by Nic Haygarth | 22/10/20 | Circular Head history, Story of the thylacine
By the 1890s farmers like Joseph Clifford and Robert Stevenson were effectively adding Tasmanian tiger farming to their portfolios of raising stock, growing crops and hunting. Since thylacines appeared on their property, they made a conscious effort to catch them alive in a footer snare or pit rather than dead in a necker snare. A tiger grew no valuable wool, but in 1890 a live wether might fetch 13 shillings, compared to £6 for an adult thylacine delivered to Sydney.[1] A dead adult thylacine, on the other hand, was worth only £1 under the government bounty scheme.
The problem with these special efforts to catch tigers alive was that hunters only had a certain amount of control over what animals ended up in their snares or pits. Twentieth-century hunters often complained about city regulators who thought it feasible to close the season on brush possum but open it for wallabies and pademelons. Inevitably, hunters caught some brush possum in their wallaby and pademelon snares during the course of the season, which could land them a hefty fine in court unless they destroyed the precious but unlawful skins.[2] John Pearce junior in the upper Derwent district claimed that he and his brothers caught seventeen tigers in ‘special neck snares’ set alongside their kangaroo snares.[3] How did the tigers recognise the ‘special neck snares’ provided for their specific use? All you could do was vary the height of the necker snare to catch the desired animal’s head as it walked. Too bad if something else stuck its head in the noose. Wombats, for example, were a hazard. Gustav Weindorfer of Cradle Valley set snares at the right height to catch Bennett’s wallabies by the neck, but also caught wombats in them.[4] Wombats were good for ‘badger’ stew and for hearth mats but the skins had no value. Robert Stevenson of Aplico, Blessington, caught wombats alive in his tiger pits—which they then set about destroying by burrowing their way out.[5]

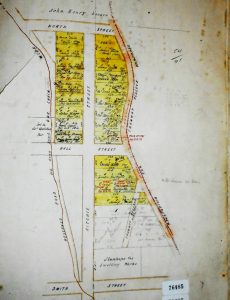
George Wainwright senior, Matilda Wainwright and children at Mount Cameron West (Preminghana) c1900. Courtesy of Kath Medwin.
These problems aside, it seems odd that the pragmatic Van Diemen’s Land Company (VDL Co), which later added fur hunting to its income stream, didn’t cotton on to the live tiger trade. They could have followed the example of George Wainwright senior, who sold a Woolnorth tiger to Fitzgerald’s Circus in 1896.[6] In 1900, for example, 22 thylacines were killed on Woolnorth, a potential income of more than £100 had the animals been taken alive. Even when, later, four living Woolnorth tigers were sold, the money stayed with the employees, with the VDL Co not even taking a commission. (It should be noted that four young tigers caught by Walter Pinkard on Woolnorth in 1901 were not accounted for in bounty payments.[7] It is possible that they were sold alive—but there are no records of a sale or even correspondence about the animals. Their fate is unknown.)


William Le Souef to Kruger, 22 October 1901: ‘The Tasmanian Wolves are all
right, so far’. Did he get them from Woolnorth? Postcard courtesy of Mike Simco.
The VDL Co’s failure to exploit the live trade for its perceived arch enemy can possibly be explained by the tunnel vision of its directors and departing Tasmanian agent and the inexperience of his successor. James Norton Smith resigned as local manager in 1902. His replacement, Scotsman Andrew Kidd (AK) McGaw, harnessed Norton Smith’s 33-year corporate knowledge by re-engaging him as farm manager. It would not have been easy for McGaw to learn the ropes in a new country, among business associates cultivated by his predecessor, and the re-engagement of Norton Smith as his second allowed him to transition into the manager position. As would be expected, McGaw stamped his authority on the agency by criticising some of Norton Smith’s policies and distancing himself from them.[8] Ahead of Ernest Warde’s engagement as ‘tigerman’, the VDL Co’s shepherd at Mount Cameron West, he scrapped Norton Smith’s recent bounty incentive scheme of £2 for a tiger killed by a man out hunting with dogs.
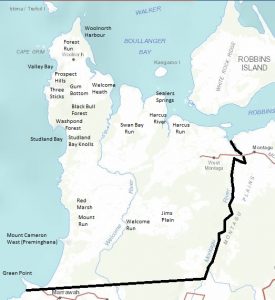
Woolnorth, showing main property features and the original boundary. Base map courtesy of DPIPWE.
After Warde’s departure in 1905, the tiger snares at Mount Cameron and Studland Bay were checked intermittently. Woolnorth overseer Thomas Lovell killed a tiger at Studland Bay in 1906, but the number of tigers and dogs reported on the property was now negligible.[9] This reflected the statewide situation, with only eighteen government thylacine bounties being paid in 1907, and only thirteen in 1908.[10]
However, the value of live tigers continued to climb as they became rarer. The first documented approach to the VDL Co for live tigers came in July 1902 from AS Le Souef of the Zoological Gardens in Melbourne, who offered £8 for a pair of adults and £5 for a pair of juveniles. He also wanted devils and tiger cats, in response to which George Wainwright junior supplied two tiger cats (spotted quolls, Dasyurus maculatus).[11] Given the tiger’s reputation as a sheep killer, native animal farming might have been a hard sell to the directors, and the company continued to use necker snares which were generally fatal to thylacines. What price would it take to change that behaviour? In July 1908 McGaw read a newspaper advertisement:
‘WANTED—Five Tasmanian tigers, handsome price for good specimens. Apply Beaumaris, Hobart.’[12]
He discovered that the proprietor of the private Beaumaris Zoo at Battery Point, Mary Grant Roberts, wanted a pair of living tigers immediately to freight to the London Zoo.[13] The Orient steamer Ortona was departing for London at the end of the month. She offered McGaw £10 for a living, uninjured pair of adults. Roberts hoped to secure the tiger caught recently by George Tripp at Watery Plains, but felt that she was competing for live captures with William McGowan of the City Park Zoo, Launceston, who advertised in the same month.[14] Eroni Brothers Circus was also in the market for living tigers.[15]

A young Mary Grant Roberts, from NS823/1/69 (Tasmanian Archive and Heritage Office).
Almost as Roberts made her offer, George Wainwright junior tracked a tiger at Mount Cameron West, but it evaded capture.[16] In the meantime Roberts was able to secure her first thylacine from the Dee River.[17]
Almost a year passed before the chance arose for the VDL Co do business, when in May 1909 Wainwright retrieved a three-quarters-grown male tiger uninjured from a necker snare.[18] Perhaps not appreciating the tiger’s youth, Roberts offered £5 plus the rail freight from either Burnie or Launceston. She wanted the animal delivered to her in Hobart within ten days in order to ship it to the London Zoo on the Persic. It would thereby replace one which had died of heat exhaustion in transit to the same destination a few months earlier.[19]
However, the overseer of a remote stock station could not meet that deadline. The delay came with a bonus—the capture of three more members of the first tiger’s family, his sisters and mother.[20] Bob Wainwright recalled his stepfather Thomas Lovell and brother George placing the animals in a cage. There was also a familiar story of tigers refusing to eat dead game: ‘They had to catch a live wallaby and throw it in, alive, and then they [the thylacines] killed it’.[21] With McGaw continuing to act as intermediary between buyer and supplier, a price of £15 was settled on for the family of four.[22]
Roberts and McGaw communicated as social equals, but their social inferiors—hunters, stockmen and an overseer—were not named in their correspondence. This made for frustrating reading when Roberts discussed hunters (‘the man’) with whom she was dealing over live tigers. She had been expecting to receive two young tigers from a Hamilton hunter for her own zoo, but these had now died, causing her to reconsider her plans for the Woolnorth family.[23]

The mother thylacine (centre) and her three young captured at Woolnorth in 1909. W Williamson photo from the Tasmanian Mail, 25 May 1916, p.18.
It wasn’t until the first week in July 1909 that the auxiliary ketch Gladys bore the crate of thylacines to Burnie, where they began the train journey to Hobart.[24] A week later they were said to be thriving in captivity.[25] Roberts was so pleased with the animals’ progress that after eight months she sent a postal order to Lovell and Wainwright as a mark of appreciation. She was impressed with the mother’s devotion to her young, believing that the death of the two Hamilton cubs was attributable to their mother’s absence.[26] However, money was becoming a concern. Buying all the tigers’ feed from a butcher was expensive, and when she received a potentially lucrative order for a tiger from a New York Zoo, she found the cost of insuring the animal over such a long journey prohibitive. On 1 March 1910 she ‘very reluctantly’ broke up the family group by dispatching the young male to the London Zoo. ‘I am keeping on the two [other juveniles]’, she wrote, ‘in the hope that they may breed, and the mother all along has been very happy with the three young ones’.[27]
Roberts was now offering £10 per adult thylacine—but there was none to sell at Woolnorth. Seventeen months later she paid Power £12 10s for his large tiger from Tyenna, and scored £30 shipping to London the last of the three young from the 1909 family group.[28] Her tiger breeding program was over, probably defeated by economics—but what might have been the rewards for perseverance? Perhaps she would have been the greatest tiger farmer of all.
[1] See, for example, ‘Commercial’, Mercury, 5 August 1890, p.2; Sarah Mitchell diary, 9 June 1890, RS32/20, Royal Society Collection (University of Tasmania Archives).
[2] See, for example, ‘Trappers fined’, Advocate, 22 October 1943, p.4.
[3] ‘Direct communication with the west coast initiated’, Mercury, 1 September 1932, p.12.
[4] G Weindorfer and G Francis, ‘Wild life in Tasmania’, Journal of the Victorian Naturalists Society, vol.36, March 1920, p.159.
[5] Lewis Stevenson, interviewed by Bob Brown, 1 December 1972 (QVMAG).
[6] ‘Circular Head notes’, Wellington Times and Agricultural and Mining Gazette, 25 June 1896, p.2.
[7] Walter Pinkard to James Norton Smith, 19 July 1901, VDL22/1/27 (TAHO).
[8] In Outward Despatch no.46, 4 January 1904, p.366, McGaw criticised Norton Smith for not doing more to arrest the encroachment of sand at Studland Bay and Mount Cameron (VDL7/1/13).
[9] Woolnorth farm diary, 30 September 1906 (VDL277/1/34). This VDL Co bounty was not paid until the following year (December 1907, p.95, VDL129/1/4). C Wilson was paid for killing two dogs found worrying sheep in 1906 (December 1906, p.58, VDL129/1/4 (TAHO).
[10] See thylacine bounty payment records in LSD247/1/3 (TAHO).
[11] AS Le Souef to James Norton Smith, 11 July 1902; Walter Pinkard to James Norton Smith, 4 August 1902, VDL22/1/28 (TAHO).
[12] ‘Wanted’, North Western Advocate and the Emu Bay Times, 1 July 1908, p.3.
[13] For Roberts, see Robert Paddle, ‘The most photographed of thylacines: Mary Roberts’ Tyenna male—including a response to Freeman (2005) and a farewell to Laird (1968)’, Australian Zoologist, vol.34, no.4, January 2008, pp.459–70.
[14] In ‘Wanted to buy’, Mercury, 18 July 1908, p.2, McGowan asked for tigers ‘dead or alive’. He had also advertised for ‘tigers … good, sound specimens, high price; also 2 or 3 dead or damaged specimens’ in the previous year (‘Wanted’, Mercury, 21 June 1907, p.2). George Tripp’s tiger must have died before it could be sold alive, since he claimed a government bounty for it (no.35, 25 July 1908, LSD247/1/3 [TAHO]).
[15] See, for example, ‘Wanted’, North Western Advocate and the Emu Bay Times, 7 March 1908, p.6.
[16] Thomas Lovell to AK McGaw, 17 July 1908, VDL22/1/34 (TAHO).
[17] ‘The Tasmanian tiger’, Mercury, 7 October 1908, p.4.
[18] Thomas Lovell to AK McGaw, 24 May 1909, VDL22/135 (TAHO). This thylacine was originally thought to be a young female, but McGaw later stated that it was a young male.
[19] Mary G Roberts to AK McGaw, 31 May 1909, VDL22/1/35 (TAHO).
[20] Thomas Lovell to AK McGaw, 1 June 1909, VDL22/1/35 (TAHO).
[21] Bob Wainwright, 86 years old, interviewed in Launceston, 27 October 1980.
[22] AK McGaw to Mary G Roberts, 9 June 1909, VDL52/1/29; Mary G Roberts to AK McGaw, 10 June 1909, VDL22/1/35 (TAHO).
[23] Mary G Roberts to AK McGaw, 21 June 1909, VDL22/1/35 (TAHO).
[24] AK McGaw to Mary G Roberts, 7 July 1909, VDL52/1/29 (TAHO); ‘Stanley’, North Western Advocate and the Emu Bay Times, 6 July 1909, p.2.
[25] W Roberts to AK McGaw, 15 July 1909, VDL22/1/35 (TAHO).
[26] In May 1912 she received two young tigers from buyer EJ Sidebottom in Launceston, paying him £20 in the belief that they were adults. They died three days later (Mary Grant Roberts diary, 6, 7 and 10 May 1912, NS823/1/8 [TAHO]).
[27] Mary G Roberts to AK McGaw, 14 March 1910, VDL22/1/36 (TAHO).
[28] Mary Grant Roberts diary, 12 August, 26 September and 24 December 1911, NS823/1/8 (TAHO).
by Nic Haygarth | 17/10/20 | Tasmanian high country history
Bullocks roared and rumbled through the bush. The screech of the bullockies and the whiplash of their silk crackers kept beast and burden on track as the rain poured, the bogs deepened and the rivers rose. This was how a farmer made a living—or a fortune—during the opening up of the Mount Bischoff Tin Mines. In the years 1873–77 men as far afield as Pipers River, Deloraine, Circular Head and New Ground (Harford/Sassafras) drove bullock or horse drays to Emu Bay to join locals carting tin ore from Bischoff to the wharf. And what a ‘road’ it was—a series of bullock-swallowing mires punctuated by stumps, rocks, holes, stiff climbs, creek fords and rickety river bridges. No one died on the road—mining at Bischoff was more dangerous—but taking leave of their loved ones each trip must have been a torment for the teamsters.

Looking across from the Stanhope (Walker and Beecraft) lease to the Mount Bischoff Co’s Bellhouse Dam and Slaughteryard Gully Face, c1883. Photo courtesy of the late John Shepherd.
The first carting season in early 1873
In the early days of Mount Bischoff, when mining was confined to rooting out tin ‘nuggets’ with a pickaxe and cradling washdirt, the claim owned by Alfred Miles (AM) Walker and Ned Beecraft of Forth was a serious rival to the Mount Bischoff Co as a tin producer. Both claims needed an outlet to their market. The decision of the Van Diemen’s Land Company (VDL Co) not to precipitate its tramway from Emu Bay left them at the mercy of road transport. So they formed a Mount Bischoff Road Trust to fund track improvements and hired drivers to haul in their stores and haul out their ore.

Cornelius Woodward as an old man. Courtesy of Rumney Smith Research.
Stowport’s Cornelius Woodward drove the first bullock dray load of Mount Bischoff Co ore towards the coast on 4 January 1873. It was a taxing trip. Woodward broke his bullock dray pole in the dreaded Nine Mile Forest, and because he had to borrow tools on foot from the Surrey Hills Station, the round trip took thirteen days. Competition for carters was fierce between the rival companies. Walker and Beecraft scored the second load out of Bischoff, driven by a man named Mott, but afterwards often had the edge on the bigger company, securing the best teams at the start of the summer carting season.

Mount Bischoff teamster, Methodist lay preacher and local historian Richard Hilder (1856–1938), seen here on the right in the back row as a member of the Burnie branch of the Tasmanian Reform League. From the Weekly Courier, 20 June 1903, p.17.
Mooreville Road farmer Richard Hilder recalled a trip in January 1873, when road conditions were at their most primitive. The Hilders, Thomas senior and junior, plus Richard, drove a six-bullock team and for safety travelled with two other teams. Camps had to be chosen carefully in order to feed and water the bullocks. Day One, nine hours of travelling, got them to Ridgley, where ‘swarms’ of tiger cats (spotted quolls) attacked their stores; the second night was spent at the 31-Mile Creek; the third night at Browns Marsh, within striking distance of Bischoff. As travellers did in the vicinity of Middlesex Station, Hilder engaged in a little Gothic convict mythology when he described fording the Hellyer River near the ‘3 feet thick stone wall of what was once the VDL Co penitentiary or barracks, now fallen into decay and silence’. This was Chilton, the station abandoned by the VDL Co when it withdrew from active farming operations decades earlier. The round trip took the Hilders eight days, including a non-travelling day spent in observance of the Sabbath—a big improvement on Woodward’s experience.[1]
The difficulty of loading ore at Emu Bay
However, the road was not the only problem. There were no proper loading facilities at Emu Bay, where the 40-foot-long jetty was built without provision for a crane.[2] The port’s exposure to the weather also meant that the steamer Pioneer, which traded weekly between Launceston and Circular Head, was often unable to load passengers and cargo on either leg of its regular voyage.[3] In December 1873 the Mount Bischoff Co sent empty ore bags from Launceston to Emu Bay on the Pioneer, and engaged drays to fetch the ore, but on two consecutive trips the steamer failed to land the ore bags.[4]

Probable section of dray track cut through light forest on the verge of Knole Plain. Nic Haygarth photo.
Improving the road for the 1873–74 carting season
The Mount Bischoff Co prepared for the next carting season by finding a shorter route to Mount Bischoff via Bunkers Hill, and surveying a road from Bischoff out into the open country.[5] AM Walker engaged six teams, and the Mount Bischoff Co also had teams waiting for the chance to start work.[6] However, damage to the road caused by the uprooting of trees discouraged teamsters, some of whom found they could get better money hauling blackwood logs. The result was that by January 1874 the Mount Bischoff Co had only delivered a miniscule six tons of ore to the smelter in Sydney.
Things had to change. Mount Bischoff Co mine manager WM Crosby selected sites for a Hellyer River bridge in March 1874, while long-standing Field brothers stockmen Charlie Drury and Martin Garrett advised about crossing sites on the Wye/Wey River.[7] However, the worst part of the road was the 6.5 km between Knole Plain and the mine, including the section of it known affectionately as ‘Bog Lane’. Richard Hilder recalled that the final stage the track
‘entered a dense undergrowth of horizontal scrub through which an actual tunnel was cut with the gnarled, leafy horizontal scrub packed thickly on either side and overhead … It was so narrow that only a team in single file could pass through its 300 yards length. The bog consisted of whitish loam mixed with enormous granite boulders and tangled roots of the horizontal’.
So vile smelling was this bog in hot weather that driver and team hurried through as quickly as possible.
Hilder told the tale of an axe which disappeared in the Bog Lane mud, only to make a miraculous reappearance about ten days later after hundreds of teams had passed over it, all of them somehow escaping injury. [8]
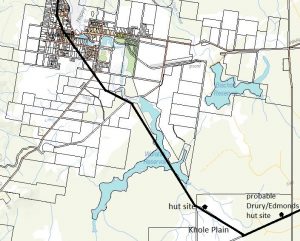
Approximate line of the original dray track through the Mount Bischoff Co land holdings at Knole Plain into the Waratah settlement, used 1872–75. The track would have passed through the site of the now closed Waratah Primary School and was on the line of Vincent Street when it became ‘Bog Lane’, the tunnel through the horizontal scrub, nearing Mount Bischoff. The Waratah Dam did not turn the upper Waratah River into an impoundment until 1911. Base map courtesy of DPIPWE.
In July 1874 the Mount Bischoff Co entered into an agreement with Charles Adams of Pipers River to cart ore, in exchange for which the Mount Bischoff Co would built stables for Adams’ horses.[9] The agreement remained essentially hypothetical until the road was rendered passable by 40 men working through the spring ahead of the official carting season in November.[10]

James and Mary Patterson
celebrating their 57th wedding anniversary. Foot & Co photo, Burnie, from the
Tasmanian Mail, 25 March 1899, p.18.
The Mount Bischoff Co fires up its Launceston Smelter
During 1874 the Mount Bischoff Co raised the first reverbatory furnace of its Launceston Smelter, ratcheting up the pressure to get a steady supply of ore from its mine. In December 1874 it appointed an Emu Bay agent to help it do so. The job of 60-year-old Northumbrian Captain James Patterson, was to arrange the dispatch of the company’s ore to the Launceston Smelter and the provision of stores and equipment to the miners.[11] Since the Emu Bay wharf was so small that two parties could not work alongside each other, Patterson had to compete with Captain William Jones, the storekeeper who doubled as agent for Walker and Beecraft.[12]

Weighing tin ingots at the Mount Bischoff Co Smelter, Launceston. Photo courtesy of the Queen Victoria Museum and Art Gallery.
The first furnace was charged with Mount Bischoff Co ore on 4 January 1875, the event being heralded by the Cornwall Chronicle newspaper as the crowning achievement of Tasmanian industry.[13] Three days later, the furnace was charged with Walker and Beecraft ore, pointing to the smelter’s future as a custom smelter.[14]
Mounting tension between companies
Back at Emu Bay, tensions between the companies escalated when JH Munce, agent for the steamer Pioneer, apparently gave the impression that Adams was the only carter to be loaded up with stores for Mount Bischoff. Some carters took umbrage and engaged with Walker.[15] Some stated that Walker treated them better loading and unloading their wagons and giving them a feed on arrival at Mount Bischoff, services which they alleged the Mount Bischoff Co refused to do.[16] Patterson denied this was the case.[17] One of the Mount Bischoff Co directors, ED Harrop, accused Walker of bribing teamsters with an offer of £8 10 shillings, a price which Walker had only paid while the road was bad, £6 being the normal rate each way. Harrop told Walker that if necessary the Mount Bischoff Co would increase the rate to £20 to win the carters back again.[18] Walker counter-claimed that Patterson tried to seduce teamsters contracted to him by offering them £9 per ton—another charge which Patterson denied.[19]

Charles and Elizabeth Adams of Pipers River. Photo courtesy of Michael Oakley.
Adams carted 100 tons of ore for the Mount Bischoff Co at £6 per ton, the directors conceding him a higher rate than originally negotiated in compensation for the tramway to the open country not having been completed, forcing Adams to load at the Waratah Falls.[20] He also carted stores up to Bischoff at £4, making his maximum potential income a staggering £1000, enough to set up a farmer for life. However, Adams found his five-horse team could move only half a ton per trip—and one trip was said to have taken him a fortnight![21] Had that been his average rate, the entire job would have taken him nearly eight years, which certainly alters the perspective on his potential fortune. The Wey and Hellyer Rivers were now bridged, but the Bischoff Road was so bad that sometimes all but the heads and backs of the horses disappeared, as if they were swimming in mud. Chinese whispers may have exaggerated reports a little, including one account related to Philosopher Smith that
‘a party going along the road had seen a hat and he took hold of it and found a man underneath with a dray and team of bullocks. I dare say by the time you receive this report in town the man will have been able to put a note in the crown of his hat just as he was sinking to say that he was there’.
Discharged cargoes and broken drays littered the roadside. In February 1875 30 teams were on the road, but Adams was far from happy with the slow progress of promised stable building at the Hampshire Hills, the Wandle River and Knole Plain. Fear for his horses’ safety in deplorable road conditions with new drivers and inadequate shelter forced him to consider withdrawal from a contract he felt the Mount Bischoff Co had already dishonoured. It was no help to Adams when in March 1875 Walker suggested that the two companies build cattle yards on VDL Co land at Browns Marsh, a proposition Norton Smith agreed to at a nominal rent.[22]
Road conditions got so bad that Patterson started paying up to £10 10s per ton, horrifying the directors. [23] Even a presiding rate of £7 failed to mollify them.[24] During the off season, Walker and Beecraft sold their Mount Bischoff claim to the Victorian-based Stanhope Tin Mining Company, and William King, Thomas Farrell, WH Atkinson and either George or William Rutherford all offered to cart for the Mount Bischoff Co for £6 per ton.[25] In the meantime, the Road Trust authorised Thomas Duncanson to spend £670 making the road useable by drays, including corduroying the Nine Mile Forest, making culverts, metalling the approaches to the Hellyer River and improving the road at the 13-Mile.[26] It was claimed that the corduroy on the long western approach to the Hellyer was being destroyed by carters who overloaded with ore in order to shut out competitors.[27]
Retribution against the King brothers
In December 1875 the King brothers were engaged at the new rate of £6, and this despite the bad road conditions. Travelling up to Mount Bischoff, two of the Kings’ bullocks ‘knocked up’ as they entered the Nine Mile Forest. The brothers shifted most of their cargo to one dray, and left the other with the two tired bullocks at the Hampshire Hills, hiding the dray with brushwood. When they returned, they found that the spokes of the dray wheels had been chopped out and the pole removed and burned, this being interpreted as punishment for ‘collaboration’ with the Mount Bischoff Co.[28]
A newspaper correspondent stated that King had six teams operating at the time, employing others to cart for him at a rate as low as £3 or £3 10 shillings per ton, while he pocketed the difference.[29] Another claimed that King engaged only two other teams at £5 per ton late in the season, gaining only a trifle from the deal.[30] Whatever the truth, many others got work at Mount Bischoff, there being 90 teams on the road during fine weather, some travelling 100 miles for the work—and most getting only £4 per ton. Some of them were turned away as the Mount Bischoff Co enforced a rule that each ore carter had to bring supplies up to Mount Bischoff. When there were no supplies to haul up, a telegram was sent to the effect that the company would now employ all carters, upon which 200 tons of tin were transported to Emu Bay in a fortnight.

The Stanhope Smelter (top of the hill at right) operated at Waratah from 1876 for only two or three years. Its woodshed and another shed remain in this cropped c1883 image, but its furnace is not visible. Note also the giant tree stump and fallen log beside the smelter. Part of the smelter tramway can be seen between the Waratah Hotel (centre of photo) and the shop on the right. The Bischoff Hotel is the building with three attic windows at extreme right. Note the houses up Smith Street at left, even what appear to be tenement house beyond the Ritchie Street corner at the top of the hill. The original 1882 Post and Telegraph Office can be seen below the smelter. The dressing sheds in the foreground belong to the Don Co (formerly Cummings & Henry, left) and the Stanhope Co (formerly Walker & Beecraft, right). Photo courtesy of the late John Shepherd (TAHO).
The Stanhope Smelter leaves ore carting to the Mount Bischoff Co
Unlike the Mount Bischoff Co, the Stanhope Co heeded German engineer Georg Ulrich’s advice to smelt at Bischoff, using wood (or at least charcoal) as fuel, engineers Nicol Turner and Scott building the first blast furnace at the corner of Ritchie and Smith Streets—right beside the early dray track to Bischoff. The outside walls of the furnace and part of the chimney were built of basalt hewn on site, while the arches of the fireplaces and the smelting hearth were constructed of firebricks packed in from Emu Bay.[31] The first firing was in January 1876, and within two months AM Walker claimed it such a success that soon it would be able to smelt 24 tons of ore per week—more than all the Bischoff mines produced together.[32]
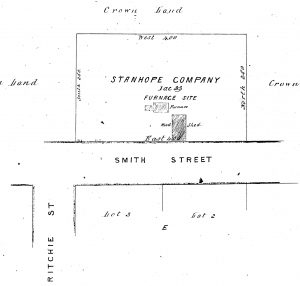
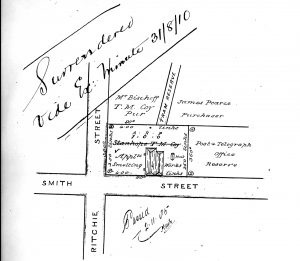
Surveys of the Stanhope Smelter site at Waratah. Note the tramway reserve by which the smelter was connected by tramway to Mount Bischoff. Part of the cutting for the tramway can still be seen behind the Bischoff Hotel. Courtesy of Mineral Resources Tasmania.
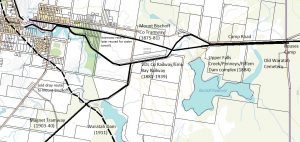
Waratah tramways and railways. From 1875, when the Mount Bischoff Co’s Tramway from the Waratah Falls reached Rouses Camp (extreme right), this became the terminus for the teamsters hauling tin ore to Emu Bay. This tramway was abandoned in 1881 when the VDL Co extended iron rails into Waratah, much of the tramway reservation being reused as the line of the Mount Bischoff Co water tunnel. Base map courtesy of DPIPWE.
While the Stanhope Co still needed stores and equipment delivered to Bischoff, it effectively dropped out of the ore carting business at this point, leaving the Mount Bischoff Co to feed its own smelter in Launceston. In February 1876, 66 teams were working for the Mount Bischoff Co, there having been 80 dray trips in the space of two weeks.[33] However, AM Walker, now a Waratah shopkeeper rather than a mine owner, continued his attacks on the Mount Bischoff Co, alleging that its timber falling caused an obstruction on the road.[34] He amplified this complaint in the middle of the year after his brother Henry Walker was killed by being thrown off the Mount Bischoff Co Tramway while it crossed a gully. Walker blamed the company for his brother’s death since, he believed, it blocked the road deliberately with a fallen tree so as to monopolise the traffic between Rouses Camp and Bischoff..[35]
The final carting season 1876–77
As the VDL Co’s Emu Bay and Mount Bischoff Tramway progressed, the teamsters knew their days were numbered, this being the last full season of dray carting. Relations between teamsters and the Mount Bischoff Co remained frosty, with Edwin Addison of New Ground presenting a raft of complaints against Patterson as the season opened.[36] In January 1877 the company announced it would pay £6 per ton down and £5 per ton up to Waratah, with teams being loaded at Rouses Camp in the order in which they arrived.[37]
The 1877 Rouses Camp snowball fight
However, things didn’t always go to plan. In April 1877 50 drivers and teams were stranded at Rouses Camp for days due to a shortage of ore bags. The beasts of burden were set loose to graze on Browns Marsh and the Racecourse (on the VDL Co’s Surrey Hills block) while their drivers socialised in Waratah. One day the drivers awoke to find six inches of snow on the ground around them, and with time to kill, the strong rivalry between bullock drivers and horse drivers actuated a fight—the weapons consisting of nature’s new bounty, the snow. Tom King led the bullockies, Jack Floyd the horsemen, with Fred Frampton acting as referee. The battle raged for two hours, divided into 20-minute sorties. Snowballs pounded flesh, men reeled from stinging attacks, retaliating in kind until late in the day when
‘with a “Hurrah, boys”, Captain Floyd ran up and down his lines of men, who, gallantly responding to his call, rallied and drove the bullock men inch by inch from the field and scattered them in the final decisive defeat’.[38]
All participants then dried off in front of a roaring fire, their surplus energy exhausted. New ore bags arrived from Emu Bay after midnight that night, enabling them to complete one of the last major deliveries of Mount Bischoff ore via the Bischoff Road to Burnie.
Richard Hilder’s final Bischoff dray trip was in the following month, hauling ‘fancy goods’ (clocks, watches, jewellery and drapery) up to Waratah for storekeepers the Messner brothers. The old difficulties still obtained. Hilder’s hopes of returning to Burnie with Bischoff ore were dashed when at the 29-Mile he broke an axle, forcing him to abandon his dray and transfer his load to those of his companions.[39] By late May 1877 the tramway had reached Hampshire, effectively halving the teamsters’ business, and by February 1878 not a bullock whip was to be heard cracking on the Bischoff Road.[40] By then the Mount Bischoff Co, surmounting all its problems, had kicked off the shareholder bonanza that eventually doled out more than £2.5 million in dividends.
Some notable Bischoff teamsters, with help from Richard Hilder
Charles Adams
In 1869 Launceston-born Adams (1834–1910) found gold nuggets on his Pipers River farm, after which time he invested in the Back Creek Alluvial Gold Mining Co and prospected for tin in the Georges Bay area (St Helens).[41] Adams visited Mount Bischoff in 1874, presumably as a prospector and/or potential investor, only three months before he made his offer to cart 100 tons of Mount Bischoff Co ore at £6 per ton.[42]
Thomas Addison aka ‘Grandfather Addison’
The ‘grand old man’. He could handle a bullock team ‘to perfection, and with a sonorous, commanding voice he guided his fine team through treacherous mud or over rocky road or the shocking broken corduroy. He had no strong apprehension of ever being stuck fast. We all loved Grandfather Addison’.[43]
Joseph Alexander
A number of members of the Alexander family carted Mount Bischoff ore. Joseph Alexander (c1841–1917), the son of Matthias Alexander, was born at Illawarra near Longford, but became a Table Cape farmer and later a publican and storekeeper in various centres along the north-west coast. [44]
S Andrews
He was the only teamster to drive a four-wheeled vehicle, with 10 or 12 Devon bullocks. His two pole bullocks drowned in a bog at the 27-Mile in the autumn of 1876 and had to be left there. Sam Dudfield attempted to go through the same bog in February 1877, and had to be rescued, revealing the wooden yoke, iron bow and putrid bullock remains still there in the bog.[45]
William ‘Hermit’ Applestall
Very tall and angular, supposedly seven feet tall but stooped, independent and morose, he drove a bullock team for William Henry Oldaker, bringing a young lad and dog for company. Applestall would camp with his team of ‘well-matched brindle bullocks’ away from everyone else, hence the nickname ‘Hermit’. He never overloaded his team, never hurried, never kept other teams waiting.[46]
William Atkinson
‘Roaring Billy’, farmer on the New Country Road south of Burnie who was noted for his good bullock team and skillful handling of same. Also hauled split timber and logs out of the forests along Mooreville Road and at Stowport.[47]
Jamie Blair
One of the ‘Scotch twins’ (with Jamie Dennison), who had the biggest and smallest draught horses on the Bischoff road. He had a ‘splaw-footed, raking, eagle-eyed animal that repeatedly stumbled and fell but was the pet of his master’ and would call out to the other ‘Scotch twin’: ‘Jamie, ma mon come smart, an’ help ma to git ma pet oop agin’.[48]
John Cassidy
The man presumably celebrated by the name Cassidys Marsh, an appetising spot on the old dray track somewhere between Knole Plain and Waratah. Probably John Martin/Macassin Cassidy (1853–1929) of Bengeo near Deloraine—more likely to be him than his father, the Irish ex-convict or immigrant John Cassidy (c1812–96).[49]
Billy Cunningham
Black River ventriloquist who amused bullock drivers with his impressions of farm animals in the dead of night, also a dab hand with a bullock whip.[50]
James Denison (Jamie Dennison)
One of the ‘Scotch twins’ (with Jamie Blair) who always drove together. Very fond of his horse Roly-Poly, the ‘miniature, nimble-footed chestnut gelding which no hardship of the Bischoff road could knock out’.[51]
Sam Dudfield
Samuel Dudfield (1855–1935) was born at Longford to two ex-convicts, James Dudfield, who described himself as a gardener, and Ann/Anne Orrell (aka Arwell/Orwell).[52] He farmed at St Marys Plain, Cam River (Tewkesbury), in the inner north-west. Richard Hilder described how he attempted to go through the 27-Mile bog that had drowned Andrews’ two bullocks in the autumn of 1876. It was now nearly a year later in February 1877, and Dudfield’s team had to be rescued, revealing Andrews’ wooden yoke, iron bow and putrid bullock remains still there in the bog.[53] Dudfield was reported to have shot a thylacine at St Marys Plain in 1895, which he intended to submit it for the government bounty.[54]
Thomas Farrell
Presumably Burnie hotelier and well-known prospector Thomas Farrell (c1857–1926).[55] Mount Farrell near Tullah is named after him, recalling his discovery of the White Hawk Mine, one of the early mines on the Mount Farrell field.[56] He discovered and for a time managed the King Island Scheelite Mine.[57]
Jack Floyd
Leader of the horsemen in their snowball fight against the bullock drivers at Rouses Camp in April 1877.[58]
Fred Frampton
From Ulverstone, he was referee in the Rouses Camp snowball fight in April 1877.[59]
M Gillam aka ‘Greasehorn’ Gillam
Disliked by some for the barrage of questions he asked about the origins and doings of the VDL Co while camped at their early settlements. He carried cart grease in a long Hereford bullock horn, hence the nickname ‘Greasehorn’.[60]
Harry Hills
Later a Mount Bischoff Co employee who also operated a dairy farm on Lot 6201, an old Mount Bischoff Co block at Knole Plain approximately 1880–84.[61] Hills was probably the first to stock Knole Plain with any success, John Bailey Williams having failed as a wool-grower there in the 1860s.[62] Hills had two large, fenced paddocks laid down with ‘artificial’ grass, and was supplying milk to Waratah.[63] His successor there was George Martin, who in 1891 advertised for sale the 100-acre Knole Plain dairy farm with a four-room cottage, detached kitchen, cowshed and stable.[64]
William House & ‘Red’ Stephen Margetts
A pair of bullock drivers ‘which no course speech or manners could in any way defile’. They were ‘courteous and kind in word and action, good and reliable drivers who could face without flinching the real danger of the road, bridge or river, considerate to their cattle, and good company to their companion drivers. Examples for all to follow on the Bischoff road 50 years ago’.[65]
Ike Hutchison
A horse driver from Penguin who was ‘far too old a man for the rough and tumble of a teamster on the Bischoff road’. ‘He spoke of them [his two horses] and caressed them like a real lover.’ At camp, with the billy boiled, he would wash and comb his horses’ manes, ‘at the same time speaking to them with soothing words and affectionately caressing them’. One night his horses escaped from camp, and so anxious was he to find them that he did not even stop to put on his boots, following with bare feet and rejoicing when they were found.[66]
Tom King
Leader of the bullockies in their snowball fight against the horse drivers at Rouses Camp in April 1877.[67]
William King
Launceston-born William King (c1823–1905) attended the Californian gold rushes and became a publican before settling down to farm at Table Cape and Boat Harbour during his last 40 years. Despite the incident where his wheel spokes were destroyed in 1875, Mount Bischoff ore carting apparently helped turn around his fortunes.[68]
John Martin
A bullock driver from Greens Creek (Harford). Hilder described his unusual way of yoking up his team of miniature bullocks and his cavalier attitude to braking them.[69]
Richard Mitchell
Presumably illiterate Cornish tin dresser Richard Mitchell (1852–1909), who left England in 1875, working briefly in New South Wales before arriving in Tasmania late that year. A man of that name carted tin for the Mount Bischoff Co from November 1875 until at least March 1876.[70] He later managed the East Bischoff Mine (1879–81) and the Waratah Alluvial (1881–85) at Mount Bischoff, but was better known for floating the Anchor Tin Mine Ltd in London in 1895, the deal being made controversial by the addition of the name of the premier, Sir Edward Braddon, to the company’s prospectus. Mitchell died in a London hotel room while trying to float a company to work the All Nations Mine near Moina.[71]
Harry Moles
A driver for Walker and Beecraft, he wore a white, long-sleeved moleskin waistcoat. ‘His voice had a pleasant drawl, and his speech was a rich corruption of good English. It was real fun to listen to Harry give a description or ask a question’.[72]
Charlie Radford
The VDL Co’s ‘reliable man’, who also spent years hauling celery pine and blackwood logs out of the forests at Mooreville Road and Stowport Road, and hauled logs to sawmills during construction of the VDL Co Tramway. He drove a team of fine bullocks. ‘For kindness, patience and goodwill no man could exceed Charlie … a real Christian gentleman.’[73]
Thomas Summers
A teamster who drove a team of five horses for his uncle, Thomas Summers of Mooreville Road. He had a mother and several children on the dray in February 1877 when he overturned the dray at the Wey River, but with no damage to the occupants.[74]
Ulo Wells
Bullock driver for FW Ford on the VDL Co tramway construction and probably also on ore carting.[75]
Cornelius Woodward
Woodward (1853–1943) carted the first load of ore from Mount Bischoff on 4 January 1873, completing the trip in thirteen days after breaking a bullock dray pole.[76]
[1] Richard Hilder, ‘By road to Bischoff in 1873’, Advocate, 10 November 1923, pp.10–11.
[2] ‘A visit to the Mount Bischoff tin mines’, Cornwall Chronicle, 27 August 1873, p.2.
[3] ‘A trip to the tin mines’, Cornwall Chronicle, 2 December 1874 p.3.
[4] William Ritchie to James Smith, 12 December 1873, no.362, NS234/3/1/2 (TAHO).
[5] James Norton Smith to James Smith, 27 November 1873; WM Crosby to James Smith, 3 December 1873, NS234/3/1/2 (TAHO). The work was carried out by James Smith and Charles Sprent respectively.
[6] William Ritchie to James Smith, 17 December 1873, no.365, NS234/3/1/2 (TAHO).
[7] William Ritchie to James Smith, 9 March 1874, no.65, NS234/3/1/3 (TAHO).
[8] Richard Hilder, ‘Lost and found’, Advocate, 27 June 1931, p.9.
[9] William Ritchie to James Smith, 6 July 1874, no.195, NS234/3/1/3 (TAHO).
[10] AM Walker to James Smith, 21 October 1874, no.321, NS234/3/1/3 (TAHO).
[11] ‘A pair of veteran colonists’, Tasmanian Mail, 25 March 1899, p.18.
[12] James Patterson to James Smith, 23 February 1875, no.89, NS234/3/1/4 (TAHO).
[13] ‘Mount Bischoff Tin Mining Company: the first smelting’, Cornwall Chronicle, 6 January 1875, p.2.
[14] EL Martin, ‘Discovery and early development, 1871–1875’, in DI Groves, EL Martin H Murchie and HK Wellington, A century of tin mining at Mount Bischoff, 1871–1971, Geological Survey Bulletin, no.54, Department of Mines, Hobart, 1972, p.33.
[15] WM Crosby to James Smith, 13 January 1875, NS234/3/1/4 (TAHO).
[16] FW Ford to James Smith, 14 January 1875, no.23, NS234/3/1/4 (TAHO).
[17] James Patterson to James Smith, 16 January 1875, no.29, NS234/3/1/4 (TAHO).
[18] AM Walker to James Smith, 14 January 1875, no.22, NS234/3/1/4 (TAHO).
[19] James Patterson to James Smith, 23 January 1875, NS234/3/1/4 (TAHO).
[20] ‘Mount Bischoff Tin Mining Company’, Tasmanian, 16 January 1875, p.4.
[21] ‘Personal’, North Western Advocate and the Emu Bay Times, 17 August 1910, p.3.
[22] Minutes of meeting of directors of the Mount Bischoff Tin Mining Co, 8 and 15 March 1875, NS911/1/1 (TAHO).
[23] Minutes of meeting of directors of the Mount Bischoff Tin Mining Co, 25 February 1875, NS911/1/1 (TAHO).
[24] Minutes of meeting of directors of the Mount Bischoff Tin Mining Co, 1 March 1875, NS911/1/1 (TAHO).
[25] ‘Our tin mines’, Cornwall Chronicle, 3 September 1875, p.3; Minutes of meeting of directors of the Mount Bischoff Tin Mining Co, 9 August 1875, 1 November 1875, 15 November 1875, 22 November 1875, NS911/1/1 (TAHO).
[26] Minutes of meeting of directors of the Mount Bischoff Tin Mining Co, 6 September 1875, NS911/1/1 (TAHO).
[27] ‘Concerning Mount Bischoff’, Launceston Examiner, 27 April 1876, p.2.
[28] ‘A dastardly act’, Tasmanian, 15 January 1876, p.12.
[29] ‘Concerning Mount Bischoff’, Launceston Examiner, 27 April 1876, p.2.
[30] ‘A Shareholder’, ‘Carting to and from Mount Bischoff’, Launceston Examiner, 23 May 1876, p.4.
[31] ‘Mount Bischoff’, Cornwall Chronicle, 13 December 1875, p.2; ‘Mining’, Launceston Examiner, 5 October 1875, p.4.
[32] AM Walker, ‘Tin smelting at Mount Bischoff’, Tasmanian, 25 March 1876, p.7.
[33] Minutes of meeting of directors of the Mount Bischoff Tin Mining Co, 21 February 1876, NS911/1/1 (TAHO).
[34] Minutes of meeting of directors of the Mount Bischoff Tin Mining Co, 24 February 1876, NS911/1/1 (TAHO).
[35] William Ritchie to James Smith, 24 July 1876, no.213, NS234/3/1/5 (TAHO).
[36] Minutes of meeting of directors of the Mount Bischoff Tin Mining Co, 7 December 1876, NS911/1/1 (TAHO).
[37] Minutes of meeting of directors of the Mount Bischoff Tin Mining Co, 14 December 1876, NS911/1/1 (TAHO).
[38] Richard Hilder, ‘By road to Mount Bischoff: Chapter 3’, Advocate, 16 October 1926, p.12.
[39] Richard Hilder, ‘By road to Mount Bischoff’: Chapter 4’, Advocate, 6 November 1926, p.26.
[40] ‘Emu Bay’, Tasmanian, 26 May 1877, p.5.
[41] Born to John and Susannah Adams on 4 October 1834, birth record no.6247/1835, registered at Launceston, RGD32/1/2 (TAHO), https://librariestas.ent.sirsidynix.net.au/client/en_AU/names/search/results?qu=charles&qu=adams&qf=NI_INDEX%09Record+type%09Births%09Births, accessed 17 October 2020; ‘Deaths’, Examiner, 15 August 1910, p.1; ‘Pipers River diggings’, Cornwall Chronicle, 11 September 1869, p.5; ‘Official notices’, Launceston Examiner, 17 February 1870, p.3; Charles Adams, ‘Discovery of tin on east coast’, Examiner, 9 May 1905, p.3.
[42] SB Emmett, ‘A trip to the tin mines at Mount Bischoff’, Launceston Examiner, 4 May 1874, p.2.
[43] Richard Hilder, ‘By road to Mount Bischoff: Chapter 3’.
[44] ’70 years on the coast’, North Western Advocate and the Emu Bay Times, 18 January 1917, p.2.
[45] Richard Hilder, ‘By road to Mount Bischoff: 2nd Chapter’, Advocate, 18 September 1926, p.14.
[46] Richard Hilder, ‘By road to Mount Bischoff: Chapter 3’.
[47] Richard Hilder, ‘The real pioneers of Emu Bay: Chapter 5’, Advocate, 5 January 1935, p.9.
[48] Richard Hilder, ‘By road to Mount Bischoff: Chapter 3’.
[49] No birth record was found for John Cassidy junior. He died 9 January 1929, supposedly aged 73 (‘Family notices’, Advocate, 10 January 1929, p.2). John Cassidy senior’s death record gives his place of birth as County Meath, Ireland. He died 16 July 1896, his age given as 84, death record no.99/1896, registered at Deloraine, RGD35/1/65 (TAHO), https://librariestas.ent.sirsidynix.net.au/client/en_AU/names/search/results?qu=john&qu=cassidy&qf=NI_INDEX%09Record+type%09Deaths%09Deaths, accessed 10 October 2020.
[50] Richard Hilder, ‘By road to Bischoff in 1873’.
[51] Richard Hilder, ‘By road to Mount Bischoff: Chapter 3’.
[52] Born 14 January 1855, birth record no.965/1855, registered at Longford, RGD33/1/33 (TAHO),
; died 17 January 1935, will no.20614, dated 20 March 1935, AD960/1/59, p.381 (TAHO), https://librariestas.ent.sirsidynix.net.au/client/en_AU/all/search/results?qu=samuel&qu=dudfield#, accessed 27 June 2019. For James Dudfield and Anne Orrell as convicts, see their application for permission to marry, 31 March 1847, CON52/1/2, p.315 (TAHO), https://librariestas.ent.sirsidynix.net.au/client/en_AU/all/search/results?qu=james&qu=dudfield, accessed 27 June 2019.
[53] Richard Hilder, ‘By road to Mount Bischoff: 2nd Chapter’.
[54] ‘News in brief’, Wellington Times and Agricultural and Mining Gazette, 10 September 1895, p.2.
[55] ‘Mr Thomas Farrell’, Advocate, 4 June 1926, p.2.
[56] See William Innes, ‘Mining pioneers: Mt Farrell silver-lead deposits: story of discovery’, Advocate, 15 June 1926, p.7.
[57] ‘King Island: scheelite’, North Western Advocate and the Emu Bay Times, 9 August 1918, p.4.
[58] Richard Hilder, ‘By road to Mount Bischoff: Chapter 3’.
[59] Richard Hilder, ‘By road to Mount Bischoff: Chapter 3’.
[60] Richard Hilder, ‘By road to Mount Bischoff: Chapter 3’.
[61] Richard Hilder, ‘Mount Bischoff Road experiences: Chapter 4’.
[62] John Bailey Williams to Charles H Smith, Du Croz & Co, 25 January 1865; and to VDL Co agent Charles Nichols, 11 April 1865, VDL22/1/3 (TAHO).
[63] ‘For sale’, Tasmanian, 17 March 1883, p.305.
[64] ‘For sale’, Daily Telegraph, 14 March 1891, p.6.
[65] Richard Hilder, ‘By road to Mount Bischoff: Chapter 3’.
[66] Richard Hilder, ‘By road to Mount Bischoff: Chapter 3’.
[67] Richard Hilder, ‘By road to Mount Bischoff: Chapter 3’.
[68] ‘Coastal news’, Examiner, 16 June 1905, p.6; ‘The story of a pioneer’, Examiner, 21 June 1905, p.6.
[69] Richard Hilder, ‘By road to Mount Bischoff: 2nd Chapter’.
[70] Minutes of meeting of directors of the Mount Bischoff Tin Mining Co, 15 November 1875 and 6 March 1876, NS911/1/1 (TAHO).
[71] For Mitchell generally see Nic Haygarth, ‘Shearing the Waratah: “Cornish” tin recovery on the Arthur River system, Tasmania, 1878–1903’, Journal of Australasian Mining History, vol.15, October 2017, pp.81–98, https://www.mininghistory.asn.au/wp-content/uploads/9.HaygarthWaratah-Final-vol.1517.compressed.pdf, accessed 10 October 2020.
[72] Richard Hilder, ‘By road to Mount Bischoff: Chapter 3’.
[73] Richard Hilder, ‘By road to Mount Bischoff: Chapter 3’.
[74] Richard Hilder, ‘By road to Mount Bischoff: Chapter 3’.
[75] Richard Hilder, ‘Late Mr Ulo Wells, Advocate, 16 April 1926, p.2.
[76] See Richard Hilder, ‘By road to Bischoff in 1873’.
by Nic Haygarth | 03/10/20 | Tasmanian high country history
In the story ‘An “island” within an island: the maritime/riverine culture of Tasmania’s Pieman River goldfield 1877–85’, I discussed how that goldfield was virtually an island within the island of Tasmania, in that it was remote, served almost entirely by sea, took sustenance from the waterways and used them for transport.[1] The telegraph reached Corinna in 1879 but for years the only other land service was the mail run from Waratah.
The mailmen were roadrunners, men compelled to walk and run—whatever it took to make up lost time—the godforsaken track on the Bischoff–Heemskirk–Pieman service. Imagine your business dealings or your affairs of the heart hinging on news that takes ten days between destinations—and there is no resort to telephone or email should that vital letter disappear in transit, as it so often did.

William Byrne, from the Weekly Courier,
15 June 1911, p.22.
Estimates of William Byrne’s mileage as West Coast postman mounted impressively during his career: 32,000 by 1884, 38,000 by 1886, more than 40,000 by 1887 and 43,000 (about 69,000 km) by the time of his death in 1911.[2] By the mid-1880s the weight on his back, and perhaps sheltering in the hollows of trees, had left him ‘slightly stooped’, but it is a wonder that wasn’t the least of his physical ailments.[3] Because the West Coast mailman never rested, battling the elements in all seasons.

The Government Store at Corinna, on the Pieman River. Sketch by O Jarman, from the Tasmanian Mail, 14 May 1881.

A sketch of the old Trial Harbour Post Office, at the
Montagu Mine, South Heemskirk tin field.
Mine manager Alex Ingleton served as the postmaster.
From the Tasmanian Mail, 11 September 1913, p.23.
How Heemskirk was left in the dark
After losing the Bischoff mail service, Byrne won the contract for the far more strenuous one between Mount Bischoff, the Heemskirk tin field and the Pieman River goldfield. This would have meant finding accommodation at Waratah. The hazards associated with delivering the mail on time included the VDL Co service arriving late into Waratah, fallen trees, flooded streams, broken bridges and sunken rowboats. The journey was by foot, since the track cut by local subscription between Waratah and the Middleton Creek diggings near the Pieman was not fit for a horse.[4] It included the infamous ‘Underground Railway’, a stretch of almost a mile which compelled users to crawl under burnt spars.[5]

The coastal route (Climie’s Trrack) through the Heemskirk tin field today. Nic Haygarth photo.

The remaining stamper battery at the Carn Brea Tin Mine near Granite Creek, Heemskirk. Nic Haygarth photo.

The Peripatetic Tin Mine stamper battery standing outside the Trial Harbour History Room. Nic Haygarth photo.
Yet it was on this track that Byrne earned his reputation as an indomitable marathon runner, setting a cracking pace in order to meet his deadline. He became famous for sleeping in hollow trees and carrying only blankets for bedding—no tent or tent fly, not even so much as a change of clothes. Arriving at camp, he would dry himself by the fire and retire to his blankets.[6] He had camps—hollow trees—at the Whyte River and Long Plain, but his favourite hollow tree was on the Magnet Range.[7] In this hollow it was said that, with his belly full of Waratah rum, he would lighten his load by stashing newspapers according to his unique system of dispensing social justice. A Heemskirk resident accompanying Byrne across the Magnet Range once witnessed the mailman take no less than 73 newspapers from the hollow tree—seventeen of which were addressed to the witness. When asked about the newspaper stash, Byrne
‘replied that he could not see why people required so many newspapers, and he made a point of here sorting them over, according to the several merits of the persons to whom they were directed. First some were directed to a Frenchman, who could not read English, and what good could newspapers be to him. They went into the tree. Next, others were directed to a man who was half blind, and reading could only injure his eyes; tree again. In the third case, newspapers were directed to a man who could not see at all; tree again, as a matter of course’.[8]
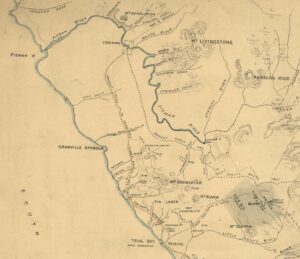
A crop from George Lovett’s 1888 exploration chart showing the track from Corinna on the Pieman River to the Heemskirk tin field, including Climie’s Track (the coastal route) used by the mailman and the Montagu Tin Mine above Trial Harbour (Bay). Cropped from AF395/1/29 (TAHO).
When in 1879 the Pieman overtook Heemskirk as a mining centre, the order of delivery was reversed—Pieman first, then onto Heemskirk. In order to service the separate goldfields on the Savage and Donaldson Rivers, Byrne had to increase his pedestrianism from the contracted two visits per month to three. River crossings were a trial. If a river was flooded his options were to fall a tree or wait for the water to subside: on one occasion the Whyte River detained him for four days.[9] For crossing the Pieman, Byrne kept a rowboat chained to a tree inside the mouth of the Savage River. He once had to fetch it down from a fork in a high tree, where it had been deposited by rising waters.[10]
Tengdahl sails into the mail run
After two years on the Pieman/Heemskirk run Byrne lost the contract—allegedly because he mistakenly tendered a price for three years instead of the required one.[11] The new mailman was well-known prospector Axel Tengdahl (1853–1919), and the successful tender £156.[12] The Swede had entered west coast lore in 1879 when he and Harry Middleton sent 250 diggers splashing in the gold-laden Middleton Creek, on the Pieman River goldfield.[13] The discoverers probably felt fortunate to be there. Tengdahl, an old salt, had ensured their safe arrival from Launceston by spontaneously piloting the steamer Sarah over the dreaded Pieman River bar.[14] These skills should have put him in good stead for the regular river crossings on the mail run.

An 1881 advert for the Amy’s West Coast service to Corinna and Trial Harbour, from the Anson Brothers’ Just the thing album (no.2), LPIC14/1/46 (Libraries Tasmania).
Tengdahl had tent camps at the Thirteen Mile (near the site of the later Heazlewood village) and Long Plain (near the latter-day Savage River township)—luxury by Byrne’s standards. The pedestrian mail service must have been exhausting. If the track wasn’t bad enough, the volume of mail was increasing, the weight of the consignment reaching about 28 kg in August 1881.[15] A regular West Coast shipping service was established in September 1881 when the steamer Amy began visiting the Pieman and Heemskirk every ten days—but this was only considered a supplement to rather than a replacement for the marathon mailman.
Meanwhile, Byrne would have been able to leave his Waratah lodgings and return full-time to the farm on Mooreville Road behind Burnie, his swag laid to rest for two years at least.

James Gaffney, from the
Tasmanian Mail, 26 June 1913, p.4.
Byrne returns as sub-contractor for Gaffney and Harvey
In December 1881 James Gaffney and Frank Harvey, Waratah butchers, building contractors, billiard hall and store proprietors, continued their rapacious expansion.[16] The contract for the Heemskirk and Pieman mail service would have fitted in well with their stores at the 20-Mile (Long Plain) and Corinna and their maintenance contract for the track to Corinna.[17] Gaffney carried the mail himself for a time, before summoning Byrne as a sub-contractor.[18]
As the weight of his load grew, Byrne extended his war on newspapers to include parcels. When someone at the Pieman or Heemskirk ordered books from a Hobart store he refused to carry the parcel without payment of a five-shilling surcharge.[19] Perhaps some of the standard mail was also disappearing into his unofficial post office on the Magnet Range, since one man complained that ‘scarcely one half of the number [of letters] posted to him … ever reached him’.[20]
After the Brown Plain rush of 1882, the Pieman River goldfield was in the doldrums. However, in April 1883, when the Amy was replaced on West Coast service by the Wakefield, the Heemskirk hard rock tin boom was at fever pitch. Nine mines equipped themselves with crushers, 75 or 80 head of stampers being erected across the field.[21] The low yield from the first crushing at the Orient Tin Mine in October 1883 put a great dampener on proceedings.[22] Confidence in the field evaporated, and the focus of attention changed to the Mount Lyell goldfield.[23]
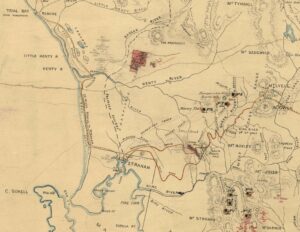
A crop from George Lovett’s 1888 exploration chart showing the track from Trial Harbour (Bay) across the sand dunes to Strahan. Cropped from AF395/1/29 (TAHO).
The Bischoff to Strahan Mail
Heemskirk residents presented Byrne with a gold watch at the end of his contract in September 1883, as thanks for ‘energy displayed in carrying mails from Mount Bischoff to Heemskirk’.[24]
However, that was not a retirement gift. Byrne’s final mail service was the run via the Pieman and Heemskirk to Strahan 1884–87. In 1884 Gaffney and Harvey began to re-establish themselves as storekeepers, hoteliers and general contractors at Long Bay (West Strahan), Macquarie Harbour, anticipating that this would become the port for the Mount Lyell gold (and later copper) field. They presumably had no interest in the new Waratah–Heemskirk–Strahan–Long Bay mail contract other than receiving their own mail. In December 1884 Byrne won the three-year contract for £295, that is, about £98 per year.[25] Why so cheap? In 1880, after all, Tengdahl had successfully tendered the Heemskirk contract with £156. Perhaps it was envisaged that the mailman would take a ship from the Pieman to Trial Harbour, thereby reducing his legwork. Government-provided traveller accommodation along the route would have obviated Byrne’s need of hollow trees: there were huts at the Thirteen-Mile (near the site of the later Heazlewood village), Eighteen-Mile (near the Heazlewood River), and the so-called Bauera Hut (between Long Plain and Browns Plain), about 25 miles from Waratah.[26]
However, most of the same problems obtained as before. The track was a sea of mud covered with fallen trees. Byrne would have been used to dealing with the Pieman, and the other major obstacle—the Henty River—had a ferry service, but the Tasman River was also known to flood. On one occasion the rowboat at the Little Henty lay at the bottom of the river.[27] Such unavoidable delays were not taken into account when Byrne was fined for breaches of contract.[28]
The mail service graduates to pack-horse
In 1887 new tenders were called for the Strahan mail contract—the successful mailman being required to provide a weekly service by pack-horse. Byrne would have found the new ways restrictive. New mailman WH Cole revealed that it was now impossible to lighten the load as the ex-mailman had done, since bags were sealed before he received them and each contained a list of contents.[29] Thus was Byrne’s personal post office on the Magnet Range consigned to history.
The insistence on pack-horse transport reflected increasing demand for an up-to-date service but not, unfortunately, improved infrastructure. In October 1889 mailman John Mayne described negotiating slippery corduroy (logs embedded in the ground as a track surface) and waist-deep mud between Waratah and the Pieman. A punt now existed at Corinna, but dangerous bridges, sand, bogs and onerous river crossings made the trip to Strahan ‘one of the most miserable tramps in Tasmania’.[30] It took extension of the VDL Co’s railway to Zeehan in 1900 to alleviate the mail misery.
Byrne was said to have suffered no ill effects from his marathon efforts, returning to his farm, devoting himself to the Roman Catholic Church and attaining the advanced age of 83.[31] Dodge the Hiluxes on Climies’ Track today, and across the exposed moors you might hear the Roadrunner’s footsteps echoing where rain, sleet and hail still hold court–but more likely it will just be your knees knocking together, or the hammering of a geological pick on some old Heemskirk tourmaline.
[1] See Journal of Australasian Mining History, vol.10, October 2012, pp.55–71, https://www.mininghistory.asn.au/wp-content/uploads/5.-Haygarth.COMPLETED5.Vol-10.compressed.pdf, accessed 2 October 2020.
[2] ‘Shaughraun’, ‘Notes off and on’, Launceston Examiner, 17 May 1884, supplement, p.1; ‘The overland route to the Mount Lyell goldfields’, Launceston Examiner, 4 September 1886, p.3; ‘Current topics’, Launceston Examiner, 30 August 1887, p.2; ‘Passing of a pioneer’, North Western Advocate and the Emu Bay Times, 7 June 1911, p.2.
[3] ‘Shaughraun’, ‘Notes off and on’, Launceston Examiner, 17 May 1884, supplement, p.1.
[4] See ‘Mount Bischoff’, Launceston Examiner, 18 July 1879, p.3; and ‘Gossan’, ‘Burnie to Corinna’, Examiner, 29 June 1900, p.7.
[5] See ‘The West Coast to Bischoff’, Tasmanian Mail, 26 March 1881, p.3.
[6] ‘Remarkable endurance’, Examiner, 10 June 1911, p.7.
[7] ‘A Traveller’, ‘From the Pieman to Bischoff’, Mercury, 16 October 1880, supplement, p.1.
[8] ‘Enquirer’, ‘Notes from North Heemskirk’, Mercury, 17 June 1882, p.2.
[9] ‘Tasmanian telegrams’, Mercury, 13 May 1879, p.2.
[10] ‘A Traveller’, ‘From the Pieman to Bischoff’, Mercury, 16 October 1880, supplement, p.1.
[11] ‘Mount Bischoff’, Mercury, 13 January 1881, p.3.
[12] ‘The Gazette’, Mercury, 29 December 1880, p.2.
[13] Glyn Roberts, The role of government in the development of the Tasmanian metal mining industry: 1803–1883, Centre for Tasmanian Historical Studies, Hobart, 1999, p.101.
[14] CJ Binks, Pioneers of Tasmania’s West Coast, Blubber Head, Hobart, 1988, pp.100–01. For his death, see ‘Death of Mr Axel Tengdahl: a pioneer of 1878’, Zeehan and Dundas Herald, 7 September 1919, p.2.
[15] ‘Tasmanian telegrams’, Mercury, 30 August 1881, p.2.
[16] For Gaffney and Harvey see Nic Haygarth, ‘Frontiersmen five: the Gaffney brothers, building, supplying and hosting Tasmania’s west coast mining fields’.
[17] ‘Official notices’, Launceston Examiner, 14 December 1881, p.3; ‘The Corinna goldfield’, Mercury, 21 January 1882, supplement, p.1; ‘Long Plains’, Tasmanian, 2 September 1882, p.973; ‘Long Plain’, Mercury, 21 October 1882, p.1; ‘West Coast notes’, Tasmanian, 10 June 1882, p.632; ‘Gazette notices’, Launceston Examiner, 26 June 1883, p.3.
[18] ‘Corinna goldfield’, Mercury, 21 January 1882, p.1; ‘The Rambler’, ‘North Heemskirk notes’, Mercury, 18 November 1882, p.3.
[19] ‘The Rambler’, ‘West Coast notes’, Mercury, 26 September 1882, p.3.
[20] ‘Visit of the Hon the Minister of Lands and Works to North Mount Heemskirk’, Launceston Examiner, 29 March 1882, p.3.
[21] See Con Henry Curtain, ‘Old times: Heemskirk mines and mining’, Examiner, 27 February 1928, p.5; and LJ Smith, ‘South Heemskirk Tin Mine’, Advocate, 11 August 1928, p.14.
[22] Editorial review of 1883, Launceston Examiner, 1 January 1884, p.2.
[23] For the Heemskirk hard rock tin boom, see Nic Haygarth, ‘”Cornwall of the Antipodes”: the “Cornish” tin boom at Mount Heemskirk, Tasmania, 1881–84’, Journal of Australasian Mining History, vol.15, October 2017, pp.65–80.
[24] Richard Hilder, ‘Among the pioneers of Emu Bay: a character sketch of Mr William Byrne’, Advocate, 2 April 1925, p.2.
[25] ‘Conveyance of mails’, Tasmanian News, 16 December 1884, p.2.
[26] ‘The West Coast’, Mercury, 19 January 1882, p.1; ‘The Corinna goldfields’, Tasmanian, 12 August 1882, p.885; ‘Shaughraun’, ‘Notes off and on’, Tasmanian, 17 May 1884, p.15; ‘West Coast notes’, Daily Telegraph, 3 June 1887, p.3.
[27] ‘Prospector’, ‘West Coast mails’, Daily Telegraph, 16 August 1887, p.3.
[28] ‘Tasmanian telegrams’, Mercury, 28 November 1887, p.3.
[29] WH Cole, ‘West Coast mails’, Mercury, 3 November 1888, p.3.
[30] John M Mayne, ‘Main road to West Coast’, Tasmanian, 12 October 1889, p.14.
[31] ‘Remarkable endurance’; Richard Hilder, ‘Among the pioneers of Emu Bay’.
by Nic Haygarth | 03/10/20 | Tasmanian high country history
William Byrne (c1828–1911) was tall, muscular, clean shaven and long-haired, and he spun a yarn like Fenimore Cooper.[1] If he lacked the zip of the Warner Brothers bird and the insight of that other roadrunner, Forrest Gump, he made up for it in persistence. It was said that had all his West Coast mail trips been strung together end to end—on a floating bridge, presumably—he could have rounded England and returned.

William Byrne, from the Weekly Courier,
15 June 1911, p.22.
Byrne’s reputed ex-soldier father John Byrne might have preferred an Irish homecoming.[2] In 1842 the Byrne family, including teenaged William and four siblings, were ensconced in a timber house at Horse Shoe Farm, Coal River, in the southern Midlands, but the lure of a fertile Van Diemen’s Land Company tenancy was apparently enough to pack them off to Cooee Creek in the north-west.[3] Success on the Victorian goldfields won William his own property at Mooreville Road, where he was said to have been one of the pioneers of the potato trade to Sydney.[4] In chartering a schooner for direct trade with Sydney, Byrne displayed the sort of initiative that would win him long-distance mail contracts. Labouring on the farm must have given him his endurance.
This 1876 Charles Sprent survey of Waratah lots shows the original dray route (left) to Mount Bischoff
known as Bog Lane. Survey 76458, courtesy of DPIPWE.
The Mount Bischoff mail
The first ‘road’ to Waratah took a wide sweep from Browns Marsh on the Surrey Hills block across Knole Plain, before approaching the town from the south-west through a muddy tunnel in the horizontal scrub known at Bog Lane. This was the track rutted out by ore carters employed by the Mount Bischoff tin mines. Early mail delivery depended on the good will of travellers between Emu Bay and the Mount. The government demanded a quid pro quo before investing in Bischoff. Chairman of directors of the Mount Bischoff Co William Ritchie reported in December 1873 that
‘the Government now virtually repudiate their promise of a pound a week towards the expense of a weekly mail. They also decline to give anything towards the road—but say that when twenty leases shall have been granted and the rent paid they will take our application into consideration’.[5]
The Mount Bischoff Co took the matter into their own hands, contracting William Byrne as its mailman at £90 per year.[6] Presumably he rode a horse where possible, leading it the rest of the way. Mine manager WM Crosby became the first Mount Bischoff postmaster, pocketing £60 per year on top of his manager’s salary.[7] Byrne did things his way, his method of carrying loose letters horrifying the Emu Bay postmistress.[8] (However, as it turned out, that was nothing compared to his treatment of newspapers.) Byrne was contracted to arrive at Waratah each Tuesday at 2pm, seven hours before the outgoing mail closed. However, he usually appeared at dusk, putting locals into a flurry answering their mail in the short time remaining.[9]
As the volume of mail increased, the Mount Bischoff Co petitioned the government, which finally agreed to take over responsibility for the entire mail service at the expiration of Byrne’s contract.[10] In the meantime, Byrne was accused of delivering mail to the wrong people because he was illiterate—but he wasn’t illiterate, and other Byrne clients vouched for his services.[11] When, inevitably, he lost his mail contract to the VDL Co’s tramway service, his clients farewelled him with a signed testimonial expressing their gratitude.[12]
A crop from Charles Sprent’s 1879 chart shows the original dray ‘road’ to Mount
Bischoff via Knole Plain, the line of the VDL Co’s horse-drawn tramway and the
later line of road into Waratah, deviating from the other near the Hellyer River.
From AF395/1/41 (TAHO).
Carrying the mail on the Emu Bay and Mount Bischoff Tramway
The VDL Co’s horse-drawn tramway was completed to its original terminus of Rouses Camp, 4 km from Waratah, in 1878. The company began to provide a tri-weekly service, contracted to arrive in Waratah at 5pm. You might expect a commercial transport operator to trounce a lone horseman for efficiency, but VDL Co manager James Norton Smith knew that rogue elements governed his service.

A VDL Co tram operating in the forest at the 29-Mile mark. It demonstrates the basic technology of a horse-drawn, timber-railed tramway. Courtesy of the Burnie Regional Museum.
Firstly, if the mail was late reaching Burnie, it was late starting for Bischoff. Then there were the employees. Through the building of the tramway, and now in its operation, the temperance wagon was frequently overturned. Daniel Shine, timekeeper at Rouses Camp, was a valuable informant on local affairs, but also a regular drunkard.[13] On two occasions Norton Smith sacked him, only to reinstate the repentant man.[14] Driver Higgs posed such a threat to the public that he was relegated to support duties.[15] Hampshire Hills stableman and storekeeper ‘Dusty’ Miller got ‘on the spree’.[16] Even tramway inspector Hugh Lynch was known to get ‘on the burst’.[17] Henry Crispin was ‘hopelessly drunk and asleep behind a log’ near Michael Bevan’s Hampshire Hotel in March 1877 when an accident happened on the line that he could have averted.[18] With so many imbibers along the way it probably wasn’t a surprise when a case of whisky consigned to Bevan disappeared in transit in 1878.[19] The publican later went to fisticuffs with tram driver William Lennard.[20]
Thirdly, there were the horses. The tramway was an equine graveyard. Many injured animals must have been shot. In 1879 Shine gave a requiem for four of the six animals meant to be in harness, telling Norton Smith:
‘”‘Black Wallace” was bled to death yesterday. “White Prince” is given over [useless]. “Punch” is expected to go the way of all flesh tomorrow, and “Wallace” … is crippled and not expected to do any more work, so that I expect it will be some time before we shall have full loading on our trucks’.[21]
Norton Smith’s accountant RA Murray recalled a horse named Boxer returning to Emu Bay
‘with his shoulders literally cut to pieces. They actually look as if a dog or some animal had eaten a piece out of them, and he is either strained in the forequarters or something internally wrong, as it is with the greatest difficulty he can walk at all’.[22]
Those with treatable conditions required careful attention. In 1882 an employee at Hampshire sent a long list of medicines required to fix the horses under his charge—including licorice powder, antimonial powder, camphor powder and tartarized antimony.[23]
Equine unpredictability also led to thrills and spills. In December 1879 the grey horse Turpin shied at the 39-mile mark, throwing Launceston brewer John Glennwright under the mail truck.[24] The passenger spat blood, sustaining injuries that his solicitor valued at £500.[25] There were other accidents with a human cause. On another occasion the brake broke near Rouse’s gate, fracturing one horse’s ribs, killing two sheep and breaking the legs of three others.[26] In January 1882 the mail coach was derailed in a collision with a trolley left on the track near Waratah, throwing passengers out of their carriage.[27]

Opening of the Emu Bay and Mount Bischoff Tramway at Rouses Camp, 1 February 1878. PH30/1/1865 (Libraries Tasmania).
Dick Leach drives the ‘rabbit hutch with wheels’
These were the variables governing delivery of the ‘Royal Mail’. However, the well-known tram driver Dick Leach (1844?–85) certainly delivered through hail, rain and snow. Born into a Bog Irish family, he grew up alongside the Gaffneys at Arms of the Creek, part of the ‘Paddys Scrub’ Irish enclave near Deloraine, his younger brother James Leach being the well-known drover and West Coast meat supplier.[28]
Leach generally wasn’t responsible for the very uncomfortable customer experience of riding the Emu Bay and Mount Bischoff Tram. One customer suggested that the passenger carriage of the ‘rabbit hutch with wheels’ might be better suited as a public toilet, while another preferred to walk back to Emu Bay than suffer a second dose of the ‘wretched vehicle … a cross between a small cattle truck and a sardine tin …’[29] It does seem to have been true, though, that Dick liked a tipple, once being given notice to apologise ‘and keep order’ after boozily abusing a customer.[30] Fortunately for him, there was no breathalyser on the tramway.
Like Byrne, Leach was branded with illiteracy. It was alleged that he carried letters up and down the line for days without delivering them ‘because he couldn’t read himself and he was too independent to ask anyone else to look at them’. If anyone complained about this behavior, the complainant stated,
‘he would grumble and say he need not carry any letters along the line at all, he only done it to oblige people, he only had to carry them from one post office to the other …’[31]
In this case it was probably true: Leach couldn’t sign his own name on his marriage certificate.[32]

Waratah in 1881, showing the Mount Bischoff Co’s bridge over the Waratah River and the Stanhope Smelter on the hill at left.
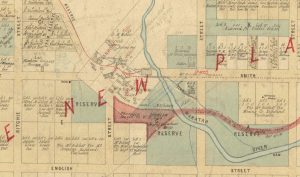
Waratah c1880, showing the Mount Bischoff Co’s tramway bridge as the only crossing of the Waratah River. The deviation of Smith Street around the Mount Bischoff Co’s machinery site is sketched in, as is the VDL Co’s proposed station and railway formation. The reserve for the post office is represented by the blank block on Smith Street, conveniently located next to the Stanhope Smelter.
Cropped from AF721/1/755 (TAHO).
In November 1881 the tramway was finally extended—with iron rails—into Waratah.[33] Since the attendant VDL Co mail service gave Bischoffites a turnaround of only two hours, they conducted much of their postal and telegraphic business by candle or lamplight in the early evening—and not in a purpose-built post office, but at the house of Charles Hall, 2IC at the Mount Bischoff Mine. At first there was no public bridge across the Waratah River. Many customers had to negotiate the narrow Mount Bischoff Company tramway bridge in the dark to reach Hall’s house in Smith Street, opposite St James’ Church.[34] The ad hoc post office was transferred to Stutterd’s house in June 1881, but evening business continued to be troublesome, customers having to provide their own lighting in order to send and collect mail or telegrams.[35] Miss Dixon was postmistress and mudlark, fulfilling the unenviable task of delivering telegrams in all weathers and all depths of mud.[36]

The first Waratah Post and Telegraph Office, 1882. Courtesy of the Waratah Museum.
The government built Waratah a post and telegraph office just as the VDL Co was unveiling its steam railway. The redundant Dick Leach moved to another mail service. He was killed when his horses shied while he was driving the coastal mail coach out of Forth in 1885, aged only 41.[37] It was reported that most of the coach passengers had abandoned the service because they believed Leach was drunk.[38] No mail reached Waratah that day as a result of his accident.[39]
[1] ‘Shaughraun’, ‘Notes off and on’, Tasmanian, 17 May 1884, p.28. American novelist James Fenimore Cooper (1789–1851) wrote romantic tales of frontier life such as The last of the Mohicans (1826) and The prairie (1827).
[2] See Richard Hilder, ‘Pioneers of Emu Bay: John Byrne of Uplands’, Advocate, 10 March 1926, p.11; Richard Hilder, ‘The real pioneers of Emu Bay and the town of Burnie’, Advocate, 10 April 1935, p.10. The story of John Byrne coming to Van Diemen’s Land as a soldier sounds rather like a convict smokescreen, except that the 1842 census record contains the claim that John Byrne and his wife arrived in the colony free. There are no Tasmanian birth records for William Byrne and his brother John, who could well have been born in New South Wales or even Ireland. Yet William Byrne claimed to have been born in Hobart.
[3] See Census of Van Diemen’s Land, 1842, CEN1/1/39–113 (TAHO), https://librariestas.ent.sirsidynix.net.au/client/en_AU/names/search/detailnonmodal/ent:$002f$002fNAME_INDEXES$002f0$002fNAME_INDEXES:473341/one?qu=john&qu=byrne&qf=NI_INDEX%09Record+type%09Census%09Census, accessed 2 October 2020. ‘Foreshore rights’, Daily Telegraph, 5 November 1901, p.4. John Byrne died at Emu Bay on 25 May 1854, aged 56, death record no.57/1854, registered at Horton (Stanley), RGD35/1/23 (TAHO), https://librariestas.ent.sirsidynix.net.au/client/en_AU/names/search/results?qu=john&qu=byrne&qf=NI_INDEX%09Record+type%09Deaths%09Deaths#, accessed 28 September 2020. He left a wife, Margaret Harris, and eight children. Margaret Byrne, née Harris, died at Emu Bay in 1885, aged 85 (‘Deaths’, Launceston Examiner, 30 September 1885, p.1).
[4] ‘Passing of a pioneer’, North Western Advocate and the Emu Bay Times, 7 June 1911, p.2; Richard Hilder, ‘The real pioneers of Emu Bay’, Advocate, 9 February 1935, p.9. Twenty-five-year-old William Byrne married 20-year-old Ann McKee on 1 February 1855 by Roman Catholic rites, marriage record no.1106/1855, registered at Oatlands, RGD37/1/14 (TAHO), https://librariestas.ent.sirsidynix.net.au/client/en_AU/names/search/results?qu=william&qu=byrne, accessed 23 September 2020. Both were ‘free’ and signed their own names. Their son John Byrne was born on 1 July 1858, birth record no.400/1858, registered at Emu Bay, RGD33/1/36 (TAHO), https://librariestas.ent.sirsidynix.net.au/client/en_AU/names/search/results?qu=NI_NAME%3D%22Mckee,%20Ann%22, accessed 23 September 2020.
Their son Alfred Byrne was born on 1 July 1858, birth record no.400/1858, registered at Emu Bay, RGD33/1/36 (TAHO), https://librariestas.ent.sirsidynix.net.au/client/en_AU/names/search/results?qu=NI_NAME%3D%22Mckee,%20Ann%22, accessed 23 September 2020. The father was a farmer at New Country, Emu Bay.
[5] William Ritchie to James Smith, 17 December 1873, NS234/3/1/2 (TAHO).
[6] Minutes of the Mount Bischoff Tin Mining Co directors’ meetings for 1875 and 1876 reveal that he received £7 10 shillings per month, or £90 per year. William Byrne’s brother John Byrne (‘senior’) and son John Byrne (‘junior’) were also on the Mount Bischoff Co payroll as ore carters in the years before the Emu Bay and Mount Bischoff Tramway was completed. See NS911/1/1 (TAHO).
[7] Minutes of Mount Bischoff Tin Mining Co directors’ meetings, 21 June 1875, NS911/1/1 (TAHO). Crosby was paid by the government; Byrne, the mailman, was paid by the Mount Bischoff Co.
[8] ‘Mount Bischoff’, Cornwall Chronicle, 19 September 1874, p.3; Minutes of Mount Bischoff Co, 6 September 1875, NS911/1/1 (TAHO).
[9] ‘Mount Bischoff’, Launceston Examiner, 20 June 1876, p.3.
[10] Minutes of Mount Bischoff Tin Mining Co directors’ meetings, 7 June 1875, 20 March and 20 April 1876, NS911/1/1 (TAHO).
[11] ‘Watchman’, ‘A grievance’, Tribune, 7 December 1878, p.2; John Lay, E Johnstone, W Nelms and E Dunstan to James Norton Smith, 16 December 1878, VDL22/1/6 (TAHO).
[12] ‘Bischoff’, Mercury, 14 May 1878, p.2; Advert, Cornwall Chronicle, 20 February 1879, p.13.
[13] See, for example, Daniel Shine on the Browns Plain rush in his letters to James Norton Smith, 15 and 20 January 1879, VDL22/1/7 (TAHO).
[14] James Norton Smith to RA Murray, 26 December 1877; Daniel Shine to James Norton Smith, 22 January 1878?, VDL22/1/5 (TAHO).
[15] Hugh Lynch to James Norton Smith, 23 April 1877; RA Murray to James Norton Smith, 26 December 1877, VDL22/1/5 (TAHO).
[16] RA Murray to James Norton Smith, 14 May 1879, VDL22/1/5 (TAHO).
[17] RA Murray to James Norton Smith, 14 May 1879.
[18] RA Murray to James Norton Smith, 20 March 1877, VDL22/1/5 (TAHO).
[19] Michael Bevan to James Norton Smith, 18 February 1878, VDL22/1/4 (TAHO).
[20] Michael Bevan to James Norton Smith, 17 February and 23 June 1880, VDL22/1/8 (TAHO).
[21] Daniel Shine to James Norton Smith, 1 October 1879, VDL22/1/7 (TAHO).
[22] RA Murray to James Norton Smith, 8 May 1877, VDL22/1/5 (TAHO).
[23] Robert Harris to James Norton Smith, 12 September 1882, VDL22/1/10 (TAHO).
[24] RA Murray to James Norton Smith, 11 December 1879, VDL22/1/7 (TAHO).
[25] Josiah Powell to James Norton Smith, 25 June 1880, VDL22/1/8 (TAHO).
[26] RA Murray to JC Climie, 16 October 1877, VDL22/1/5 (TAHO).
[27] ‘Observer’, ‘The late accident at Waratah’, Launceston Examiner, 6 January 1882, p.3; ‘Fortnightly summary of news for home readers’, Mercury, 2 January 1882, p.1.
[28] See 1848 census record for John Leach and family, CEN1/1/104 (TAHO), https://librariestas.ent.sirsidynix.net.au/client/en_AU/names/search/results?qu=NI_NAME%3D%22Leach,%20John%22, accessed 25 September 2020. Richard Leach appears to have been the cause of the marriage of 30-year-old John Leach and 21-year-old Anne Mullins, both ex-convicts, at Launceston in 1844. No birth certificate has been found for him, but he was said to be 41-year-old at his death.
For James Leach see Nic Haygarth, ‘Frontiersmen five: the Gaffney brothers, building, supplying and hosting Tasmania’s west coast mining fields’, Journal of Australasian Mining History, vol.17, October 2019, pp.59–71.
[29] ‘A Late Victim’, ‘Railway to Mount Bischoff’, Launceston Examiner, 9 September 1879, p.3; ‘Sicnarf Gink’ (Francis King), ‘Mount Bischoff Tramway’, Launceston Examiner, 11 September 1879, p.3.
[30] TD Patterson to RA Murray, 14 July 1882; James Norton Smith note on letter dated 15 July 1882, VDL22/1/10 (TAHO).
[31] John Deacon to James Norton Smith, 26 October 1882, VDL22/1/10 (TAHO).
[32] Twenty-seven-year-old Richard Leach married 32-year-old Elizabeth Lawson by Australasian Wesleyan rites on 25 December 1871 at the house of George Lawson, Chudleigh, marriage record no.79/1871, registered at Deloraine, RGD37/1/30 (TAHO), https://librariestas.ent.sirsidynix.net.au/client/en_AU/names/search/results?qu=richard&qu=leach, accessed 26 September 2020.
[33] ‘Waratah’, Mercury, 23 November 1881, p.1.
[34] ‘Bischoff’, Tasmanian Mail, 19 July 1879, 1879, p.15; ‘Mount Bischoff’, Tasmanian Mail, 9 October 1880, p.4.
[35] ‘Mount Bischoff’, Mercury, 23 July 1881, p.2; ‘The Owl’, ‘Records of a fortnight in Waratah’, Launceston Examiner, 30 August 1883, p.4.
[36] ‘Silverpen’ (Henry Glennie), ‘From Launceston to Waratah, Mount Bischoff’, Launceston Examiner, 17 September 1883, p.3.
[37] ‘Hamilton-on-Forth: fatal accident at the Forth’, Daily Telegraph, 8 June 1885, p.3.
[38] ‘Late coach accident’, Launceston Examiner, 9 June 1885, p.3.
[39] Accident to the NW mail coach’, Launceston Examiner, 8 June 1885, p.3.
by Nic Haygarth | 13/06/20 | Tasmanian high country history, Tasmanian nature tourism history
When I was a Tasmanian child the school-ma’amish Mrs Marsh demonstrated the mastery held by Colgate toothpaste over a piece of chalk. Or something. ‘It gets in?’, chirped this harridan’s childhood charges, as she pulled the chalk from a bottle of red dye and snapped it in half. Sure enough, the red dye had suffused the chalk. Apparently it did get in.
Quite what this had to do with the whitening powers of toothpaste was and is beyond me, but I still thought of her when, abandoning the TV, I gazed at Black Bluff gleaming on the skyline. If ever a mountain had the Colgate ring of confidence it was this one. Its winter coat seemed brighter, thicker and longer-lasting than those of Mount Roland and Western Bluff. Of the peaks I saw regularly during the course of my north-west-coastal school days only Mount Ironstone, behind Deloraine, rivalled it as a snow-cone.


(Top) George (GP) Taylor at a one-room Levenvale, Taylors Flats, Loongana, 1926. (Above) Later he added another gable containing a second room. The head of Black Bluff is lost in cloud. Photos by Ron Smith and Chris Binks respectively.
So I wasn’t surprised to learn that, in the late 1920s and 1930s, when Tasmanians began to attack their peaks on homemade skis and toboggans, Black Bluff came in for some serious scrutiny. In the winter of 1928 Ulverstone jeweller and photographer George (GP) Taylor and Cradle Mountain Reserve Board Secretary Ron Smith climbed the bluff to test its suitability for winter sports. ‘In frosty weather after a fall of snow’, they wrote, ‘skiing and tobogganing could be carried on successfully, and the accessibility of the mountain from the coast should make it a popular winter resort, provided sufficient accommodation is available on the mountain’.[1]
Base map from LISTMap, courtesy of DPIPWE.
The Ulverstone Tourist and Progress Association had surveyed a Black Bluff track from near Taylor’s Loongana shack Levenvale, but on the back of this report the Public Works Department’s Paddy Doyle cut a better one (the Brookes Track) which opened in January 1930.[2] Further afield near Cradle Mountain, Waldheim Chalet tourism operator Gustav Weindorfer must have noted events at Black Bluff apprehensively. For years he had been encouraging the development of hiking and winter sports at Cradle Mountain with modest return. Both were starting to take off now, but a new mountain playground at Black Bluff—a place you could park your car under—might scotch his business.



Action from the ski club’s first outing on 26 June 1932. (Top) Jack Breheny, Lola Vollprecht and Sid Butler on the ski slope above Paddys Lake. (Middle: left to right) Sid Butler, NB (‘Darkie’) Wilson, Bill Mitchell, Jack Breheny, Lola Vollprecht, Peter Roger-Jones, Gifford Brownrigg, club secretary George Cruickshank, Cecil Rawson, Vince Taylor and (far right) club president George Taylor. (Above): Stella Pemberton, Gifford Brownrigg, George Cruickshank and Mrs Gillam climbing the Brookes Track near the later chalet site.
Photos courtesy of the late Jack Breheny.
As it turned out, Weindorfer was in his grave by the time Ulverstone enthusiasts pressed the issue of forming a ski club.[3] The club took its cues from the Legges-Tor-based Northern Tasmanian Alpine Club (NTAC), dubbing itself the North West Alpine Club. The club’s first outing was in June 1932, when a delegation from the NTAC consisting of Jack Branagan, Reg Hall, Bill Mitchell and Eileen Perrin visited Black Bluff in tandem with about 50 local members.[4] Taylor’s two-room Levenvale, 90 minutes by car from Ulverstone, seemed an ideal base camp, with skiers relaxing by its roaring fire and in its bunks. Even veteran skier ET Emmett threatened to test the new ski field.[5] As was the case at Cradle Mountain, conditions were not often optimal for skiing, but another successful outing was staged on 6 August 1933.



(Top and middle) Skiers on the slope above Paddys Lake during the 1932 season; and (above) the Tourist Bureau uses a photo of Black Bluff skiing to promote winter sports during the 1930s. All three are Mel Nichols photos. Top is from the Illustrated Tasmanian Mail, 1 December 1932; centre from the Weekly Courier, 13 July 1932, p.24.
In 1935 an enlarged club rode ‘a wave of enthusiasm and activity’.[6] Some of that was directed at changing the club’s name to the Black Bluff Ski Club and erecting a twelve-bunk ski chalet at a spot below Paddys Lake known as Boozers Rest.[7] Benefiting from a £15 Tourism Department grant, club members split timber and hauled it up to the 950-metre mark, and during the winter and spring of 1935 working bees soon completed the two-room hut with spacious fireplace.[8]
This, surely, would bind members socially just as the NTAC had bonded over chalet building. Skiers now had a refuge from the weather and, conveniently, skis and toboggans could be left on the mountain. What could possibly go wrong?



(Top) Tobogganing on the saddle above Paddys Lake, 6 August 1933. (Middle) George Hodgkinson, Jack Breheny and George Cruickshank on the ski slope. (Above) Bill Breheny takes a break above Paddys Lake. Photos courtesy of the late Jack Breheny.
A few things. World War Two (1939–45) played a part in the club’s fortunes. While Hobart and Launceston were no closer to their ski fields than Ulverstone, they had bigger population bases to draw upon in the event of the original enthusiasts petering out, moving on or mobilising as part of the war effort. However, something else preceded that. In winter with snow on the ground and ice on the lake it was probably hard to imagine a bushfire roaring down on the chalet, but that is exactly what happened in mid-summer, January 1939. The building was destroyed. The ‘boozers’ lost their roost.[9] There was no impetus to rebuild even in the post-war period when nature sports and studies boomed. Now you can drive to a ski field—why climb?

Mrs Marsh probably knew nothing of climate change, and the effect it had on toothpaste … or snowfall. Unreliable snowfalls are the bugbear of skiers, but in my child’s eye Black Bluff still has its pearlies out, beckoning those bright young things who knew how to Charleston and how to wear a sou’wester.
[1] GP Taylor and RE Smith, ‘Black Bluff Mountain: winter sports and mountaineering near Ulverstone’, 21 August 1928, report to the Tasmanian Government Tourist Bureau.
[2] ‘Ulverstone: Black Bluff Track opened’, Examiner, 28 January 1930, p.5.
[3] ‘NW Tasmanian Alpine Club’, Australian and New Zealand ski year book, New South Wales Ski Council, Sydney, 1933, p.228.
[4] ‘Mountain sports’, Mercury, 29 June 1932, p.5.
[5] ‘Winter sports: visitors to Tasmania’, Mercury, 22 July 1932, p.6.
[6] ‘Black Bluff Ski Club’, Australian and New Zealand ski year book, New South Wales Ski Council, Sydney, 1935, p.234.
[7] ‘North West Alpine Club’, Advocate, 22 May 1935, p.6; ‘Ski club hut’, Advocate, 25 May 1935, p.6.
[8] ‘Ulverstone’, Advocate, 27 June 1935, p.6; ’Black Bluff hut’, Advocate, 17 July 1935, p.6; ‘Trip to Black Bluff’, Advocate, 3 September 1935, p.6.
[9] GP Taylor, ‘Bush fires’, Advocate, 30 January 1939, p.6.