawmill boarding-house keeper Hayes—the only problem being delivery of said stores from their position up river.[9] While Harrison went home by horse tram and car, Easton had to help Armstrong the packer retrieve the stores.[10]

Martha Crole and her daughters. From the Weekly Courier, 10 April 1919, p.22.

The Crole house at Trowutta. From the Weekly Courier, 10 April 1919, p.22.
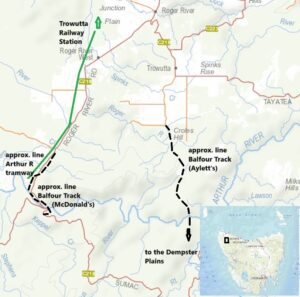
‘Tiger country’ around the Arthur River
If not for the injury Harrison may have secured more than furs over the Arthur. One of the European pioneers in that area was grazier Fred Dempster (1863–1946), who appears to have rediscovered pastures celebrated by John Helder Wedge in 1828.[11] Out on his run in 1915 Dempster met a breakfast gatecrasher with cold steel. The elderly tiger reportedly measured 7 feet from nose to tail and being something of a gourmet registered 224 lbs on Dempster’s bathroom scales.[12] In dramatising this shooting, anonymous newspaper correspondent ‘Agricola’ mixed familiar thylacine attributes with the fanciful idea of its ferocity:
This part is the home of the true Tasmanian tiger … This animal must not be confounded with the smaller cat-headed species [he perhaps means the ‘tiger cat’, that is, spotted-tailed quoll, Dasyurus maculatus] so prevalent beyond Waratah, Henrietta and other places. The true species is absolutely fearless in man’s presence, and if he smells meat will follow the wayfarer on the lonely bush tracks for miles, stopping when he does and going on when he resumes his walk. It has been proved beyond question that these brutes will not shift off the paths when met by man, and they will always attack when cornered.[13]
One mainland newspaper was apparently so confused by ‘Agricola’s’ account that he called Dempster’s thylacine ‘a huge tiger cat’.[14]
Trowutta people had no problem distinguishing quoll from tiger. They caught the latter unwittingly while snaring. Fred and Martha Crole and family of Trowutta made hundreds of snares on a sewing machine, eating the wallaby meat and selling the skins they caught. One of their boys, Arthur Crole (1895–1972), landed a tiger alive in a snare, killed it, tanned the hide and used it as a bedside rug.[15] While south of the Arthur, Harrison and Easton were unlucky not to run into Trowutta farmers Fred and Violet Purdy, who caught a tiger in a footer snare there during the 1926 season. When the Purdys approached the captured animal it broke the snare and disappeared. However, tigers also frequently visited their hut south of the river at night and they saw their footprints in the mud next morning.[16] Violet Purdy claimed to have spent six months straight living in the ‘wild bush’ (the hunting season in 1926 was only July and August), and her observations of the thylacine suggest someone with at least second-hand knowledge. Like ‘Agricola’, she knew of the tiger’s reputed habit of refusing to move off a track to let a human pass. Unlike him, she attested to the animal’s shyness. Purdy recommended ‘a couple of good cattle dogs’ as the means of tracking it down. She and her husband found thylacine tracks at the Frankland River as they crossed it to reach the Dempster Plains.[17] Decades later Purdy regaled the Animals’ and Birds’ Protection Board with her tales, illustrating them with a map of ‘tiger country’ between Trowutta and the Dempster Plains.

‘Tiger country’ between Trowutta and Dempster Plains, as it looked in 1926, according to Mrs V Kenevan,
formerly Violet Purdy of Trowutta. From AA612/1/59 (TA).
Snaring at Woolnorth
By the time Easton got home to Wynyard, Harrison, apparently recovered from his knee injury, had arranged for them both to snare at Woolnorth, where no swags needed to be carried, since stores were supplied. The VDL Co employed hunters every season to kill ‘game’, this serving the dual purpose of saving the grass for the stock and bringing the company income at a time of low agricultural prices. At this time hunters paid a royalty of one in six skins to the company.
Easton’s diary entries give rare insight into a hunting engagement. Harrison and Easton took the train to Smithton and caught the mail truck to Montagu, from which they were borne by chaise cart to the Woolnorth homestead. That night the snarers were put in a cottage generally reserved for the VDL Co agent, AK McGaw.[18] Next day station manager George Wainwright junior showed them their lodgings (tents next to a lagoon which served as the water supply) and how snaring (using springer snares but also neck snares along fences) and skinning were done at Woolnorth. Wainwright, an old hand, claimed to be able to skin 30 animals per hour.[19] Storms, horse leeches, which had a way of attaching themselves to the human scalp, and cutting springers and pegs kept the snarers very well occupied between snare inspections, an 11-km-long daily routine. The game was nearly all wallaby and ringtails, and Harrison and Easton dried their skins not in a skin shed but by hanging them in trees.[20] Bathing meant a sponge bath with a prospecting dish full of cold water—which also constituted the laundry facilities.[21] The last day of the season at Woolnorth was traditionally an all-in animal shoot, after which the season’s skins were baled, treated with an arsenic solution to kill insects and delivered to a skins dealer.[22] In the two-month 1926 season the VDL Co made £493 from the fur industry, a big reduction on the previous year (£1296) when the season had lasted three months.[23]
However, Harrison didn’t last the distance, calling it quits on 13 August after barely two weeks, leaving Easton to carry on alone until the season ended eighteen days later. Their skin tally at 13 August stood at 16½ dozen—198 skins or 99 apiece.[24]
Returning to ‘tiger country’
Once again ‘Tiger’ Harrison was in the wrong place at the wrong time to live up to his nickname. While he was working at tiger-free Woolnorth, timber worker, hunter and sometime miner Alf Forward snared two tigers, one alive, one choked to death by a stiff spring in a necker snare at the Salmon River Sawmill south of Smithton.[25] Forward is said to have exhibited the living one in Smithton before selling it to Harrison.[26] He almost had another live one in the following month, when a tiger detained by Forward’s snare for two days bit his capturer’s hand, thereby effecting its escape.[27]
Harrison eventually decided to cut out the middle-man. From 1927 he conducted expeditions specifically to obtain living thylacines to sell. He had no luck until in June 1929 he caught one 3 km south-west of Takone.[28] The Arthur River catchment remained ‘tiger country’ in the mid-1930s when ‘Pax’ (Michael Finnerty) and Roy Marthick claimed to have seen them while prospecting.[29] The question of whether they are there today still entertains Tarkine tourists and the worldwide thylacine mafia.
[1] MA Summers’ report, 14 May 1937, AA612/1/59 H/60/34 (Tasmanian Archives, henceforth TA).
[2 Payment recorded 7 July 1925. On 9 June 1925: ‘W Simpson taken animals to Montagu’; 22 June 1925: ‘W Simpson went to Montagu with load of animals’, Woolnorth farm diary, VDL277/1/53 (TA).
[3] Payment recorded on 13 October 1925. On 4 October 1925 George Wainwright junior and his wife departed Woolnorth for the Launceston Agricultural Show (Woolnorth farm diary VDL277/1/53). It is possible that he took a crate of animals on the train to Hobart.
[4] GW Easton diary, 1 July 1926 (held by Libby Mercer, Hobart).
[5] GW Easton diary, 1–14 July 1926.
[6] GW Easton diary, 15 July 1926.
[7] GW Easton diary, 16 July 1926.
[8] GW Easton diary, 18 July 1926.
[9] GW Easton diary, 23 July 1926.
[10] GW Easton diary, 25 and 26 July 1926.
[11] JH Wedge, ‘Official report of journeys made by JH Wedge, Esq, Assistant Surveyor, in the North-West Portion of Van Diemen’s Land, in the early part of the year 1828’, reprinted in Venturing westward: accounts of pioneering exploration in northern and western Tasmania by Messrs Gould, Gunn, Hellyer, Frodsham, Counsel and Sprent [and Wedge], Government Printer, Hobart, 1987, p.38.
[12] See for example ‘Boat Harbour’, North West Post, 22 February 1915, p.2. Dempster probably didn’t have any bathroom scales with him. Rather mysteriously, the author of ‘A huge tiger cat’, Westralian Worker, 19 March 1915, p.6, put the animal’s weight as ‘2 cwt’ (224 lbs).
[13] ‘Agricola’, ‘Farm jottings’, North West Post, 24 February 1915, p.4. In another column ‘Agricola’ claimed with equal dubiousness that under Mount Pearse trappers caught tigers in pits, and that if more than one tiger was collected in the same pit at the same time the captured animals would fight to the death. See ‘Agricola’, ‘Farm jottings’, North West Post, 10 July 1914, p.4.
[14] ‘A huge tiger cat’, Westralian Worker, 19 March 1915, p.6.
[15] Fred and Graham Crole, in Women’s stories: different stories—different lives—different experiences: a Circular Head oral history project (compiled and edited by Pat Brown and Helene Williamson), Forest, Tas, 2009, p.192.
[16] The hut was on Aylett’s Track to Balfour.
[17] Violet Kenevan, Kingswood, New South Wales, to secretary of the Animals’ and Birds’ Protection Board, 30 October 1956, AA612/1/59 (TA).
[18 GW Easton diary, 27 July 1926.
[19] GW Easton diary, 30 July 1926.
[20] GW Easton diary, 18 August 1926.
[21] GW Easton diary, 15 August 1926.
[22] GW Easton diary, 31 August and 6–9 September 1926; Woolnorth farm diary, 31 August 1926, VDL277/1/54 (TA).
[23] The figures are from VDL129/1/7 (TA).
[24] GW Easton diary, 13 August 1926.
[25] ‘Hyena choked in snare at Salmon River’, Circular Head Chronicle, 11 August 1926, p.5.
[26] ‘TT, from New Town’, ‘Tasmanian tiger’, Mercury, 24 August 1954, p.4, claimed that Alf Forward caught the animal in a kangaroo snare at the Salmon River ‘less than 30 years ago’ and sold it to Harrison after putting it on show in Smithton.
[27] ‘Hand bitten by a hyena’, Circular Head Chronicle, 29 September 1926, p.5.
[28 GW Easton diary, 17 June 1929; Circular Head Chronicle, 29 May 1929.
[29] See ‘Pax’ (Michael Finnerty), ‘A “bush-whacker’s” experience in the north-west’, Mercury, 6 May 1937, p.8; Roy Marthick to the Fauna Board, 10 February 1937 (TA); Roy Marthick quoted by Charles Barrett, ‘Out in the open: nature study for the schools’, Weekly Times (Melbourne), 10 July 1937, p.44.
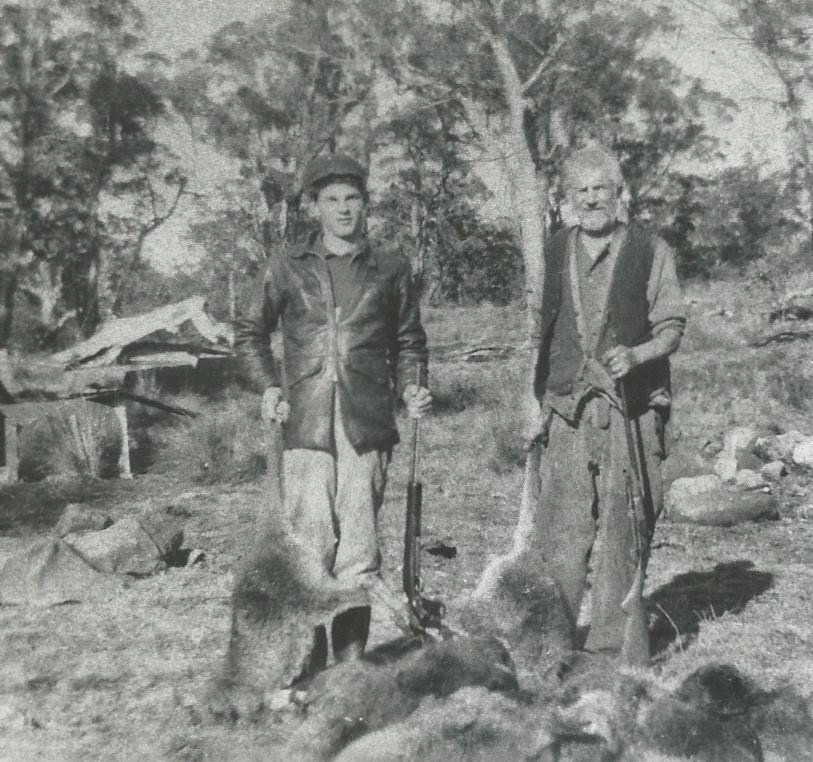

by Nic Haygarth | 06/10/24 | Tasmanian high country history
The collection of farms known as Narrawa in north-western Tasmania produced some tough old buggers. The small community west of Wilmot was home to the Carters, Vernhams, Williamses, Bramichs, Lehmans and others, bush farmers resigned to grubbing out, burning and stump jacking their way to cleared pasture. Crops like potatoes were planted in the ashes of the burnt trees as the beginning of farming operations.

Jack (aka Johnny) Carter, Bill ‘Yorky’ Smith and Jack ‘Boy’ Griffiths clearing land at Narrawa. Griffiths, standing precariously on the log stack, was later killed in a similar operation on the Williams farm. Courtesy of Peter Carter.
After the harvest came the hunt. This was a chance to earn enough money to keep self and family for the rest of the year. Each hunter had his own territory somewhere in the north-western highlands.
Harry ‘Poke’ Vernham/Vernon/Varnham (c1885–c1954)[1]
By the age of 20 Narrawa farmer Charles Henry Vernham already knew his way around Cradle Mountain, being conscripted in the search for hunter Bert Hanson who had gone missing near there in a winter fog.
[2] Harry excited more legends than probably any other bushman in his neck of the woods. He was a small man who, paradoxically, wore sandshoes (sneakers) in the bush. Harry was ‘square as a brick’ but so tough ‘you could drive nails into him and you wouldn’t hurt him’.
[3] Two stories bear out his toughness. In the snaring season of 1906 Harry cut his knee with an axe in the snow at Henrietta south of Wynyard. He covered the wound with salt and bandaged it with a green wallaby skin, telling his hunting partner ‘You’ll have to do all the snaring. I’ll peg out the skins and do all the cooking’.
[4] Eventually Harry presented himself to a doctor, who told him that he was just in time to prevent the onset of gangrene.
[5] Harry was then admitted to the Devon Cottage Hospital at Latrobe.
[6] Hearing of her son’s accident, Harry’s mother walked about 30 km from Wilmot to Latrobe to prevent a surgeon amputating his leg. She succeeded, but Harry was left with a stiff leg for the rest of his life.
[7]

A young Harry Vernham sitting second from right in the second Bert Hanson search party, Weekly Courier, 30 September 1905, p.20.
On another occasion Harry’s nose was virtually detached from his face in a motorcycle accident.
[8] A doctor told him, ‘I’d better give you a whiff of something before I stitch it back on’. Harry is said to have replied, ‘I didn’t have a whiff when it come off so I don’t need one putting it back on’.
[9]
Hunting exploits
In 1914 Harry married Annie Eliza Carter, from the neighbouring family.
[10] They had a boy and three girls over the next four years, but Harry’s nickname Poke suggests that his sex life didn’t end there. At least the hunting seasons were celibate. Harry and his brother George Matthew ‘Native’ Vernham (1889–1966)
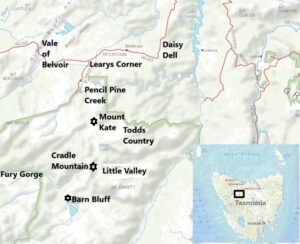
[11] had a hut on the south-eastern side of Mount Kate and a little log hut near the site of the present-day Cradle Mountain Lodge, the latter being pretty schmick as it was a lock-up affair.
[12] Other Harry Vernham hunting companions included Ernest ‘Son’ Bramich (1914) and Harry Leach (1933).
[13] Ted Murfet recalled camping with Harry in later years at Middlesex Station, the Twin Creeks Sawmill huts, the hut at Learys Corner, Daisy Dell and Robertson’s on the track into the Vale of Belvoir.
[14] They took a dozen balls of hemp for a season and used an old eggbeater to make up their treadle snares on a board about 1.2 m long. Usually they’d need 1000 snares for the season. In their worst season the pair shared £300 and in their best the take was £700—£350 each.
[15] By this time Harry had moved beyond the medicinal qualities of a green wallaby skin, developing new home remedies. He treated an ulcer on his leg with a plaster of onion wrapped up in a sock as a bandage and addressed a cold with swigs of Worcestershire sauce.
[16]

Harry Vernham (right) hunting much later in life. Courtesy of David Ball.
TOPOGRAPHIC BASEMAP FROM THELIST© STATE OF TASMANIA
The slow farm development ritual undertaken at Narrawa also applied to the Connell family when they took up the Dunlavin property at the top of Chinamans Hill, Lower Wilmot, in the 1890s. While his older brother Lionel Connell (1884–1960) became a miner, Gordon stayed on the farm.
[18] He married Alice Jacklin in 1911, and the couple had at least four children during the next decade.
[19] In 1915/16 Lionel Connell and Dick Nichols built a hunting hut in the Little Valley, south of Lake Rodway, and in 1917, when Lionel took a 3-month sabbatical from the Shepherd and Murphy Mine to go hunting, his younger brother Gordon joined him at Cradle.
[20] Known as Bull because of his huge shoulders and great physical strength, Gordon hunted with Lionel as far south as the plains between Barn Bluff and the Fury River. He also worked over the so-called Todds Country at the head of the Campbell River.
[21] Gordon had a big kangaroo dog called Slocum which would take him to his kills. One day Gordon put his feet up and smoked for 30 minutes before Slocum returned. ‘Where is he then?’, the master prompted, setting the dog off towards Lake Carruthers to a big kangaroo he’d killed. But Slocum wasn’t finished, refusing to budge. ‘Well where is he then?’. Off they went again beyond Lake Carruthers to another big kangaroo carcass.
[22]

Gordon Connell, courtesy of Malcolm Dick.
Gordon hunted with Harry Vernham at Cradle in 1925 and 1926 and in other years around Middlesex and the Vale of Belvoir.
[23] They developed a regime of line camps or temporary shelters to get around their extensive snare lines, arriving at base camp only every three days. Gordon recalled icicles forming on Harry’s formidable body hair as he lugged his bag of skins about the snare lines. When Harry stripped off his shirt a huge cloud of steam arose from his singlet, an unusual form of enveloping fog. Wild bulls remaining from Field brothers’ Middlesex grazing operation were an occasional problem for hunters. The worst of these was a territorial bull called Bob because of the ‘bob’ in his tail. Another bull they put a bullet in roared back to life as they approached its apparent corpse. Gordon had a way of cutting a cartridge with a knife to concentrate its potency, but on this occasion it seems to have had the opposite effect.
[24]
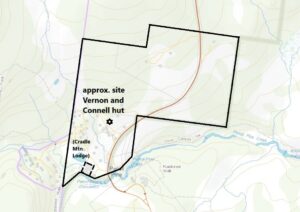
The Vernham and Connell 99-acre block at Pencil Pine Creek. TOPOGRAPHIC BASEMAP FROM THELIST© STATE OF TASMANIA

How the area looked in 1949, showing the position of the hunting hut. Crop from aerial photo 0196_483, 15 April 1949.
In the 1930s Poke and Bull selected and started to pay off a 99-acre-block at Pencil Pine Creek enclosing the log hut and the old FH Haines sawmill site—land now partly occupied by Cradle Mountain Lodge, the Cradle Mountain shop and rangers’ quarters. Presumably they were either safeguarding their hold on valuable hunting territory or foresaw future tourism development. The pair failed to pay it off, and Lionel and Margaret Connell took over the payments. Lionel’s family were still using the log hut in 1940. Like most hunting huts in the area it had a skin shed chimney, that is, a very large timber chimney in which skins were pegged to dry close to the fire.
[25]
The tiger stories
Peter Carter, Harry Vernham’s nephew, claimed that Harry caught thylacines (Tasmanian tigers) in ‘hell-necker’ or ‘hellfire necker’ snares positioned at each end of a hollow log that contained a live wallaby. The ‘hellfire’ appears to have been a heavy-duty neck snare—not terribly surprising, as plenty of tigers were strangled in neck snares. What is surprising is Peter’s claim that his uncle sold skun tigers, that is, tiger carcasses, for £5. Perhaps he meant that he sold tiger skins for £5.
[26] Harry Vernham’s name was never entered on the list of payees for the £1 per head government thylacine bounty, although it is possible he claimed bounties through an intermediary. Still, the question needs to be asked why he went to so much trouble to strangle a tiger in a neck snare, when he could just have easily snared it alive by the paw in a foot or treadle device which would have earned him much more money. The story would only make sense if Harry had learned the whereabouts of a tiger or family of tigers and set up the hollow log trap as above, making sure the wallaby was restrained so that it couldn’t spring the snares while making its escape. Prices paid for tigers, dead or alive, varied wildly, so it’s hard to put even an approximate year on Vernham’s tiger sales.
[27]
Gordon Connell is another name missing from the government tiger bounty register. He once caught a thylacine dead in the snare—presumably a necker snare which strangled it—but he encountered others in the wild. Bull was said to have found a thylacine lair in one of three rock shelters down in the Fury Gorge while hunting nearby. He shouldn’t have been surprised then when, hunting the button-grass plains above it out of season, he heard an animal yelp. A big kangaroo hopped up the slope, as if disturbed, convincing Gordon and his mate that the police were below them. Then a tiger came up the slope in pursuit of the kangaroo. At regular intervals it stopped and gave three sharp yelps before continuing the chase, as did a second tiger behind it.
[28]
What a pity neither Poke nor Bull put pen to paper! We know so little about hunters’ experiences with tigers, but at least these anecdotes give glimpses of what they passed down through family and the hunting community.
[1] Years of birth and death are from Ancestry.com.au, no birth certificate or will was found.
[2] ‘Lost in the snow: a second search party’,
North Western Advocate and the Emu Bay Times, 25 July 1905, p.3.
[3] Peter Carter, interviewed by David Bannear, 16 July 1990, in
What’s the land for?: people’s experiences of Tasmania’s Central Plateau region, Central Plateau Oral History Project, Hobart, 1991, vol.3, p.4.
[4] Warren Connell, interviewed 8 September 1997; David Ball, interviewed 25 April 2020.
[5] Warren Connell.
[6] ‘Latrobe’,
North Western Advocate and the Emu Bay Times, 29 August 1906, p.2.
[7] Len Fisher,
Wilmot: those were the days, pp.46–47
[8] ‘Ulverstone’,
Advocate, 26 March 1934, p.6.
[9] David Ball, 24 April 2020. Ted Murfet also told this story to Len Fisher in
Wilmot: those were the days, the author, Devonport, 1990, p.82.
[10] Married 15 October 1914, marriage record no.801/1914, registered at Wilmot (TA).
[11] Born to Blackwood Hill, West Tamar labourer William Varnam [sic] and Christina Bowers on 1 February 1889, birth record no.736/1889, registered at Beaconsfield, RGD33/1/68 (TA),
https://librariestas.ent.sirsidynix.net.au/client/en_AU/names/search/results?qu=george&qu=varnham, accessed 3 October 2023; died 7 February 1966, Will no.47656, AD960/1/105 (TA),
https://librariestas.ent.sirsidynix.net.au/client/en_AU/names/search/results?qu=george&qu=vernham, accessed 3 October 2023.
[12] Gustav Weindorfer diary, 12 July 1914 (Pencil Pine Creek), 23 July 1914 (east side Mount Kate), NS234/27/1/4 (TA); 10 July and 10 August 1925 (Pencil Pine Creek) (QVMAG). Es Connell, interviewed by Nic Haygarth on 23 September 1997, confirmed the location of this hut.
[13] Gustav Weindorfer, in his diary, 16 and 18 June 1914, NS234/27/1/4 (TA), recorded Harry Vernham and Bramich hunting Cradle Valley and Hounslow Heath with dogs. For Leach see ‘Taking game in close season alleged’,
Advocate, 12 September 1933, p.2.
[14] Ted Murfet, interviewed 15 October 1995.
[15] Ted Murfet, interviewed 15 October 1995.
[16] Ted Murfet, in Len Fisher,
Wilmot: those were the days, the author, Devonport, 1990, p.81.
[17] Born 29 April 1889 to Michael Connell and Frances Sayer, birth registration no.2639/1889, registered at Port Frederick, RGD33/1/68 (TA),
https://librariestas.ent.sirsidynix.net.au/client/en_AU/names/search/results?qu=gordon&qu=murray&qu=connell#, accessed 18 August 2024. The family was living at Torquay (East Devonport).
[18] Commonwealth Electoral Roll, Division of Wilmot, Subdivision of Kentish, 1914, p.10;
Wise’s Tasmanian Post Office Directory, 1919, p.277.
[19] Married 28 March 1911, file no.1384/1911, registered at Gunns Plains (TA).
[20] Gustav Weindorfer diary 29 December 1915 (Lionel Connell and Dick Nichols arrive at Cradle from Moina), NS234/27/1/5 (TA); 1–26 April 1917, NS234/27/1/7 (TA). Weindorfer possibly also referred to Gordon Connell in diary entries in May and June 1917, NS234/27/1/7 (TA).
[21] Todds Country was a name given by snarers to territory hunted by Bill Todd (1855–1926).
[22] Warren Connell.
[23] Gustav Weindorfer diary, 14 July 1925 and 23 March 1926 (QVMAG).
[24] Warren Connell.
[25] RE Smith diary, 29 June 1940, NS234/16/1/40 (TA).
[26] Peter Carter, p.10.
[27] For example,in James 1928 Harrison sold a tiger carcass to Colin MacKenzie in Melbourne for £12 (Harrison’s notebook). In 1930 Wilf Batty sold the carcass of the tiger he killed at Mawbanna for £5 (Wilf Batty; quoted in ‘The $55,000 search to find a Tasmanian tiger’,
Australian Women’s Weekly, 24 September 1980, p.41).
[28] Warren Connell.
by Nic Haygarth | 22/10/20 | Circular Head history, Story of the thylacine
By the 1890s farmers like Joseph Clifford and Robert Stevenson were effectively adding Tasmanian tiger farming to their portfolios of raising stock, growing crops and hunting. Since thylacines appeared on their property, they made a conscious effort to catch them alive in a footer snare or pit rather than dead in a necker snare. A tiger grew no valuable wool, but in 1890 a live wether might fetch 13 shillings, compared to £6 for an adult thylacine delivered to Sydney.[1] A dead adult thylacine, on the other hand, was worth only £1 under the government bounty scheme.
The problem with these special efforts to catch tigers alive was that hunters only had a certain amount of control over what animals ended up in their snares or pits. Twentieth-century hunters often complained about city regulators who thought it feasible to close the season on brush possum but open it for wallabies and pademelons. Inevitably, hunters caught some brush possum in their wallaby and pademelon snares during the course of the season, which could land them a hefty fine in court unless they destroyed the precious but unlawful skins.[2] John Pearce junior in the upper Derwent district claimed that he and his brothers caught seventeen tigers in ‘special neck snares’ set alongside their kangaroo snares.[3] How did the tigers recognise the ‘special neck snares’ provided for their specific use? All you could do was vary the height of the necker snare to catch the desired animal’s head as it walked. Too bad if something else stuck its head in the noose. Wombats, for example, were a hazard. Gustav Weindorfer of Cradle Valley set snares at the right height to catch Bennett’s wallabies by the neck, but also caught wombats in them.[4] Wombats were good for ‘badger’ stew and for hearth mats but the skins had no value. Robert Stevenson of Aplico, Blessington, caught wombats alive in his tiger pits—which they then set about destroying by burrowing their way out.[5]

George Wainwright senior, Matilda Wainwright and children at Mount Cameron West (Preminghana) c1900. Courtesy of Kath Medwin.
These problems aside, it seems odd that the pragmatic Van Diemen’s Land Company (VDL Co), which later added fur hunting to its income stream, didn’t cotton on to the live tiger trade. They could have followed the example of George Wainwright senior, who sold a Woolnorth tiger to Fitzgerald’s Circus in 1896.[6] In 1900, for example, 22 thylacines were killed on Woolnorth, a potential income of more than £100 had the animals been taken alive. Even when, later, four living Woolnorth tigers were sold, the money stayed with the employees, with the VDL Co not even taking a commission. (It should be noted that four young tigers caught by Walter Pinkard on Woolnorth in 1901 were not accounted for in bounty payments.[7] It is possible that they were sold alive—but there are no records of a sale or even correspondence about the animals. Their fate is unknown.)


William Le Souef to Kruger, 22 October 1901: ‘The Tasmanian Wolves are all
right, so far’. Did he get them from Woolnorth? Postcard courtesy of Mike Simco.
The VDL Co’s failure to exploit the live trade for its perceived arch enemy can possibly be explained by the tunnel vision of its directors and departing Tasmanian agent and the inexperience of his successor. James Norton Smith resigned as local manager in 1902. His replacement, Scotsman Andrew Kidd (AK) McGaw, harnessed Norton Smith’s 33-year corporate knowledge by re-engaging him as farm manager. It would not have been easy for McGaw to learn the ropes in a new country, among business associates cultivated by his predecessor, and the re-engagement of Norton Smith as his second allowed him to transition into the manager position. As would be expected, McGaw stamped his authority on the agency by criticising some of Norton Smith’s policies and distancing himself from them.[8] Ahead of Ernest Warde’s engagement as ‘tigerman’, the VDL Co’s shepherd at Mount Cameron West, he scrapped Norton Smith’s recent bounty incentive scheme of £2 for a tiger killed by a man out hunting with dogs.
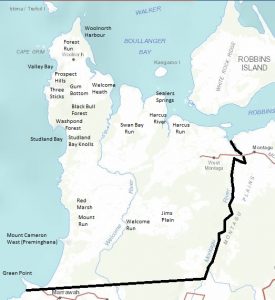
Woolnorth, showing main property features and the original boundary. Base map courtesy of DPIPWE.
After Warde’s departure in 1905, the tiger snares at Mount Cameron and Studland Bay were checked intermittently. Woolnorth overseer Thomas Lovell killed a tiger at Studland Bay in 1906, but the number of tigers and dogs reported on the property was now negligible.[9] This reflected the statewide situation, with only eighteen government thylacine bounties being paid in 1907, and only thirteen in 1908.[10]
However, the value of live tigers continued to climb as they became rarer. The first documented approach to the VDL Co for live tigers came in July 1902 from AS Le Souef of the Zoological Gardens in Melbourne, who offered £8 for a pair of adults and £5 for a pair of juveniles. He also wanted devils and tiger cats, in response to which George Wainwright junior supplied two tiger cats (spotted quolls, Dasyurus maculatus).[11] Given the tiger’s reputation as a sheep killer, native animal farming might have been a hard sell to the directors, and the company continued to use necker snares which were generally fatal to thylacines. What price would it take to change that behaviour? In July 1908 McGaw read a newspaper advertisement:
‘WANTED—Five Tasmanian tigers, handsome price for good specimens. Apply Beaumaris, Hobart.’[12]
He discovered that the proprietor of the private Beaumaris Zoo at Battery Point, Mary Grant Roberts, wanted a pair of living tigers immediately to freight to the London Zoo.[13] The Orient steamer Ortona was departing for London at the end of the month. She offered McGaw £10 for a living, uninjured pair of adults. Roberts hoped to secure the tiger caught recently by George Tripp at Watery Plains, but felt that she was competing for live captures with William McGowan of the City Park Zoo, Launceston, who advertised in the same month.[14] Eroni Brothers Circus was also in the market for living tigers.[15]

A young Mary Grant Roberts, from NS823/1/69 (Tasmanian Archive and Heritage Office).
Almost as Roberts made her offer, George Wainwright junior tracked a tiger at Mount Cameron West, but it evaded capture.[16] In the meantime Roberts was able to secure her first thylacine from the Dee River.[17]
Almost a year passed before the chance arose for the VDL Co do business, when in May 1909 Wainwright retrieved a three-quarters-grown male tiger uninjured from a necker snare.[18] Perhaps not appreciating the tiger’s youth, Roberts offered £5 plus the rail freight from either Burnie or Launceston. She wanted the animal delivered to her in Hobart within ten days in order to ship it to the London Zoo on the Persic. It would thereby replace one which had died of heat exhaustion in transit to the same destination a few months earlier.[19]
However, the overseer of a remote stock station could not meet that deadline. The delay came with a bonus—the capture of three more members of the first tiger’s family, his sisters and mother.[20] Bob Wainwright recalled his stepfather Thomas Lovell and brother George placing the animals in a cage. There was also a familiar story of tigers refusing to eat dead game: ‘They had to catch a live wallaby and throw it in, alive, and then they [the thylacines] killed it’.[21] With McGaw continuing to act as intermediary between buyer and supplier, a price of £15 was settled on for the family of four.[22]
Roberts and McGaw communicated as social equals, but their social inferiors—hunters, stockmen and an overseer—were not named in their correspondence. This made for frustrating reading when Roberts discussed hunters (‘the man’) with whom she was dealing over live tigers. She had been expecting to receive two young tigers from a Hamilton hunter for her own zoo, but these had now died, causing her to reconsider her plans for the Woolnorth family.[23]

The mother thylacine (centre) and her three young captured at Woolnorth in 1909. W Williamson photo from the Tasmanian Mail, 25 May 1916, p.18.
It wasn’t until the first week in July 1909 that the auxiliary ketch Gladys bore the crate of thylacines to Burnie, where they began the train journey to Hobart.[24] A week later they were said to be thriving in captivity.[25] Roberts was so pleased with the animals’ progress that after eight months she sent a postal order to Lovell and Wainwright as a mark of appreciation. She was impressed with the mother’s devotion to her young, believing that the death of the two Hamilton cubs was attributable to their mother’s absence.[26] However, money was becoming a concern. Buying all the tigers’ feed from a butcher was expensive, and when she received a potentially lucrative order for a tiger from a New York Zoo, she found the cost of insuring the animal over such a long journey prohibitive. On 1 March 1910 she ‘very reluctantly’ broke up the family group by dispatching the young male to the London Zoo. ‘I am keeping on the two [other juveniles]’, she wrote, ‘in the hope that they may breed, and the mother all along has been very happy with the three young ones’.[27]
Roberts was now offering £10 per adult thylacine—but there was none to sell at Woolnorth. Seventeen months later she paid Power £12 10s for his large tiger from Tyenna, and scored £30 shipping to London the last of the three young from the 1909 family group.[28] Her tiger breeding program was over, probably defeated by economics—but what might have been the rewards for perseverance? Perhaps she would have been the greatest tiger farmer of all.
[1] See, for example, ‘Commercial’, Mercury, 5 August 1890, p.2; Sarah Mitchell diary, 9 June 1890, RS32/20, Royal Society Collection (University of Tasmania Archives).
[2] See, for example, ‘Trappers fined’, Advocate, 22 October 1943, p.4.
[3] ‘Direct communication with the west coast initiated’, Mercury, 1 September 1932, p.12.
[4] G Weindorfer and G Francis, ‘Wild life in Tasmania’, Journal of the Victorian Naturalists Society, vol.36, March 1920, p.159.
[5] Lewis Stevenson, interviewed by Bob Brown, 1 December 1972 (QVMAG).
[6] ‘Circular Head notes’, Wellington Times and Agricultural and Mining Gazette, 25 June 1896, p.2.
[7] Walter Pinkard to James Norton Smith, 19 July 1901, VDL22/1/27 (TAHO).
[8] In Outward Despatch no.46, 4 January 1904, p.366, McGaw criticised Norton Smith for not doing more to arrest the encroachment of sand at Studland Bay and Mount Cameron (VDL7/1/13).
[9] Woolnorth farm diary, 30 September 1906 (VDL277/1/34). This VDL Co bounty was not paid until the following year (December 1907, p.95, VDL129/1/4). C Wilson was paid for killing two dogs found worrying sheep in 1906 (December 1906, p.58, VDL129/1/4 (TAHO).
[10] See thylacine bounty payment records in LSD247/1/3 (TAHO).
[11] AS Le Souef to James Norton Smith, 11 July 1902; Walter Pinkard to James Norton Smith, 4 August 1902, VDL22/1/28 (TAHO).
[12] ‘Wanted’, North Western Advocate and the Emu Bay Times, 1 July 1908, p.3.
[13] For Roberts, see Robert Paddle, ‘The most photographed of thylacines: Mary Roberts’ Tyenna male—including a response to Freeman (2005) and a farewell to Laird (1968)’, Australian Zoologist, vol.34, no.4, January 2008, pp.459–70.
[14] In ‘Wanted to buy’, Mercury, 18 July 1908, p.2, McGowan asked for tigers ‘dead or alive’. He had also advertised for ‘tigers … good, sound specimens, high price; also 2 or 3 dead or damaged specimens’ in the previous year (‘Wanted’, Mercury, 21 June 1907, p.2). George Tripp’s tiger must have died before it could be sold alive, since he claimed a government bounty for it (no.35, 25 July 1908, LSD247/1/3 [TAHO]).
[15] See, for example, ‘Wanted’, North Western Advocate and the Emu Bay Times, 7 March 1908, p.6.
[16] Thomas Lovell to AK McGaw, 17 July 1908, VDL22/1/34 (TAHO).
[17] ‘The Tasmanian tiger’, Mercury, 7 October 1908, p.4.
[18] Thomas Lovell to AK McGaw, 24 May 1909, VDL22/135 (TAHO). This thylacine was originally thought to be a young female, but McGaw later stated that it was a young male.
[19] Mary G Roberts to AK McGaw, 31 May 1909, VDL22/1/35 (TAHO).
[20] Thomas Lovell to AK McGaw, 1 June 1909, VDL22/1/35 (TAHO).
[21] Bob Wainwright, 86 years old, interviewed in Launceston, 27 October 1980.
[22] AK McGaw to Mary G Roberts, 9 June 1909, VDL52/1/29; Mary G Roberts to AK McGaw, 10 June 1909, VDL22/1/35 (TAHO).
[23] Mary G Roberts to AK McGaw, 21 June 1909, VDL22/1/35 (TAHO).
[24] AK McGaw to Mary G Roberts, 7 July 1909, VDL52/1/29 (TAHO); ‘Stanley’, North Western Advocate and the Emu Bay Times, 6 July 1909, p.2.
[25] W Roberts to AK McGaw, 15 July 1909, VDL22/1/35 (TAHO).
[26] In May 1912 she received two young tigers from buyer EJ Sidebottom in Launceston, paying him £20 in the belief that they were adults. They died three days later (Mary Grant Roberts diary, 6, 7 and 10 May 1912, NS823/1/8 [TAHO]).
[27] Mary G Roberts to AK McGaw, 14 March 1910, VDL22/1/36 (TAHO).
[28] Mary Grant Roberts diary, 12 August, 26 September and 24 December 1911, NS823/1/8 (TAHO).
by Nic Haygarth | 18/04/20 | Tasmanian high country history
When 52-year-old Maria Francis died of heart disease at Middlesex Station in 1883, Jack Francis lost not only his partner and mother to his child but his scribe.[1] For years his more literate half had been penning his letters. Delivering her corpse to Chudleigh for inquest and burial was probably a task beyond any grieving husband, and the job fell to Constable Billy Roden, who endured the gruesome homeward journey with the body tied to a pack horse.[2]
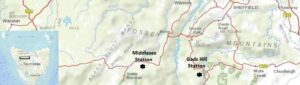
Base map courtesy of DPIPWE.
By then Jack seems to have been considering retirement. He had bought two bush blocks totalling 80 acres west of Mole Creek, and through the early 1890s appears to have alternated between one of these properties and Middlesex, probably developing a farm in collaboration with son George Francis on the 49-acre block in limestone country at Circular Ponds.[3]

Jack Francis and second partner Mary Ann Francis (Sarah Wilcox), probably at their home at Circular Ponds (Mayberry) in the 1890s. Photo courtesy of Shirley Powley.
Here Jack took up with the twice-married Mary Ann (real name Sarah) Wilcox (1841–1915), who had eight adult children of her own.[4] Shockingly, as the passing photographer Frank Styant Browne discovered in 1899, Mary Ann’s riding style emulated that of her predecessor Maria Francis (see ‘Jack the Shepherd or Barometer Boy: Middlesex Plains stockman Jack Francis’). However, Mary Ann was decidedly cagey about her masculine riding gait, dismounting to deny Styant Browne the opportunity to commit it to posterity with one of his ‘vicious little hand cameras’.[5]
Perhaps Mary Ann didn’t fancy the high country lifestyle, because when Richard Field offered Jack the overseer’s job at Gads Hill in about 1901 he took the gig alone.[6] This encore performance from the highland stockman continued until he grew feeble within a few years of his death in 1912.[7]
Mary Ann seems to have been missing when the old man died. Son George Francis and Mary Ann’s married daughter Christina Holmes thanked the sympathisers—and Christina, not George or Mary Ann, received the Circular Ponds property in Jack’s will.[8] Perhaps Jack had already given George the proceeds of the other, 31-acre block at Mole Creek.[9]

Field stockmen Dick Brown (left) and George Francis (right) renovating the hut at the Lea River (Black Bluff) Gold Mine for WM Black in 1905. Ronald Smith photo courtesy of the late Charles Smith.
By the time Mary Ann Wilcox died in Launceston three years later, George Francis had long abandoned the farming life for the high country. He was at Middlesex in 1905 when he renovated a hut and took part in the search for missing hunter Bert Hanson at Cradle Mountain.[10] Working out of Middlesex station, he combined stock-riding for JT Field with hunting and prospecting.
Like fellow hunters Paddy Hartnett and Frank Brown, Francis lost a small fortune when the declaration of World War One in July 1914 closed access to the European fur market, rendering his winter’s work officially worthless. At the time he had 4 cwt of ‘kangaroo and wallaby’ (Bennett’s wallaby and pademelon) and 60 ‘opossum’ (brush possum?). By the prices obtaining just before the closure they would have been worth hundreds of pounds.[11] Sheffield Police confiscated the season’s hauls from hunters, who could not legally possess unsold skins out of season.
The full list of skins confiscated by Sheffield Police on 1 August 1914 gives a snapshot of the hunting industry in the Kentish back country. Some famous names are missing from the list. Experienced high country snarer William Aylett junior was now Waratah-based and may have been snaring elsewhere.[12] Bert Nichols was splitting palings at Middlesex by 1914 but may not have yet started snaring there.[13] Paddy Hartnett concentrated his efforts in the Upper Mersey, probably never snaring the Middlesex/Cradle region. His double failure at the start of the war—losing his income from nearly a ton of skins, and being rejected for military service—drove him to drink.[14]
‘Return of skins on hand on the 1st day of August [1914] and in my possession’, Sheffield Police Station.
| Name |
Location |
Kangaroo/wallaby |
Wallaby |
Possum |
| George Francis |
Msex Station |
448 lbs |
|
60 skins |
| Frank Brown |
Msex Station |
562 skins+ 560 lbs |
|
108 skins |
| DW Thomas |
Lorinna |
960 lbs |
|
310 skins |
| William McCoy |
Claude Road |
600 lbs |
|
66 skins |
| Charles McCoy |
Claude Road |
40 lbs |
|
|
| Geo [sic] Weindorfer |
Cradle Valley |
31 skins |
|
4 skins |
| Percy Lucas |
Wilmot |
408 skins |
|
56 skins |
| G Coles |
Storekeeper, Wilmot |
|
5 skins |
|
| Jack Linnane |
Wilmot |
|
15 skins |
|
| WM Black |
Black Bluff |
50 skins |
|
3 skins |
| James Perry |
Lower Wilmot |
|
2 skins |
13 skins |
Most of those deprived of skins were bush farmers or farm labourers who hunted as a secondary (primary?) income, while George Coles was probably a middleman between hunter and skin buyer:
Frank Brown (1862–1923). Son of ex-convict Field stockman John Brown, he was one of four brothers who followed in their father’s footsteps (the others were Humphrey Brown c1855–1925, John Thomas [Jacky] Brown, 1857–c1910 and Richard [Dick] Brown). He appears to have been resident stockman at Field brothers’ Gads Hill Station in 1892.[15] Frank and Louisa Brown were resident at JT Field’s Middlesex Station c1905–17. He died when based at Richard Field’s Gads Hill run in 1923, aged 59, while inspecting or setting snares on Bald Hill.[16]
David William Thomas (c1886–1932) of Railton bought an 88-acre farm on the main road at Lorinna from Harry Forward in 1912.[17] His 1914 skins tally suggests that farming was not his main source of income—so the loss must have been devastating. Other Lorinna hunters like Harold Tuson were working in the Wallace River Gorge between the Du Cane Range and the Ossa range of the mountains.
William Ernest (Cloggy) McCoy (1879–1968), brother of Charles Arthur McCoy below, was born to VDL-born William McCoy and Berkshire-born immigrant Mary Smith at Sheffield.[18] He was the grandson of ex-convict John McCoy and the uncle of the well-known snarer Tommy McCoy (1899–1952).[19]
Charles Arthur (Tibbly) McCoy (1870–1962) was born to VDL-born William McCoy and Berkshire-born immigrant Mary Smith at Barrington.[20] He was the grandson of ex-convict John McCoy. Charles McCoy caught a tiger at Middlesex, depositing its skins at the Sheffield Police Office on 30 December 1901.[21] He was the uncle of the later well-known snarer Tommy McCoy.
Gustav Weindorfer (1874–1932), tourism operator at Waldheim, Cradle Valley, during the years 1912 to 1932. By his own accounts during 1914 he shot 30 ‘kangaroos’, eight wombats, six ringtails and one brush possum, as well as taking one ‘kangaroo’ in a necker snare.[22] While the closure of the skins market would have handicapped this struggling businessman, these skins would have been useful domestically, and the wombat and wallaby meat would have gone in the stew.
Percy Theodore Lucas (c1886–1965) was a Wilmot labourer in 1914, which probably means that he worked on a farm.[23] Nothing is known about his hunting activities.

TJ Clerke’s Wilmot store, Percy Lodge photo from the Weekly Courier, 22 April 1905, p.19.
George Coles (1855–1931) was the Wilmot storekeeper whose sons, including George James Coles (1885–1977), started the chain of Coles stores in Collingwood, Victoria.[24] George Coles bought TJ Clerke’s Wilmot store in 1912, operating it until after World War One. In 1921 the store was totally destroyed by fire, although a general store has continued to operate on the same site up to the present.[25] The five skins in George Coles’ possession had probably been traded by a hunter for stores. Coles probably sold them to a visiting skin buyer when the opportunity arose.[26]
John Augustus (Jack) Linnane (1873–1949) was born at Ulverstone but arrived in the Wilmot district in 1893 at the age of nineteen, becoming a farmer there.[27] Like George Francis, Linnane joined the search party for missing hunter Bert Hanson at Cradle Mountain in 1905, suggesting that he knew the country well.[28] His abandoned hunting camp near the base of Mount Kate was still visible in 1908.[29] Enough remained to show that Linnane was one of the first to adopt the skin shed chimney for drying skins.[30] He also engaged in rabbit trapping.[31] In 1914 he was listed on the electoral roll as a Wilmot labourer, but exactly where he was hunting at that time is unknown.[32]

Kate Weindorfer, Ronald Smith and WM Black on top of Cradle Mountain, 4 January 1910. Gustav Weindorfer photo courtesy of the late Charles Smith.
Walter Malcolm (WM) Black (1864–1923) was a gold miner and hunter at the Lea River/Black Bluff Gold Mine in the years 1905–15. The son of Victorian grazier Archibald Black, WM Black was a ‘remittance man’, that is, he was paid to stay away from his family under the terms an out-of-court payment of £7124 from his father’s will.[33] He joined the First Remounts (Australian Imperial Force) in October 1915 by falsifying his age in order to qualify.[34] See my earlier blog ‘The rain on the plain falls mainly outside the gauge, or how a black sheep brought meteorology to Middlesex’.[35]
James Perry (1871–1948), brother of a well-known Middlesex area hunter, Tom Perry (1869–1928), who was active in the high country by about 1905. Whether James Perry’s few skins were taken around Wilmot or further afield is unknown.
No tigers at Middlesex/Cradle Mountain?
George Francis survived the financial setback of 1914. Gustav Weindorfer in his diaries alluded to collaboration with him on prospecting and mining activities, but they hunted in different areas. In 1919 Francis co-authored the three-part paper ‘Wild life in Tasmania’ with Weindorfer, which documented their extensive knowledge of native animals, principally gained by hunting them. At the time, the authors claimed, they were the only permanent inhabitants of the Middlesex-Cradle Mountain area, boasting nine years (Weindorfer) and 50 years’ (Francis) residency. They also made the interesting claim that the ‘stupid’ wombat survived as well as it did in this area because it had no natural predators, since the thylacine did not then and probably never had frequented ‘the open bush land of these higher elevations’.[36] While this suggests that George Francis had never encountered a thylacine around Middlesex, it’s hard to believe that his father Jack Francis didn’t, especially given the story that Jack’s early foray into the Vale of Belvoir as a shepherd for William Kimberley was tiger-riddled.[37] It’s also a pity the authors didn’t consult the likes of Middlesex tiger slayers Charlie McCoy (see above) and James Mapps—or rig up a séance with the late George Augustus Robinson and James ‘Philosopher’ Smith.
The dog of GA Robinson, the so-called ‘conciliator’ of the Tasmanian Aborigines, killed a mother thylacine on the Middlesex Plains in 1830.[38] Decades later, ‘Philosopher’ Smith the mineral prospector came to regard Tiger Plain, on the northern edge of the Lea River, as the most tiger-infested place he visited during his expeditions. It was popular among the carnivores, he thought, because the Middlesex stockman’s dogs by driving game in that direction provided a ready food source. ‘I thought it necessary’, he wrote about his experience with tigers,
‘to be on my guard against them by keeping a fire as much as I could and having at hand a weapon with which to defend myself in the event of being attacked by one or more of them … ‘[39]
Smith killed a female tiger on Tiger Plain and took its four pups from her pouch but found they could not digest prospector food (presumably damper, potatoes, bully beef, wallaby or wombat).[40] Philosopher’s son Ron Smith had no reason to doubt his father, as he found a thylacine skull on his property at Cradle Valley in 1913 which is now lodged in Launceston’s Queen Victoria Museum and Art Gallery.[41] There were still tigers in the Middlesex region at the cusp of the twentieth century. Like ‘Tibbly’ McCoy, James Mapps claimed a government thylacine bounty at this time, probably while working as a tributor at the Glynn Gold Mine at the top of the Five Mile Rise near Middlesex.[42]
George Francis in his will described himself as a ‘shepherd of Middlesex Plains’, yet he met his maker in the Campbell Town Hospital. His parents were dead and he had no remaining relatives. The sole beneficiary of his will was Golconda farmer and road contractor William Thomas Knight (1862–1938), probably an old hunting mate.[43] Francis’s job at Middlesex was filled by the so-called ‘mystery man’ Dave Courtney (see my blog ‘Eskimos and polar bears: Dave Courtney comes in from the cold’), whose life, as it turns out, is an open book compared to that of his elusive predecessor.
[1] Died 11 October 1883, death record no.167/1883, registered at Deloraine, RGD35/1/52 (TAHO), https://librariestas.ent.sirsidynix.net.au/client/en_AU/names/search/results?qu=maria&qu=francis#, accessed 15 February 2020; inquest dated 13 October 1883, SC195/1/63/8739 (TAHO), https://stors.tas.gov.au/SC195-1-63-8739, accessed 15 February 2020. A pre-inquest newspaper reporter incorrectly attributed her death to suicide by strychnine poisoning (editorial, Launceston Examiner, 23 October 1883, p.1).
[2] It is likely that Jack Francis and Gads Hill stockman Harry Stanley conveyed Maria Francis’s body to Gads Hill Station, where Roden took delivery of it. See ‘A veteran drover’, Examiner, 7 March 1912, p.4; and ‘Supposed case of poisoning at Chudleigh’, Launceston Examiner, 13 October 1883, p.2. Later Roden had the job of removing Stanley’s body for an inquest at Chudleigh (Dan Griffin, ‘Deloraine’, Tasmanian Mail, 13 August 1898, p.26).
[3][3] For the land grant, see Deeds of land grants, Lot 5654RD1/1/069–71In 1890, 1892 and 1894 John and George Francis were both listed as farmers at Mole Creek (Wise’s Tasmanian Post Office directory, 1890–91, p.200; 1892–93, p.288; 1894–95, p.260). Jack Francis was reported to have left Middlesex in March 1885, being replaced by Jacky Brown (James Rowe to James Norton Smith, 10 March 1885; and to RA Murray, 24 September 1885, VDL22/1/13 [TAHO]). However, he appears to have returned periodically.
[4] She was born to splitter John Wilcox and Rosetta Graves at Longford on 17 July 1841, birth record no.3183/1847 (sic), registered at Longford, RGD32/1/3 (TAHO), https://librariestas.ent.sirsidynix.net.au/client/en_AU/all/search/results?qu=sarah&qu=wilcox, accessed 14 March 2020; died 25 October 1915 at Launceston (‘Deaths’, Examiner, 8 November 1915, p.1). Mary Ann’s youngest child, Eva Grace Lowe, was born in 1879.
[5] Frank Styant Browne, Voyages in a caravan: the illustrated logs of Frank Styant Browne (ed. Paul AC Richards, Barbara Valentine and Peter Richardson), Launceston Library, Brobok and Friends of the Library, 2002, p.84.
[6] Wise’s Tasmanian Post Office directory for the period 1901–08 listed Jack Francis as an overseer at Gads Hill or Liena, while Mary, as she was described, was listed as a farmer at Liena, meaning Circular Ponds (1901, p.322; 1902, p.341; 1904, p.204; 1906, p.189; 1907, p.192; 1908, p.197).
[7] ‘A veteran drover’.
[8] ‘Return thanks’, Examiner, 2 March 1912, p.1; purchase grant, vol.36, folio 116, application no.3454 RP, 1 July 1912.
[9] Jack Francis bought purchase grant vol.18, folio 113, Lot 5654, on 25 November 1872. He divided it in half, selling the two lots on 6 May 1902 to Arthur Joseph How and Andrew Ambrose How for £30 each.
[10] ‘The mountain mystery: search for Bert Hanson’, North Western Advocate and the Emu Bay Times, 1 August 1905, p.3.
[11] 1 August 1914, ‘Daily Record of Crime Occurrences Sheffield 1901–1916’, POL386/1/1 (TAHO).
[12] See ‘William Aylett: career bushman’ in Simon Cubit and Nic Haygarth, Mountain men: stories from the Tasmanian high country, Forty South Publishing, Hobart, 2015, pp.42–43.
[13] See ‘Bert Nichols: hunter and overland track pioneer’, in Simon Cubit and Nic Haygarth, Mountain men: stories from the Tasmanian high country, Forty South Publishing, Hobart, 2015, p.114.
[14] See ‘Paddy Hartnett: bushman and highland guide’, in Simon Cubit and Nic Haygarth, Mountain men: stories from the Tasmanian high country, Forty South Publishing, Hobart, 2015, p.93.
[15] On 20 April 1892 (p.179) Frank Brown reported stolen a horse which was kept at Gads Hill, Deloraine Police felony reports, POL126/1/2 (TAHO).
[16] ‘Well-known stockrider’s death’, Advocate, 4 June 1923, p.2.
[17] ‘Lorinna’, North West Post, 28 August 1912, p.2; ‘Obituary: Mr DW Thomas, Railton’, Advocate, 21 April 1932, p.2.
[18] Born 21 March 1879, birth record no.2069, registered at Port Sorell, RGD33/1/57 (TAHO), https://librariestas.ent.sirsidynix.net.au/client/en_AU/names/search/results?qu=william&qu=ernest&qu=mccoy. Accessed 10 April 2020.
[19] Born 26 June 1870, birth record no.1409/1870, registered at Port Sorell, RGD33/1/48 (TAHO), https://librariestas.ent.sirsidynix.net.au/client/en_AU/names/search/results?qu=charles&qu=mccoy, accessed 15 September 2019; died 23 September 1962, buried in the Claude Road Methodist Cemetery (TAMIOT). For John McCoy as a convict tried at Perth, Scotland in 1792 and transported on the Pitt in 1811, see Australian convict musters, 1811, p.196, microfilm HO10, pieces 5, 19‒20, 32‒51 (National Archives of the UK, Kew, England).
[20] Born 26 June 1870, birth record no.1409/1870, registered at Port Sorell, RGD33/1/48 (TAHO), https://librariestas.ent.sirsidynix.net.au/client/en_AU/names/search/results?qu=charles&qu=mccoy, accessed 15 September 2019; died 23 September 1962, buried in the Claude Road Methodist Cemetery (TAMIOT). For John McCoy as a convict tried at Perth, Scotland in 1792 and transported on the Pitt in 1811, see Australian convict musters, 1811, p.196, microfilm HO10, pieces 5, 19‒20, 32‒51 (National Archives of the UK, Kew, England).
[21] 30 December 1901, ‘Daily Record of Crime Occurrences Sheffield 1901–1916’, POL386/1/1 (TAHO).
[22] Gustav Weindorfer diaries, 1914, NS234/27/1/4 (TAHO).
[23] Commonwealth Electoral Roll, Division of Wilmot, Subdivision of Kentish, 1914, p.27.
[24] ‘About people’, Age, 22 December 1931, p.8.
[25] ‘Fire at Sheffield [sic]’, Mercury, 8 November 1921, p.5.
[26] Coles held a tanner’s licence in 1914 (‘Tanners’ licences’, Tasmania Police Gazette, 1 May 1914, p.109), but the legal requirement was that skins had to be sold to a registered skin buyer. Despite this, plenty of people tanned and sold their own skins privately.
[27] ‘”Back to Wilmot” celebration’, Advocate, 12 April 1948, p.2.
[28] 10 July 1905, ‘Daily Record of Crime Occurrences Sheffield 1901–1916’, POL386/1/1 (TAHO).
[29] Ronald Smith, account of trip to Cradle Mountain with Bob and Ted Addams, January 1908, held by Peter Smith, Legana.
[30] Ronald Smith, account of trip to Cradle Mountain with Bob and Ted Addams, January 1908, held by Peter Smith, Legana.
[31] On 18 April 1910, Linnane reported the theft of 200 rabbit skins from his hut valued at £2, ‘Daily Record of Crime Occurrences Sheffield 1901–1916’, POL386/1/1 (TAHO).
[32] Commonwealth Electoral Roll, Division of Wilmot, Subdivision of Kentish, 1914, p.26.
[33] ‘Supreme Court’, Age, 27 February 1885, p.6.
[34] World War One service record, https://www.awm.gov.au/people/rolls/R1791278/, accessed 22 March 2020.
[35] Nic Haygarth website, http://nichaygarth.com/index.php/tag/walter-malcom-black/, accessed 22 March 2020.
[36] G Weindorfer and G Francis, ‘Wild life in Tasmania’, Victorian Naturalist, vol.36, March 1920, p.158.
[37] ‘The Tramp’ (Dan Griffin), ’In the Vale of Belvoir’, Mercury, 15 February 1897, p.2.
[38] George Augustus Robinson, Friendly mission: the Tasmanian journals and papers of George Augustus Robinson, 1829-1834 (ed. Brian Plomley), Tasmanian Historical Research Association, Hobart, 1966; 22 August 1830, p.159.
[39] James Smith to James Fenton, 14 November 1890, no.450, NS234/ 2/1/15 (TAHO).
[40] ‘JS (Forth)’ (James Smith), ‘Tasmanian tigers’, Launceston Examiner, 22 November 1862, p.2.
[41] Ron Smith to Kathie Carruthers, 26 September 1911, NS234/22/1/1 (TAHO); email from Tammy Gordon, QVMAG, 2019.
[42] Bounty no.242, 30 August 1898, LSD247/1/ 2 (TAHO); ‘Court of Mines’, Launceston Examiner, 22 September 1897, p.3; 30 September 1897, p.3.
[43] Will no.14589, administered 7 March 1924, AD960/1/48, p.189 (TAHO), https://librariestas.ent.sirsidynix.net.au/client/en_AU/names/search/results?qu=george&qu=francis, accessed 15 March 2020; ‘Funeral of Mr WF [sic] Knight’, Examiner, 15 April 1938, p.15.
by Nic Haygarth | 05/03/20 | Tasmanian high country history
The palm of being Waratah’s first alcoholic probably belonged to its first resident doctor, John Waldo Pring, a Crimean War veteran who drank himself to death in the years 1876–79.[1] One of his lowest moments came in March 1876 when he escorted a disguised detective to a sly grog shop for a snort.[2] Another who upset early Waratah’s temperance wagon was former Sussex labourer Charlie Drury (c1819–76), who traded native animal hides for rum. For decades before Waratah was born Drury lived a twilight existence remote from civilisation, with often only his dogs, his drink and the spirit world for companions. He even went out on a bender, leaving a legacy of decimated wildlife, delusional folklore and fire-managed grasslands to the hunters and graziers who followed him.
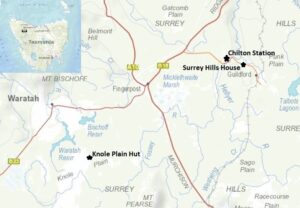
Mount Bischoff, Waratah, Knole Plain and the Surrey Hills. Map courtesy of DPIPWE.
Transported at 20 on a fifteen-year sentence for larceny, the 178-cm tall Drury was no mal-nourished urchin.[3] James ‘Philosopher’ Smith rather generously called him ‘a sturdy type of an Englishman’.[4] Drury could read—books and newspapers were delivered to him in the back country—although no letters survive to testify to his fluency with the pen.[5] Arriving in Van Diemen’s Land in July 1839, he went straight into the assigned service of British pastoral enterprise the Van Diemen’s Land Company (the VDL Co) at the Surrey Hills, working with hutkeeper Edward Garrett and stockkeeper Richard Lennard (c1811–94).[6] The area between the Hellyer River and Knole Plain would be his home for most of his remaining life. His early services to the VDL Co were valued at only £15 per year (when he was stationed at Emu Bay 1845–46) but rose to £30, a typical stockman’s wage of the time, in the years 1850–52.[7] Hunting would have brought in much more than that.
Drury would have been thrown out of his official work when the VDL Co shut down all operations in 1852. He attended the Victorian gold rushes in February of that year, but would have returned to his old haunts after northern graziers the Field brothers (William, John, Thomas and Charles) rented the Surrey Hills in 1853, living chiefly off the proceeds of his unfettered hunting.[8] Of course he also had the gold ‘bug’, finding a little gold at Cattley Plain under the Black Bluff Range in 1857 or 1858.[9]
The old lag was joined at the Surrey Hills by fellow ex-convict Martin Garrett (aka Garrett Martin, c1806–88), who had racked up an impressive record of robbery in Dublin, bushranging in New South Wales and probation served at Port Arthur. Not bad for a dairyman![10] Both men took to hunting, with a little prospecting on the side.[11] Like other highland hunter-stockmen such as Jack Francis of Middlesex Plains, Drury had a little cottage industry going, his specialty being the whittling of celery-top-pine walking sticks manufactured on commission.[12] It would be surprising if he didn’t also make and sell possum-skin rugs, which could fetch £2 each. The two men lived in a surprisingly sumptuous eight-room house with a blacksmith’s shop, stable, out-houses and cattle yards about two kilometres east of the Hellyer River.[13] The cottage was designed for the VDL Co by none other than onetime colonial architect John Lee Archer—something of a comedown from his work on Parliament House and the treasured Ross Bridge.[14]
Drury’s twilight zone
Decades of isolation in the boondocks of failed VDL Co settlements may have taken their toll on Drury. Even well after the tribal Aboriginal people had been driven out of the north-west, the ‘ghosts’ of their clashes with the VDL Co and the isolation played havoc with him. The company’s old Chilton homestead up above the Hellyer River was said to be haunted by the spirits of murdered Aboriginals. Drury reputedly enjoyed being lulled to sleep there by ghostly ‘music’, until one night a more lively manifestation left him crouched in the fireplace with his gun drawn.[15]
Drury sold skins to his former VDL Co workmate and ex-convict Richard Lennard, who was now keeper of the Ship Inn at Burnie. Lennard would regularly bring a horse and dray up to Drury containing grog and rations, returning to Burnie with the skins. On one occasion when Lennard was arriving at Surrey Hills, Drury came out to meet him, calling out, ‘I know what you are going to tell me—Jack Flowers is dead.’ This referred to the ex-convict known as ‘Forky Jack’, a previous workmate, who had died recently. Lennard knew that Drury had had no contact with the outside world during that time, so how could he possibly know of Flowers’ death? ‘He passed over here’, Drury told him, calling ‘Charlie [distant], Charlie [loud], Charlie [distant]’—on his way to hell.[16] James ‘Philosopher’ Smith got the same story from Drury, who had heard Flowers calling him ‘in the most hasty manner possible while very quickly passing through the air’. The hallucination, if that is what it was, apparently occurred at about the time of Flowers’ death.[17]
Drury had other supernatural experiences/hallucinations and beliefs. One day he was out hunting not far from home when it came on dark. He sat down under a tree for a nap, intending to hunt badgers (wombats) when the moon rose. He was awoken by a clap on the shoulder and the words, ‘Charlie! Didn’t you say you were going to start out after the badgers as soon as the moon was up? Here it is more than three hands high’. The speaker, Drury told his friend William Lennard, wore a sleeved waistcoat and an English top hat. Drury gathered his dogs, including Long Jim, who his new friend pointed out to him a little way off, and as he did so the apparition ‘backed away through a swamp and faded out’.[18]
On another occasion Drury and William Lennard were camped at an isolated place called Sutelmans Park somewhere near Bonds Plain (east of the Vale of Belvoir). Come morning Drury declined to leave camp, having been warned by the banshee (a female Irish spirit who heralds death) during the night that some misfortune would befall him if he did so. Lennard persuaded Drury to disregard the warning, and they went out hunting with Drury’s favourite dog Turk. Later that morning they found the dog dead. ‘There you are’, Drury remarked, ‘what did I tell you?’ Drury then tried to bring the dog back to life by ‘wailing’ over it. Lennard recalled laughing at him for being so foolish, whereupon Drury ‘levelled his gun at him and threatened to blow his head off’. Realising the precariousness of his position, Lennard quickly came to his senses.[19]
In the early 1870s Drury’s unusual ways made it into an international travel book. When an 1871 party visited the Surrey Hills, Drury fed them cold beef, and the visitors got to try those famous possum-skin rugs, which, as was customary, were alive with fleas. While his guests battled these, Drury went badger hunting by the light of the moon with about a dozen kangaroo-dogs, bringing home three skins and one entire animal—presumably for breakfast. As he explained at the dining table, ‘the morning after I have been out badger-hunting at night I always eat two pounds of meat for breakfast, to make up for the waste created by want of sleep’. Drury also recalled his pack of ferocious hunting dogs falling in with a ‘flock’ of seven ‘hyenas’, four thylacines being killed at a time when, unfortunately for him, there was no government thylacine bounty.[20]
Drury and the Bischoff tin
Through the 1850s and 1860s the VDL Co was tantalised by reports of gold discoveries on or near its land. The company’s local agent, James Norton Smith, appears to have placed some faith in Drury as a potential gold discoverer, following his claim to have found gold at the Cattley Plain, and as late as 1872 offered him prospecting tools and discussed a reward for discovery of payable gold.[21]
Prospector James ‘Philosopher’ Smith got to know Drury, calling at his cottage in December 1871 when short of food after discovering one of the world’s greatest tin lodes at Mount Bischoff. Drury had seen Smith pass by on his way to Bischoff, and now expressed surprise that he was able to stay out in the bush so long. He also told Smith that he had no food—a statement that no doubt sent a shock wave through the enervated prospector. However, relief was at hand:
‘He [Drury] replied that what he meant was that he had no beef but had kangaroo, bread and tea. He hurriedly invited me into the house and commenced to prepare a meal with the utmost celerity. He slung a camp oven containing fat and then seized a chopper with one hand and a leg of kangaroo with the other and in a few minutes he had some of the meat frying while he also attended to the tea kettle.’[22]
Smith would have found accounts of this visit written long after his death harder to swallow. In 1908 and 1923 claims were made that Smith found the Mount Bischoff tin in Drury’s hut. ‘There’s a mountain of it just outside there’, Drury apparently told Philosopher, sending him a few metres to the summit of the mountain.[23] Why anyone who had been at Waratah in its early days, when Mount Bischoff was accessed via a tunnel through the horizontal scrub, would suggest the existence of a stockman’s hut in such a position it is hard to imagine.
Drury was the stuff of which disenfranchised prospectors are made, the bumpkin shepherd who stumbles upon a fortune. The strongest argument against the Drury discovery story—apart from his stock of hallucinations—is Smith’s unblemished reputation for integrity. The closest that Drury is likely to have got to the Bischoff scrub is the very edge, where the wallabies snoozed before making their way to the grassy plains at night to feed.
Protective of his father’s reputation and achievements, Garn Smith interviewed Jesse Wiseman and William Lennard, both of whom had hunted with Drury in the early 1870s. Both said that Drury never claimed to have found the Mount Bischoff tin.[24] Wiseman recalled Drury saying, ‘Just fancy us hunting about here all these times and not knowing anything about [the Mount Bischoff tin]‘.[25]
Yet other Drury acquaintances told a different story. An anonymous source claimed that ‘old Charlie Drury made no secret about telling travellers in those days that he directed Mr James Smith to where the tin was, he having a few specimens of this strange metal in his hut, which he showed to “Philosopher” Smith, who continued the quest …’[26]
Grazier John Bailey Williams was another to vouch for Drury, telling Lou Atkinson ‘I ought to have found Bischoff as Drury told me of the mineral, but I paid no attention to him. I had heard so many wild stories of this sort’.[27] Williams had encountered Drury while trying to run sheep in the open grasslands at Knole Plain in 1864–65.[28] His application to lease 6500 acres of Crown land there foundered, with many sheep reportedly starving to death.[29] Well might he have wished for a tinstone saviour!
However, it seems that wild stories were Drury’s stock in trade. It wouldn’t be at all surprising if the old sot had mineral samples in his hut—but it would be a great shock if they were cassiterite specimens.[30]
Opportunity knocks
The Mount Bischoff Tin Mine and its new trade route with Emu Bay brought financial opportunity to previously remote hunter-stockmen. Fields’ Hampshire Hills overseer Harry Shaw wanted to set up an ‘eating house’ along the road. [31] Garrett must have had similar commerce in mind when he tried to buy land at the Hampshire Hills.[32] He later drove the VDL Co Tram between Emu Bay and Bischoff and worked as a blacksmith at the Wheal Bischoff Co Mine.[33] Drury became a commercial operator. He and his mate John Edmunds established a base on the hunting ground of Knole Plain, leaving Garrett to hunt the Surrey Hills. Their hut stood right along the track to the mountain, on grasslands that the Mount Bischoff Tin Mining Company wanted to keep for feed for the bullock and horse teams carting between Waratah and the port at Emu Bay. They were professional hunters paying a £1 annual licence and returning up to £70 per season for shooting 600 to 1000 wallabies as well as the brush possums which formed their possum-skin rugs—at least that was told they told a visiting reporter.[34] The suggestion that such men obeyed government regulations is ludicrous. Additional money was to be had packing supplies for mining companies, as well as supplying Waratah with wallaby meat and some of the grog that they received from Emu Bay.[35] Feeding 20 kangaroo dogs alone would necessitate constant hunting.

Mount Bischoff from Knole Plain, 2009. Nic Haygarth photo.
The new trade route through to Emu Bay also gave hunters like Drury and Garrett better access to skin buyers—although their attempt to sell the skins of Drury’s beloved badger seems to have foundered. [36] While Garrett and Drury were out hunting, their charges—the Field brothers’ notoriously wandering cattle—wandered onto Waratah dinner plates, much to their owners’ disgust. In 1874 Thomas Field called for police intervention.
So did the Mount Bischoff Company when the first pub opened in town.[37] Drury’s unofficial pub never closed. One man was discharged from Walker and Beecraft’s tin claim for getting drunk there.[38] Drury himself was likely to get ‘on the spree’ at any time, making him an unreliable employee.[39] There was a celebrated incident in which Drury got hammered on a keg of rum and accidentally burned down his and Edmunds’ hut, destroying not only his own skins and stores but supplies belonging to prospectors Orr and Lempriere and surveyor Charles Sprent. The only thing salvaged was the keg, to which the hunter was said to have clung ‘with the affection of a miser’.[40]
Drink eventually killed Drury in his hut at Knole Plain. James Smith learned that:
‘His end was a melancholy one. He had been drinking somewhat heavily when two Christian men from Waratah went to see him at his hut … While talking to his new friends he lay down on his bed and seemed to doze but when after a time one of them tried to rouse him it was found that he was dead.’[41]
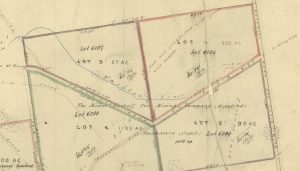
Detail from Charles Sprent’s January 1874 map, ‘Plan of agricultural sections on Knole Plain, County of Russell’, showing ‘hut and kennels’ (upper right, just above the road reserve. AF396/1/806 (TAHO).

Potential rubble from Drury’s hut protruding from the furrows of a future plantation on Knole Plain in 2009. Presumably Drury remains buried here, although the eucalypt that marked the spot is long gone. Nic Haygarth photo.
Finding Drury
Drury is said to have been buried beneath a eucalypt near his hut on Knole Plain.[42] Did anything remain there of either his hut or his grave? Examining an old map of Knole Plain more than a decade ago, Burnie surveyor and historian Brian Rollins found the notation ‘hut and kennels’. Brian was interested to find a James Sprent survey cairn that was marked on the same map. We resolved to combine our interests and, under the stewardship of Robert Onfray from Gunns, we made a trip to the Knole Plain area. We found ploughed remains of a long-fallen building which suggested Drury’s hut or some later version of it. No weathered cross tilted over the detritus. No bleached bones poked out of the furrows of the plantation coup. Perhaps Charlie Drury is six feet under the tussock grass, raising a toast with his insubstantial friends, his beloved dogs crashing through some underworld after twilit kangaroo, badger and tiger.
[1] ‘Mount Bischoff’, Devon Herald, 27 September 1879, p.2; he died of natural causes, 19 September 1879, inquest SC195/1/60/8154 (Tasmanian Archive and Heritage Office, afterwards TAHO), https://stors.tas.gov.au/SC195-1-60-8154, accessed 29 February 2020.
[2] ‘Sly grog selling at Mount Bischoff, Cornwall Chronicle, 27 March 1876, p.3.
[3] Drury was transported on the Marquis of Hastings. See his conduct record, CON31/1/12, image 31 (TAHO), https://stors.tas.gov.au/CON31-1-12$init=CON31-1-12p31, accessed 1 March 2020, also Description list, CON18/1/16, p.200 (TAHO), https://librariestas.ent.sirsidynix.net.au/client/en_AU/names/search/results?qu=charles&qu=drury#, accessed 23 February 2020.
[4] James Smith notes, ‘Exploring’, NS234/14/1/ 3 (TAHO).
[5] Cavanagh (?) to James Smith, 24 January 1875, no.38, NS234/3/1/4 (TAHO).
[6] VDL61/1/2 (TAHO). For Lennard see conduct record, CON31/1/27, image 179 (TAHO), https://stors.tas.gov.au/CON31-1-27$init=CON31-1-27p179, accessed 1 March 2020.
[7] VDL133/1/1 (TAHO).
[8] From Launceston to Melbourne on the City of Melbourne, 3 February 1852, POL220/1/1, p.558 (TAHO), https://librariestas.ent.sirsidynix.net.au/client/en_AU/names/search/results?qu=charles&qu=drury#, accessed 23 February 2020. Drury’s sentence expired in March 1853, leaving him free to choose his employer (‘Convict Department’, Launceston Examiner, 19 March 1853, p.6).
[9] See WR Bell, ‘Report on the hydraulic gold workings at Lower Mayday Plain …’, 14 May 1896, EBR13/1/2 (TAHO). In June 1858 a prospector W MacNab testing the Hampshire and Surrey Hills for gold complained that a mining cradle he expected to use had been removed for use by a stockkeeper from the Surrey Hills Station. See W MacNab to James Gibson, VDL Co agent, 9 June 1858, VDL22/1/2 (TAHO).
[10] See his conduct record, CON39/1/2, p.334 (TAHO), https://librariestas.ent.sirsidynix.net.au/client/en_AU/all/search/results?qu=Martin&qu=garrett, accessed 23 February 2020. After a stint in the New Town Invalid Depot (admitted 24 November 1886 to 17 December 1886, POL709/1/21, p.207) Garrett died of ‘dropsy’ (oedema, fluid retention) in Launceston in 1888 when he was said to be 82 years old (2 December 1888, death record no.391/1888, registered in Launceston, RGD35/1/57 [TAHO]).
[11] Garrett may have discovered the barytes deposit at the Two Hummocks near Fields’ Thompsons Park Station (James Smith to Ritchie and Parker, 10 July 1875, no.327, VDL22/1/4 [TAHO]).
[12] Richard Hilder, ‘The good old days’, Advocate, 5 January 1925, p.4; Charles Drury to James Norton Smith, 24 July 1872, VDL22/1/4 (TAHO).
[13] ‘Country news’, Tasmanian, 30 August 1873, p.5; G Priestley, ‘Search for Mr D Landale’, Weekly Examiner, 11 October 1873, p.19.
[14] Agreement between the VDL Co and builder George Fann, 4 March 1851, VDL19/1/1 (TAHO). Fann was paid £150 for the job on 19 April 1852 (VDL133/1/1, p.153 [TAHO]). Archer sent two designs for a stockkeeper’s hut to James Gibson on 17 February 1851, although unfortunately the designs cannot be found on file (VDL34/1/1, Personal letters received by James Gibson [TAHO]). See also the 1842 census record for Richard Lennard, who was then living at the VDL Co’s old Chilton homestead. He was one of ten men from the ages of 21 to 45 resident there at the time, only one of whom arrived in the colony free, while another qualified under ‘other free persons’. Two who were in ‘government employment, six in ‘private assignment’. Two were ‘mechanics or artificers’, two were ‘shepherds or others in the care of sheep’, five were ‘gardeners, stockmen or persons employed in agriculture’ and one was a ‘domestic servant’ (CEN1/1/8, Circular Head, p.63 [TAHO], https://librariestas.ent.sirsidynix.net.au/client/en_AU/all/search/results?qu=richard&qu=lennard, accessed 1 March 2020).
[15] William Lennard, quote by RS Sanderson, ‘Discovery of Tin at Mount Bischoff’, RS Sanderson to Arch Meston, May 1923?, M53/3/6 (Meston Papers, University of Tasmania Archives, Hobart).
[16] William Lennard, quoted by RS Sanderson, ‘Discovery of Tin at Mount Bischoff’.
[17] James Smith notes, ‘Exploring’, NS234/14/1/ 3 (TAHO).
[18] William Lennard, quoted by RS Sanderson, ‘Discovery of Tin at Mount Bischoff’.
[19] William Lennard, quoted by RS Sanderson, ‘Discovery of Tin at Mount Bischoff’.
[20] Anonymous, Rough notes of journeys made in the years 1868, ’69, ’70, ’71, ’72 and ’73 in Syria, down the Tigris … and Australasia, Trubner & Co, London, 1875, pp.263–64.
[21] James Norton Smith to VDL Co Court of Directors, Outward Despatch 38, 15 May 1872, p.482, VDL1/1/6; James Norton Smith to Charles Drury, 12 June 1872, p.493, VDL7/1/1 (TAHO).
[22] James Smith notes, ‘Exploring’, NS234/14/1/ 3 (TAHO).
[23] ‘Patsey’ Robinson, quoted in ‘The oldest inhabitants’, Zeehan and Dundas Herald, 24 April 1908, p.2.
[24] GH Smith, ‘The true story of Bischoff’, Advocate, 1 May 1923, p.6.
[25] Jesse Wiseman quoted by RS Sanderson, ‘Discovery of tin at Mount Bischoff’.
[26] ‘1866’, ‘Discovery of tin at Mount Bischoff’, Advocate, 30 April 1923, p.6.
[27] John Bailey Williams, quoted by RS Sanderson, Discovery of Tin at Mount Bischoff’.
[28] John Bailey Williams to Charles H Smith, Du Croz & Co, 25 January 1865; and to VDL Co agent Charles Nichols, 11 April 1865, VDL22/1/3 (TAHO).
[29] Thomas Barrett to R Symmons, 2 March 1867, VDL22/1/3 (TAHO).
[30][30] Thomas Broad claimed to have seen tin specimens in Drury’s hut—but did Broad have enough expertise in mineralogy to make that call? See Thomas Broad, ‘Mt Bischoff’s early days’, Advocate, 3 May 1923, p.2.
[31] James Smith to Ferd Kayser, 15 January 1876, NS234/2/1/2 (TAHO).
[32] James Smith to Martin Garrett, 30 June 1875, no.310, NS234/2/1/2 (TAHO).
[33] Hugh Lynch to James Norton Smith, 23 April 1877, VDL22/1/5; Daniel Shine to James Norton Smith, 27 October 1879, VDL22/1/7 (TAHO).
[34] ‘Country news’, Tasmanian, 30 August 1873, p.5.
[35] For packing, see WR Bell to James Smith, 20 July 1875, no.335; and Joseph Harman to James Smith, 11 October 1875, no.450, NS234/3/1/4 (TAHO).
[36] AM Walker to James Smith, 11 February 1873, no.115, NS234/3/1/2 (TAHO).
[37] Minutes of directors’ meetings, Mount Bischoff Tin Mining Company, 7 September 1875, NS911/1/1 (TAHO).
[38] Mary Jane Love to James Smith, 12 October 1873, no.290/291, NS234/3/1/2 (TAHO).
[39] William Ritchie to James Smith, 9 March 1874, NS234/3/1/3 (TAHO).
[40] ‘Trip to Mount Bischoff’, Mercury, 18 December 1873, p.3.
[41] James Smith notes, ‘Exploring’, NS234/14/1/ 3 (TAHO). Drury died 3 March 1876, death record no.151/1876, registered at Emu Bay, RGD35/1/45 (TAHO), https://librariestas.ent.sirsidynix.net.au/client/en_AU/names/search/results?qu=charles&qu=drury#, accessed 23 February 2020. Cause of death was given as ‘excessive drinking’.
[42] ‘An Old Hand’, ‘The O’Malley and the Labor Movement in Tasmania’, Zeehan and Dundas Herald, 28 May 1908, p.2.